Measuring the Properties of Stars (ch. 17)
... The only method for directly determining the masses of stars is from binary stars, using Newton’s form of Kepler’s 3rd law. There are three types of binary stars, which depend on how close they are to each other, their relative brightnesses, the distance of the binary, and other factors: a.Visual bi ...
... The only method for directly determining the masses of stars is from binary stars, using Newton’s form of Kepler’s 3rd law. There are three types of binary stars, which depend on how close they are to each other, their relative brightnesses, the distance of the binary, and other factors: a.Visual bi ...
01.05.10 Centuries-Old Star Mystery Coming to a Close For almost
... Now, new observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope -- in combination with archived ultraviolet, visible and other infrared data -- point to one of two competing theories, and a likely solution to this age-old puzzle. One theory holds that the bright star is a massive supergiant, periodically ...
... Now, new observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope -- in combination with archived ultraviolet, visible and other infrared data -- point to one of two competing theories, and a likely solution to this age-old puzzle. One theory holds that the bright star is a massive supergiant, periodically ...
Devika kamath Institute of Astronomy, KU. Leuven, Belgium
... FIELDS OF THE POST-RGB STARS The number of stars we expect to see at any given time in the top 1 magnitude of the RGB is k = 2.77 x106 × birthrate tip-RGB Total number of stars observed in the top 1 magnitude of the RGB in the fields searched for post-RGB stars is 118927 (from SAGE) ...
... FIELDS OF THE POST-RGB STARS The number of stars we expect to see at any given time in the top 1 magnitude of the RGB is k = 2.77 x106 × birthrate tip-RGB Total number of stars observed in the top 1 magnitude of the RGB in the fields searched for post-RGB stars is 118927 (from SAGE) ...
The most important questions to study for the exam
... • It contains the biggest and brightest stars. • It contains the greatest number of stars. • It consists almost entirely of hot, bright stars. 8. A certain star is seen to have a relatively low surface temperature but a very high luminosity. What can we conclude from these observations? • The star i ...
... • It contains the biggest and brightest stars. • It contains the greatest number of stars. • It consists almost entirely of hot, bright stars. 8. A certain star is seen to have a relatively low surface temperature but a very high luminosity. What can we conclude from these observations? • The star i ...
Class 26: EXAM 2
... A) They all have substantial atmospheres. B) They are relatively smaller than the outer planets. C) Their orbits are relatively closely spaced. D) They all have solid, rocky surfaces. E) They have very few, if any, satellites. 14) Which of the following is not a characteristic of the outer planets? ...
... A) They all have substantial atmospheres. B) They are relatively smaller than the outer planets. C) Their orbits are relatively closely spaced. D) They all have solid, rocky surfaces. E) They have very few, if any, satellites. 14) Which of the following is not a characteristic of the outer planets? ...
Surveys of Stars, The interstellar medium
... ISM and stars are the components of the “machine” that makes the universe evolve: the cycle of star formation and death, and the chemical enrichment of the cosmos. ISM also “disturbs” observations, since it absorbs light and ...
... ISM and stars are the components of the “machine” that makes the universe evolve: the cycle of star formation and death, and the chemical enrichment of the cosmos. ISM also “disturbs” observations, since it absorbs light and ...
Planetarium Key Points
... Geographic Latitude is the elevation of the visible pole and, roughly, of Polaris The motion of the sphere seems uniform, for this reason it was the source for time telling, but the time scale that comes from is NOT uniform: rotation is slowing down, the day is longer and longer at the rate of 2 ...
... Geographic Latitude is the elevation of the visible pole and, roughly, of Polaris The motion of the sphere seems uniform, for this reason it was the source for time telling, but the time scale that comes from is NOT uniform: rotation is slowing down, the day is longer and longer at the rate of 2 ...
The First Stars - Amazon Web Services
... call this a white dwarf. The atmosphere is ejected in the beautiful phenomenon that we see as a planetary nebula. The white dwarf gradually cools down. Our galaxy is teeming with old white dwarfs, descendants of sun-like stars. A star that is ten or thirty times the mass of the sun has a much more a ...
... call this a white dwarf. The atmosphere is ejected in the beautiful phenomenon that we see as a planetary nebula. The white dwarf gradually cools down. Our galaxy is teeming with old white dwarfs, descendants of sun-like stars. A star that is ten or thirty times the mass of the sun has a much more a ...
Power Point Presentation
... Earth masses) with radius 1.3 times Jupiter density 0.39 g/cm3 (< water!) It transits the star every 3.5 days Its atmosphere is very hot (1100oC) since it is only 6.4 million km from the star When the planet passed in front of the star, the star’s light passed through the planet’s atmosphere and s ...
... Earth masses) with radius 1.3 times Jupiter density 0.39 g/cm3 (< water!) It transits the star every 3.5 days Its atmosphere is very hot (1100oC) since it is only 6.4 million km from the star When the planet passed in front of the star, the star’s light passed through the planet’s atmosphere and s ...
