Solutions to Homework #4, AST 203, Spring 2012
... Hint: the Earth is still very far from this planetary system. Solution We are observing this transit from very far away, so the distance between the planet and the host star will not affect the answer. The difference is just the cross sectional area of the planet. Jupiter’s radius is 11 times the Ea ...
... Hint: the Earth is still very far from this planetary system. Solution We are observing this transit from very far away, so the distance between the planet and the host star will not affect the answer. The difference is just the cross sectional area of the planet. Jupiter’s radius is 11 times the Ea ...
00 T Tauri Stars Have Extensive Coronae?
... T Tauri stars are low-mass (:::; 3 M0 pre-main-sequence stars. They have been recognized the first time as an individual group of stars in 1945 by Alfred Joy. They show irregular photometrie variability and are located without exception in, or very close to, dark clouds. In 1958 another pioneer of v ...
... T Tauri stars are low-mass (:::; 3 M0 pre-main-sequence stars. They have been recognized the first time as an individual group of stars in 1945 by Alfred Joy. They show irregular photometrie variability and are located without exception in, or very close to, dark clouds. In 1958 another pioneer of v ...
THE CHANGING SKY
... → These buttons allow you to change the time of your observation. → E : Enter any time and date. → 1 , 5 , 10 : Advance time by 1, 5, or 10 minutes (left mouse button = forward in time, right mouse button = backward in time). → H , D , W , M , Y : Advance time by one hour, day, week, month, year (le ...
... → These buttons allow you to change the time of your observation. → E : Enter any time and date. → 1 , 5 , 10 : Advance time by 1, 5, or 10 minutes (left mouse button = forward in time, right mouse button = backward in time). → H , D , W , M , Y : Advance time by one hour, day, week, month, year (le ...
What is a planet? - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... Queloz using the “Doppler Wobble” method – Most successful detection method by far, but other methods like transits are now very successful – 502 exoplanets in total found to date by all methods – ~100 found since I gave this lecture last year ...
... Queloz using the “Doppler Wobble” method – Most successful detection method by far, but other methods like transits are now very successful – 502 exoplanets in total found to date by all methods – ~100 found since I gave this lecture last year ...
script (powerpoint)
... object. Planet e is confirmed as bound to HR 8799 and it is moving 46 ± 10 mas/year counter-clockwise. The orbits of the solar system's giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) are drawn to scale (light gray circles). With a period of ~50 years, the orbit of HR 8799e will be rapidly const ...
... object. Planet e is confirmed as bound to HR 8799 and it is moving 46 ± 10 mas/year counter-clockwise. The orbits of the solar system's giant planets (Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune) are drawn to scale (light gray circles). With a period of ~50 years, the orbit of HR 8799e will be rapidly const ...
Discovery of a strong magnetic field in the rapidly rotating B2 Vn star
... Large Program. HR 7355 is both the most rapidly rotating known main-sequence magnetic star and the most rapidly rotating He-strong star, with v sin i = 300 ± 15km s−1 and a rotational period of 0.521 4404 ± 0.000 0006 d. We have modelled our eight longitudinal magnetic field measurements assuming an ...
... Large Program. HR 7355 is both the most rapidly rotating known main-sequence magnetic star and the most rapidly rotating He-strong star, with v sin i = 300 ± 15km s−1 and a rotational period of 0.521 4404 ± 0.000 0006 d. We have modelled our eight longitudinal magnetic field measurements assuming an ...
5 Habitable zones and Planetary atmospheres
... Lower UV flux of M dwarfs implies smaller planetary atmosphere erosion. However, young M dwarfs are extremely active and stay active for longer periods of time! Potential for very severe erosion of atmospheres due to X-rays, flares, etc. Mid-to-early K stars should be considered along with G stars a ...
... Lower UV flux of M dwarfs implies smaller planetary atmosphere erosion. However, young M dwarfs are extremely active and stay active for longer periods of time! Potential for very severe erosion of atmospheres due to X-rays, flares, etc. Mid-to-early K stars should be considered along with G stars a ...
GRAVITATIONAL RADIATION FROM ACCRETING NEUTRON STARS
... If the star is spinning up on a timescale of 1012 s, then during the observation period it will have changed its frequency by no more than one part in 105 , or 10−2 Hz. The second derivative should be smaller, of order the square of this dimensionless ratio, or one part in 1010 . This would be just ...
... If the star is spinning up on a timescale of 1012 s, then during the observation period it will have changed its frequency by no more than one part in 105 , or 10−2 Hz. The second derivative should be smaller, of order the square of this dimensionless ratio, or one part in 1010 . This would be just ...
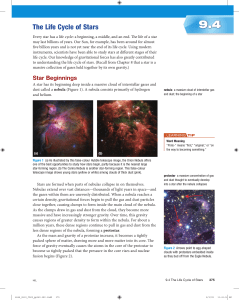
The Life Cycle of Stars
... In about 5 billion years, our Sun will become a red giant. A star with a mass that is equal to or smaller than that of the Sun becomes a red giant, whereas a star with a mass that is 10 times (or more) larger than that of the Sun becomes a red supergiant. As a red giant ages it consumes the remainin ...
... In about 5 billion years, our Sun will become a red giant. A star with a mass that is equal to or smaller than that of the Sun becomes a red giant, whereas a star with a mass that is 10 times (or more) larger than that of the Sun becomes a red supergiant. As a red giant ages it consumes the remainin ...
