Lesson 13 - Oregon State University
... short lifetimes, now extinct • Population II stars (H, He, 1% heavier elements) • Population I stars (H, He, 2-5% heavier elements) Includes our sun. ...
... short lifetimes, now extinct • Population II stars (H, He, 1% heavier elements) • Population I stars (H, He, 2-5% heavier elements) Includes our sun. ...
Ans. - Testlabz.com
... during the day. Why are they visible only at night? Ans. We cannot see the stars during the day because of the bright sunlight. Bright sun light is so strong that it suppresses the light coming from the stars, and hence, they are not visible to us although they are present in the sky. Q.35. Why do t ...
... during the day. Why are they visible only at night? Ans. We cannot see the stars during the day because of the bright sunlight. Bright sun light is so strong that it suppresses the light coming from the stars, and hence, they are not visible to us although they are present in the sky. Q.35. Why do t ...
HIERARCHICAL GALAXY ASSEMBLY AND ITS MANIFESTATIONS
... luminosity and colour like single stellar population models, with epoch of formation z~3-5: passive evolution Hierarchical semi-analytic models produce slower and more prolonged evolution, and lower masses at high redshift, ...
... luminosity and colour like single stellar population models, with epoch of formation z~3-5: passive evolution Hierarchical semi-analytic models produce slower and more prolonged evolution, and lower masses at high redshift, ...
Chapter 10
... An H–R diagram of the 100 brightest stars looks quite different. These stars are all more luminous than the Sun. Two new categories appear here – the red giants and the blue giants. Clearly, the brightest stars in the sky appear bright because of their enormous luminosities, not their ...
... An H–R diagram of the 100 brightest stars looks quite different. These stars are all more luminous than the Sun. Two new categories appear here – the red giants and the blue giants. Clearly, the brightest stars in the sky appear bright because of their enormous luminosities, not their ...
Full Programme and Abstracts - UK Exoplanet community meeting
... Earth is the best studied planet we know. A century’s work on terrestrial samples has interrogated 90% of its history, and revealed the physics of processes from the formation of the core to the rise of atmospheric oxygen. This detailed understanding can benefit our perspective of exo-planetary syst ...
... Earth is the best studied planet we know. A century’s work on terrestrial samples has interrogated 90% of its history, and revealed the physics of processes from the formation of the core to the rise of atmospheric oxygen. This detailed understanding can benefit our perspective of exo-planetary syst ...
Module code: AA1
... reason their below average luminosity is sufficient to make them appear on the list of the 20 brightest stars. The sample group of the nearest stars is more representative than the group of the brightest stars when wanting to make a statement about the main type of stars in our galaxy as they do not ...
... reason their below average luminosity is sufficient to make them appear on the list of the 20 brightest stars. The sample group of the nearest stars is more representative than the group of the brightest stars when wanting to make a statement about the main type of stars in our galaxy as they do not ...
How Big is the Universe
... How Big Is Our Universe? How many times have you wondered about all the things that we see in the night sky? The universe contains everything: all the star systems, galaxies, gas, dust, and everything else. ...
... How Big Is Our Universe? How many times have you wondered about all the things that we see in the night sky? The universe contains everything: all the star systems, galaxies, gas, dust, and everything else. ...
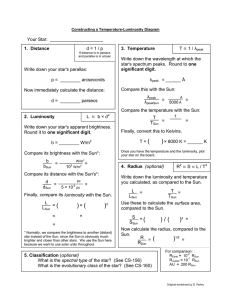
Your Star: _____________________ d = 1 / p
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
... In this exercise, we will use the observed properties (parallax, apparent brightness, and spectrum peak) of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns i ...
ISA_lecture01 - School of Physics
... (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) ...
... (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. A “dwarf planet” is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now start to look at the evolution of stars, from birth to death. Stars start out a ...
... stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now start to look at the evolution of stars, from birth to death. Stars start out a ...
