Genetic analysis of dopaminergic system development in zebrafish
... control of vertebrate nervous system development. Here, we present an overview on the formation of dopaminergic neuronal groups in zebrafish and compare the positions of DA neurons in fish and mammals using the neuromere model of the vertebrate brain. Based on mutant analysis, we evaluate the role of ...
... control of vertebrate nervous system development. Here, we present an overview on the formation of dopaminergic neuronal groups in zebrafish and compare the positions of DA neurons in fish and mammals using the neuromere model of the vertebrate brain. Based on mutant analysis, we evaluate the role of ...
What and Where Pathways
... Figure 4.2 (a) Inputs and outputs of an LGN neuron. The neuron receives signals from the retina and also receives signals from the cortex, from elsewhere in the thalamus (T), from other LGN neurons (L), and from the brain stem. Excitatory synapses are indicated by Y’s and inhibitory ones by T’s. (b ...
... Figure 4.2 (a) Inputs and outputs of an LGN neuron. The neuron receives signals from the retina and also receives signals from the cortex, from elsewhere in the thalamus (T), from other LGN neurons (L), and from the brain stem. Excitatory synapses are indicated by Y’s and inhibitory ones by T’s. (b ...
Enlightenment - The Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science
... link between neural activity and behavior (8). Multielectrode arrays or single electrodes can record extracellular signals from both single cells and population activity (local field potentials); patch clamping methods are used to record with great precision from single neurons; and optogenetic volt ...
... link between neural activity and behavior (8). Multielectrode arrays or single electrodes can record extracellular signals from both single cells and population activity (local field potentials); patch clamping methods are used to record with great precision from single neurons; and optogenetic volt ...
Document
... *a high concentration of Na ions is on the outside of the cell membrane & a high concentration of K ions is on the inside *in a resting cell, more positive ions leave the cell than enter it, so the inside of the cell membrane develops a negative charge with respect to the outside; this takes ATP to ...
... *a high concentration of Na ions is on the outside of the cell membrane & a high concentration of K ions is on the inside *in a resting cell, more positive ions leave the cell than enter it, so the inside of the cell membrane develops a negative charge with respect to the outside; this takes ATP to ...
GENERAL CONCEPTS OF NERVOUS SYSTEM
... • The brain + the spinal cord. – The center of integration and control. – Peripheral Nervous System: ...
... • The brain + the spinal cord. – The center of integration and control. – Peripheral Nervous System: ...
Photon Microscopy in Living Brain Tissue
... cytes were transferred onto the slice. After 15 min, most of the stimulated T cells either adhered to the slice surface or had already invaded the brain parenchyma (Gimsa et al., 2000). This was not the case for unstimulated T cells, which were almost never detected within the parenchyma of the brai ...
... cytes were transferred onto the slice. After 15 min, most of the stimulated T cells either adhered to the slice surface or had already invaded the brain parenchyma (Gimsa et al., 2000). This was not the case for unstimulated T cells, which were almost never detected within the parenchyma of the brai ...
NeuralNets273ASpring09
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
... • Neurons communicate by receiving signals on their dendrites. Adding these signals and firing off a new signal along the axon if the total input exceeds a threshold. • The axon connects to new dendrites through synapses which can learn how much signal is transmitted. • McCulloch and Pitt (’43) buil ...
TENS/5.
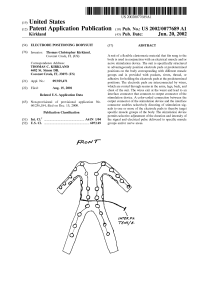
... advantageously hold and position electrode pads at prede termined positions on the body corresponding With speci?c placed at positions 30 strategically located on the suit at locations Which correspond to the particular muscle groups and/or nerve areas Which can be selectively treated. Wiring ...
... advantageously hold and position electrode pads at prede termined positions on the body corresponding With speci?c placed at positions 30 strategically located on the suit at locations Which correspond to the particular muscle groups and/or nerve areas Which can be selectively treated. Wiring ...