Chapter 12
... 6. Cepheids could be valuable distance indicators if the distance to one could be determined. None are close enough to be measured by parallax, but beginning in 1917, Shapley worked out a complex statistical method to determine distances to Cepheids in our Galaxy. 7. Shapley’s work led to a period-l ...
... 6. Cepheids could be valuable distance indicators if the distance to one could be determined. None are close enough to be measured by parallax, but beginning in 1917, Shapley worked out a complex statistical method to determine distances to Cepheids in our Galaxy. 7. Shapley’s work led to a period-l ...
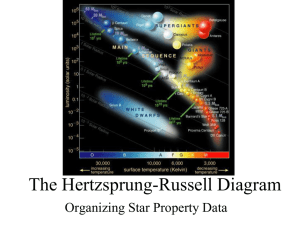
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
13 The Family of Stars
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence because this is where most stars are. The white dwarf region ...
... The Hertzsprung–Russell Diagram Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence because this is where most stars are. The white dwarf region ...
Lecture 19 Review
... We have talked about our Sun. From a large gas cloud it collapses to a protostar, heating up, compressing, finally igniting. In the process planets are formed from some remaining high angular momentum solar gas and dust particles. A great deal of gas and dust is blown off in the process. This all ha ...
... We have talked about our Sun. From a large gas cloud it collapses to a protostar, heating up, compressing, finally igniting. In the process planets are formed from some remaining high angular momentum solar gas and dust particles. A great deal of gas and dust is blown off in the process. This all ha ...
LAB #6 - GEOCITIES.ws
... If we use stars in the same cluster, we are using stars at essentially the same distance from us. A comparison of the apparent magnitude is thus a comparison of their intrinsic brightness, or luminosities. We can plot the apparent magnitudes of the stars versus their temperature. The temperature is ...
... If we use stars in the same cluster, we are using stars at essentially the same distance from us. A comparison of the apparent magnitude is thus a comparison of their intrinsic brightness, or luminosities. We can plot the apparent magnitudes of the stars versus their temperature. The temperature is ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Distances to Stars
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
Chapter 4: The Solar System
... • Earth and Mars rotate at about the same rate; Venus and Mercury are much slower, and Venus rotates in the opposite ...
... • Earth and Mars rotate at about the same rate; Venus and Mercury are much slower, and Venus rotates in the opposite ...
Astronomy Teleclass Webinar!
... The Sun rotates once every 27 days at its equator and 31 days at the poles. The core temperature of the Sun is 15 million degrees Celsius. A planet has three criteria: It orbits the Sun, has cleared its orbit of smaller objects, and is large enough so its own gravity makes it round. There are th ...
... The Sun rotates once every 27 days at its equator and 31 days at the poles. The core temperature of the Sun is 15 million degrees Celsius. A planet has three criteria: It orbits the Sun, has cleared its orbit of smaller objects, and is large enough so its own gravity makes it round. There are th ...
Lecture 13, PPT version
... Spherical groupings of 10,000 to 1 million stars (about 158 known in our Galaxy). All of the stars formed at roughly the same time. Globular clusters have lots of RED stars, but no BLUE stars (because they died long ago and were not “replenished”). ...
... Spherical groupings of 10,000 to 1 million stars (about 158 known in our Galaxy). All of the stars formed at roughly the same time. Globular clusters have lots of RED stars, but no BLUE stars (because they died long ago and were not “replenished”). ...
Your Birthday on Another Planet
... the Sun. If we could live on another planet, our birthdays would occur more or less frequently depending on the planet’s revolution period (the time taken to complete one full trip around the Sun). On a few planets, we couldn’t even celebrate our first birthday because we wouldn’t live long enough t ...
... the Sun. If we could live on another planet, our birthdays would occur more or less frequently depending on the planet’s revolution period (the time taken to complete one full trip around the Sun). On a few planets, we couldn’t even celebrate our first birthday because we wouldn’t live long enough t ...
Cluster and Association Members
... BRITE target stars as members of star clusters For a given apparent magnitude limit of targets stars (V = 4 mag) we can immediately calculate the distance limit for different absolute magnitudes. At maximum (not taking reddening into account) MV = −6 mag (early O) we can reach 1000 pc whereas the dis ...
... BRITE target stars as members of star clusters For a given apparent magnitude limit of targets stars (V = 4 mag) we can immediately calculate the distance limit for different absolute magnitudes. At maximum (not taking reddening into account) MV = −6 mag (early O) we can reach 1000 pc whereas the dis ...
Astronomy 100—Exam 2
... D. it possessed angular momentum and it has collapsed by a very large factor. E. the energy from the supernova explosion that formed them made them spin faster. 36. The proton-proton chain needs high temperature because A. of the ground state energy of the hydrogen atom. B. of the presence of helium ...
... D. it possessed angular momentum and it has collapsed by a very large factor. E. the energy from the supernova explosion that formed them made them spin faster. 36. The proton-proton chain needs high temperature because A. of the ground state energy of the hydrogen atom. B. of the presence of helium ...