Summary: Star Formation Near and Far
... infall effects can indeed be seen when one looks hard enough. Even though we still do not understand in any detail the origin of the jets, we can no longer doubt, after seeing the striking HST picture of the HH30 jet emerging from the center of a protostellar disk, that jets originate from the inner ...
... infall effects can indeed be seen when one looks hard enough. Even though we still do not understand in any detail the origin of the jets, we can no longer doubt, after seeing the striking HST picture of the HH30 jet emerging from the center of a protostellar disk, that jets originate from the inner ...
Uranus - WordPress.com
... Below are key people, locations and other information about the discoveries of Ceres, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. Research these discoveries, and write 4 paragraphs, using each of the terms below in the paragraphs. (Press Enter for hints) Here are some examples… Uranus was discovered in 1781, when W ...
... Below are key people, locations and other information about the discoveries of Ceres, Uranus, Neptune and Pluto. Research these discoveries, and write 4 paragraphs, using each of the terms below in the paragraphs. (Press Enter for hints) Here are some examples… Uranus was discovered in 1781, when W ...
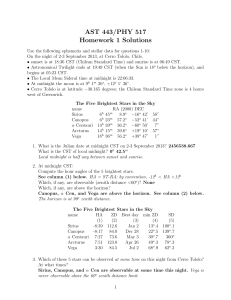
AST 443/PHY 517 Homework 1 Solutions
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
... 4. Which of these 5 stars is closest to the moon? What is the angular distance? Sirius, at about 44.3 degrees 5. The sidereal time at midnight advances by 3m 56s each day. What are the best days to observe these targets? See column (3) above. 6. What is the minimum zenith distance for each star? Se ...
The Ultraluminous X-ray Source in Holmberg IX and its Environment
... The two main hypotheses to explain the high luminosity of ULXs are intermediate mass black holes (IMBHs) having 102 to 105 solar masses (Colbert & Mushotzky 1999) or non-isotropic emission beamed into our line-of-sight (King et al. 2001). Here, we are interested in one of these objects, Holmberg IX ...
... The two main hypotheses to explain the high luminosity of ULXs are intermediate mass black holes (IMBHs) having 102 to 105 solar masses (Colbert & Mushotzky 1999) or non-isotropic emission beamed into our line-of-sight (King et al. 2001). Here, we are interested in one of these objects, Holmberg IX ...
Satellities - stoweschools.com
... Velocity of the Geostationary Satellite with respect to the sun ...
... Velocity of the Geostationary Satellite with respect to the sun ...
June 2017
... Red Giants (for example, Betelgeuse) and White Dwarf stars. Giant stars have diameters many 70 times that of the Sun. The diagonal band is called the Main Sequence but must not be seen as an evolutionary path. In the course of a star’s life it could go through different stages causing it to appear i ...
... Red Giants (for example, Betelgeuse) and White Dwarf stars. Giant stars have diameters many 70 times that of the Sun. The diagonal band is called the Main Sequence but must not be seen as an evolutionary path. In the course of a star’s life it could go through different stages causing it to appear i ...
Pitt County Schools
... understanding of stars, including our Sun. 5.05 Analyze the basic properties of a star: star’s distance, temperature, luminosity, composition, radius, mass, and radial velocity. Explain clearly the magnitude scale of stars, and its relationship to factors of brightness. Define and calculate absolu ...
... understanding of stars, including our Sun. 5.05 Analyze the basic properties of a star: star’s distance, temperature, luminosity, composition, radius, mass, and radial velocity. Explain clearly the magnitude scale of stars, and its relationship to factors of brightness. Define and calculate absolu ...
Of Orbs and Orbits
... Dynamic Time is based on planetary motions, rather than the more irregular rotation of the Earth. The difference between UTC and DT should be under 0.1 h during the period tabulated ...
... Dynamic Time is based on planetary motions, rather than the more irregular rotation of the Earth. The difference between UTC and DT should be under 0.1 h during the period tabulated ...