Introduction to Stars: Their Properties
... 2. m of star C is 12, m of star D is 2: How many times brighter is star D than star C? (Or, equally stated, how many times dimmer is star C than star D?) a) 10 ...
... 2. m of star C is 12, m of star D is 2: How many times brighter is star D than star C? (Or, equally stated, how many times dimmer is star C than star D?) a) 10 ...
Events: - Temecula Valley Astronomers
... a few degrees. You will see two stars running up and down from each other. These are Delta on the bottom and Gamma on the top. If you look just to the right of these two stars, about half way between them, you will see a nice open cluster called M-44 or “Beehive Cluster”. M-44 is an easy find using ...
... a few degrees. You will see two stars running up and down from each other. These are Delta on the bottom and Gamma on the top. If you look just to the right of these two stars, about half way between them, you will see a nice open cluster called M-44 or “Beehive Cluster”. M-44 is an easy find using ...
TAP 704- 8: The ladder of astronomical distances
... The prestigious meeting of the International Astronomical Union in 1976 was startled to be told that the Universe is only half as big as the astronomers present all thought, and therefore only half as old. The challenger was the French-American astronomer Gerard de Vaucouleurs; the leader of the cha ...
... The prestigious meeting of the International Astronomical Union in 1976 was startled to be told that the Universe is only half as big as the astronomers present all thought, and therefore only half as old. The challenger was the French-American astronomer Gerard de Vaucouleurs; the leader of the cha ...
Ch. 27
... Kepler’s third law describes the relationship between the average distance of a planet from the sun and the planet’s ___?___ ...
... Kepler’s third law describes the relationship between the average distance of a planet from the sun and the planet’s ___?___ ...
Lecture 18
... stars being rare (therefore distant). Observation is rather uncertain. b) Stars today form out of gas that also contains dust, so the opacity is larger than the Thomson value. Radiation pressure is therefore important for less luminous (less massive) stars too. c) Stars don’t form from spherically s ...
... stars being rare (therefore distant). Observation is rather uncertain. b) Stars today form out of gas that also contains dust, so the opacity is larger than the Thomson value. Radiation pressure is therefore important for less luminous (less massive) stars too. c) Stars don’t form from spherically s ...
Hypervelocity Globular: A beacon of merging clusters Oleg Gnedin with Alexey Vikhlinin
... (University of Michigan) ...
... (University of Michigan) ...
Flagship imaging SAG report
... to infer the presence of unseen planets. Objective 11: Understand the time evolution of circumstellar disk properties around a wider star sample at greater distances, from early protoplanetary stages through mature main sequence debris disks. Discussion These Objectives are not prioritized, but repr ...
... to infer the presence of unseen planets. Objective 11: Understand the time evolution of circumstellar disk properties around a wider star sample at greater distances, from early protoplanetary stages through mature main sequence debris disks. Discussion These Objectives are not prioritized, but repr ...
Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... measure of the quantity of each color of light (or more specifically, the amount of each wavelength of light). It is a powerful tool in astronomy. In fact, most of what we know in astronomy is a result of spectroscopy: it can reveal the temperature, velocity and composition of an object as well as b ...
... measure of the quantity of each color of light (or more specifically, the amount of each wavelength of light). It is a powerful tool in astronomy. In fact, most of what we know in astronomy is a result of spectroscopy: it can reveal the temperature, velocity and composition of an object as well as b ...
Introduction to Celestial Spheres (Professor Powerpoint)
... you’ll see stars rise in the south east, go to the highest point and set in the southwest, a shorter arc across the sky. ...
... you’ll see stars rise in the south east, go to the highest point and set in the southwest, a shorter arc across the sky. ...
ppt
... Middle stage The condensated dustmaterial, the (planetesimal→ planetesimals collide with each other protoplanet) building larger, a few 1000 km size objects (Moon-size), the protoplanets. Last stage The few dozens protoplanets on a ~108 (protoplanet→ million year timescale undergo giant planet) impa ...
... Middle stage The condensated dustmaterial, the (planetesimal→ planetesimals collide with each other protoplanet) building larger, a few 1000 km size objects (Moon-size), the protoplanets. Last stage The few dozens protoplanets on a ~108 (protoplanet→ million year timescale undergo giant planet) impa ...
My power point presentation on spectroscopy of stars (ppt file)
... structure of stellar atmosphere as input • The programme reads in atomic line (and other) data, solves equation of radiative transfer for many wavelengths, and compares resulting spectrum with observed one • If desired, the programme can iterate parameters to improve fit to observations 21 October 2 ...
... structure of stellar atmosphere as input • The programme reads in atomic line (and other) data, solves equation of radiative transfer for many wavelengths, and compares resulting spectrum with observed one • If desired, the programme can iterate parameters to improve fit to observations 21 October 2 ...
lec01_26sep2011
... Whatever the sun's nature, it must have encompassed all of the planets; and considering the enormous distances separating these bodies, it must have been a fluid of an immense extent. In order to have given the planets almost circular motions in the same direction, this fluid must have surrounded th ...
... Whatever the sun's nature, it must have encompassed all of the planets; and considering the enormous distances separating these bodies, it must have been a fluid of an immense extent. In order to have given the planets almost circular motions in the same direction, this fluid must have surrounded th ...