Detection of RNA in the central and peripheral nervous system using
... protein-coding potential. Most recent statistics from GENCODE3 (v25, March 2016) show that the human genome contains 23,025 non-coding genes, surpassing the number of protein-coding genes (19,950). About 70% (15,767) of these non-coding genes code for long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Recent studies h ...
... protein-coding potential. Most recent statistics from GENCODE3 (v25, March 2016) show that the human genome contains 23,025 non-coding genes, surpassing the number of protein-coding genes (19,950). About 70% (15,767) of these non-coding genes code for long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs). Recent studies h ...
BRAIN FOUNDATION RESEARCH REPORTS Author: Dr Tim
... brain cells?” Summary: Background. In rodents we had shown that the number of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive (TH+) or dopaminergic neurones is altered up or down by ±10-15% following 1-2 weeks exposure to environmental or behavioural stimuli, including length of light:dark cycle (photoperiod), ...
... brain cells?” Summary: Background. In rodents we had shown that the number of tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive (TH+) or dopaminergic neurones is altered up or down by ±10-15% following 1-2 weeks exposure to environmental or behavioural stimuli, including length of light:dark cycle (photoperiod), ...
Nervous System Lect/96
... terminates in end bulbs (boutons) which interact with other neurons or non-nerve cells, forming synapses. Synapses transmit information to the next cell in the circuit. Most neurons have only one axon; a very few have no axon at all. Axons may be short, or very ...
... terminates in end bulbs (boutons) which interact with other neurons or non-nerve cells, forming synapses. Synapses transmit information to the next cell in the circuit. Most neurons have only one axon; a very few have no axon at all. Axons may be short, or very ...
Slayt 1 - Department of Information Technologies
... – Image and data compression, automated information services, real-time translation of spoken language, customer payment processing systems ...
... – Image and data compression, automated information services, real-time translation of spoken language, customer payment processing systems ...
31.1 Really Neurons
... Name and describe the three types of neurons Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. Interneurons process the information from sensory neurons and send commands to other interneurons or motor neurons ...
... Name and describe the three types of neurons Sensory neurons carry impulses from the sense organs. Motor neurons carry impulses from the brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands. Interneurons process the information from sensory neurons and send commands to other interneurons or motor neurons ...
Chapter 4: The Cytology of Neurons
... Neurons are highly polarized The cell function of neurons are compartmentalized, contributing to the processing of electrical signals -cell body (soma): RNA/proteins synthesis -dendrites: thin processes to receive synaptic input from other neurons -axons: another thin process to propagate electric i ...
... Neurons are highly polarized The cell function of neurons are compartmentalized, contributing to the processing of electrical signals -cell body (soma): RNA/proteins synthesis -dendrites: thin processes to receive synaptic input from other neurons -axons: another thin process to propagate electric i ...
Intrinsic firing patterns of diverse neocortical neurons
... As their name implies, the neurons most commonly encountered in electrophysiological studies generate what Mountcastle and his colleagues TM were the first to call 'regular' action potentials. Most published intracellular recordings from neocortex in vivo have been from RS neurons (e.g. Refs 5, 6). ...
... As their name implies, the neurons most commonly encountered in electrophysiological studies generate what Mountcastle and his colleagues TM were the first to call 'regular' action potentials. Most published intracellular recordings from neocortex in vivo have been from RS neurons (e.g. Refs 5, 6). ...
Sensory nerve conduction studies
... reference electrode may be used instead of a needle. Type of stimulating electrodes: Near nerve needle electrodes. Stimulation site: The cathode is placed on the medial side close to the base of the toe. Each toe, I-V, is studied separately. The cathode is inserted trough the skin from the dorsal si ...
... reference electrode may be used instead of a needle. Type of stimulating electrodes: Near nerve needle electrodes. Stimulation site: The cathode is placed on the medial side close to the base of the toe. Each toe, I-V, is studied separately. The cathode is inserted trough the skin from the dorsal si ...
