death_low_mass
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
... • Stars form in clusters, with all types of stars forming. O,B,A,F,G,K,M • Spiral arms barely move, but gas clouds and stars orbit around the galaxy moving in and out of spiral arms • From the HR diagram, by far the most luminous stars are the O-type stars. Their luminosity can be 100,000 times the ...
DIPLOMA THESIS Spectroscopic study of the star 70 Virginis and its
... Firstly, WGESP states that “rather than try to construct a detailed definition of a planet which is designed to cover all future possibilities, the WGESP has agreed to restrict itself to developing a working definition applicable to the cases where there already are claimed detections?” 9 . Definite ...
... Firstly, WGESP states that “rather than try to construct a detailed definition of a planet which is designed to cover all future possibilities, the WGESP has agreed to restrict itself to developing a working definition applicable to the cases where there already are claimed detections?” 9 . Definite ...
The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • At the very bottom of the main sequence, massive stars being cool because of their great mass • At the very top of the main sequence, massive stars being very hot and active • In the middle of the main sequence, with very hot but less massive stars positioned higher and massive red giant stars pos ...
... • At the very bottom of the main sequence, massive stars being cool because of their great mass • At the very top of the main sequence, massive stars being very hot and active • In the middle of the main sequence, with very hot but less massive stars positioned higher and massive red giant stars pos ...
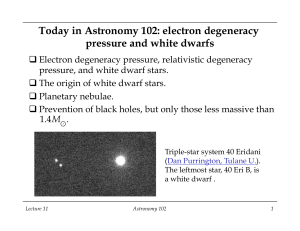
Today in Astronomy 102: electron degeneracy pressure and white
... Start with a normal star like the Sun. Fusion of protons into helium in the star’s center generates heat and pressure that can support the weight of the star. The Sun was mostly made of hydrogen (=1 proton + 1 electron) when it was born, and started with enough hydrogen to last like this for more th ...
... Start with a normal star like the Sun. Fusion of protons into helium in the star’s center generates heat and pressure that can support the weight of the star. The Sun was mostly made of hydrogen (=1 proton + 1 electron) when it was born, and started with enough hydrogen to last like this for more th ...
Extreme Optics and the Search for Earth-Like Planets
... application of optimization technology. The general area is optical design. The specific problem is to design a telescope capable of achieving the extremely high contrast needed to image planets around nearby stars. We have a close-up view of only one star, our Sun. As we all known this particular s ...
... application of optimization technology. The general area is optical design. The specific problem is to design a telescope capable of achieving the extremely high contrast needed to image planets around nearby stars. We have a close-up view of only one star, our Sun. As we all known this particular s ...
Structure of the Solar System - Beck-Shop
... and now there are known to be more than 60 satellites (see Appendix A) with indirect evidence for the existence of others. In addition there are currently more than 10,000 catalogued asteroid orbits and more than 500 reliable orbits for comets. Numerous bodies have been discovered with orbits beyond ...
... and now there are known to be more than 60 satellites (see Appendix A) with indirect evidence for the existence of others. In addition there are currently more than 10,000 catalogued asteroid orbits and more than 500 reliable orbits for comets. Numerous bodies have been discovered with orbits beyond ...
Debris Disks: Seeing Dust, Thinking of Planetesimals and Planets
... Abstract Debris disks are optically thin, almost gas-free dusty disks observed around a significant fraction of main-sequence stars older than about 10 Myr. Since the circumstellar dust is short-lived, the very existence of these disks is considered as evidence that dust-producing planetesimals are ...
... Abstract Debris disks are optically thin, almost gas-free dusty disks observed around a significant fraction of main-sequence stars older than about 10 Myr. Since the circumstellar dust is short-lived, the very existence of these disks is considered as evidence that dust-producing planetesimals are ...
Fulltext PDF
... components, viz. – disc, halo, and bulge (Figure 1). The halo is made up of an older population of stars that constitute globular clusters. Globular clusters are made up of low metallicity, dense aggregates of 50,000–100,000 stars, gravitationally bound with orbits that are randomly distributed, whi ...
... components, viz. – disc, halo, and bulge (Figure 1). The halo is made up of an older population of stars that constitute globular clusters. Globular clusters are made up of low metallicity, dense aggregates of 50,000–100,000 stars, gravitationally bound with orbits that are randomly distributed, whi ...
Unit 3 - Lesson 8.9 Life of Stars Challenge
... These coloured Super Giants have luminosities often 1,000,000X greater than the Sun The explosive death of a star A cloud of hydrogen gas and dust in space. When the gravitational and pressure forces within the initial cloud become unbalanced, the cloud collapses and breaks into small fragments. The ...
... These coloured Super Giants have luminosities often 1,000,000X greater than the Sun The explosive death of a star A cloud of hydrogen gas and dust in space. When the gravitational and pressure forces within the initial cloud become unbalanced, the cloud collapses and breaks into small fragments. The ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now start to look at the evolution of stars, from birth to death. Stars start out a ...
... stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now start to look at the evolution of stars, from birth to death. Stars start out a ...
The Detection and Characterization of Extrasolar Planets
... measurements can also be used to infer the presence of multiple planets, and indeed, many such systems have been detected [9]. 2.2. The Transit Method The transit method is probably the most obvious of the indirect exoplanet detection methods. It involves simply observing stars and waiting for small ...
... measurements can also be used to infer the presence of multiple planets, and indeed, many such systems have been detected [9]. 2.2. The Transit Method The transit method is probably the most obvious of the indirect exoplanet detection methods. It involves simply observing stars and waiting for small ...
Chapter 16 Star Birth Where do stars form? Star
... • The random motions of different sections of the cloud cause it to become lumpy ...
... • The random motions of different sections of the cloud cause it to become lumpy ...
Slide 1
... Slow rotation in luminous E’s implies that such objects are flattened by velocity anisotropy rather than rotation. Schwarzchild (1982) showed that: •This argues for triaxial objects – many giant E’s have not relaxed enough to develop an axis of symmetry •equilibrium triaxial systems could exist with ...
... Slow rotation in luminous E’s implies that such objects are flattened by velocity anisotropy rather than rotation. Schwarzchild (1982) showed that: •This argues for triaxial objects – many giant E’s have not relaxed enough to develop an axis of symmetry •equilibrium triaxial systems could exist with ...
Migrating Dust Particles
... size they drifted towards the Sun. This material was later accreted to planetesimals which are held together by self-gravity. As the planetesimals extend their gravitational range they have a run-away growth towards becoming planets. In this step the planetesimals grow more the larger they get. This ...
... size they drifted towards the Sun. This material was later accreted to planetesimals which are held together by self-gravity. As the planetesimals extend their gravitational range they have a run-away growth towards becoming planets. In this step the planetesimals grow more the larger they get. This ...
Low-Mass Star Formation Triggered by Supernova in Primordial
... H2 and HD increase by about 103 times compared with primordial composition because of re-ionization caused by SNR shock Fragmentation (or low mass star formation) condition: ...
... H2 and HD increase by about 103 times compared with primordial composition because of re-ionization caused by SNR shock Fragmentation (or low mass star formation) condition: ...
File
... attraction on each other increases. • This pulls more nearby particles toward an area of increasing mass, and regions of dense matter begin to build up within the nebula. ...
... attraction on each other increases. • This pulls more nearby particles toward an area of increasing mass, and regions of dense matter begin to build up within the nebula. ...