Nervous System: Nervous Tissue (Chapter 12) Lecture Materials for
... -creates high [K+] inside and high [Na+]outside! When Na+ channel opens:! - Na+ flows into cell:! !1. Favored by diffusion gradient! !2. Favored by electrical gradient! open channel = $resistance = #ion flow/current! When K+ channel opens:! - K+ flows out of cell:! !1. Favored by diffusion gradient ...
... -creates high [K+] inside and high [Na+]outside! When Na+ channel opens:! - Na+ flows into cell:! !1. Favored by diffusion gradient! !2. Favored by electrical gradient! open channel = $resistance = #ion flow/current! When K+ channel opens:! - K+ flows out of cell:! !1. Favored by diffusion gradient ...
chapter 11-nerve tissue
... a. The Cell Body-contains the organelles and cytoplasm of the neuron. b. Dendrites-highly-branched structures that emerge from the cell body. 1) These carry impulses into the cell body of a neuron. These are not covered by myelin sheaths in neurons. c. Axons-long projection extending from the cell b ...
... a. The Cell Body-contains the organelles and cytoplasm of the neuron. b. Dendrites-highly-branched structures that emerge from the cell body. 1) These carry impulses into the cell body of a neuron. These are not covered by myelin sheaths in neurons. c. Axons-long projection extending from the cell b ...
Nerve Cross Section
... Identify the following components of a cross sectioned nerve using diagrams and prepared slides: myelin sheath, nerve fibers, fascicles, endoneurium, perineurium and epineurium ...
... Identify the following components of a cross sectioned nerve using diagrams and prepared slides: myelin sheath, nerve fibers, fascicles, endoneurium, perineurium and epineurium ...
last lecture neurophysiology - Evans Laboratory: Environmental
... • this increase in internal Ca+2 concentration triggers the release of SYNAPTIC VESICLES, synaptic vesicles contain neurotransmitters, which are then released across the synapse ...
... • this increase in internal Ca+2 concentration triggers the release of SYNAPTIC VESICLES, synaptic vesicles contain neurotransmitters, which are then released across the synapse ...
Document
... from which several long cilia radiate down into the olfactory epithelium and into the mucus, where the air and odorant molecules stimulate the neuron. ...
... from which several long cilia radiate down into the olfactory epithelium and into the mucus, where the air and odorant molecules stimulate the neuron. ...
Psychiatry`s age of enlightenment
... A main advantage of optogenetics over other traditional approaches to neuromodulation, such as electrophysiology, is the spatial resolution that can be achieved. For instance, in a heterogeneous population of neurons, an electrode would stimulate all neurons within the vicinity, regardless of subtyp ...
... A main advantage of optogenetics over other traditional approaches to neuromodulation, such as electrophysiology, is the spatial resolution that can be achieved. For instance, in a heterogeneous population of neurons, an electrode would stimulate all neurons within the vicinity, regardless of subtyp ...
The Scientist » Magazine » Lab Tools
... cortical spheroid sits to the right of an intact embryonic generate such cortical spheroids using cells isolated mouse brain. At this stage of the spheroid’s development, astrocytes are beginning to appear and from people with autism or schizophrenia, which neurons are forming connections. (Bottom) ...
... cortical spheroid sits to the right of an intact embryonic generate such cortical spheroids using cells isolated mouse brain. At this stage of the spheroid’s development, astrocytes are beginning to appear and from people with autism or schizophrenia, which neurons are forming connections. (Bottom) ...
Chapter Two - Texas Christian University
... polarity which results in a graded potential. When there are enough graded potentials in succession, channels open allowing positive ions from the outside to enter the interior of the neuron. Entrance of the positive ions into the cell body depolarizes the neuron, changing the interior from negative ...
... polarity which results in a graded potential. When there are enough graded potentials in succession, channels open allowing positive ions from the outside to enter the interior of the neuron. Entrance of the positive ions into the cell body depolarizes the neuron, changing the interior from negative ...