Unit 3A Nervous System - Teacher Version
... • Afferent (Sensory) Neurons carry messages from tissues and sensory organs to the brain and spinal cord for processing ...
... • Afferent (Sensory) Neurons carry messages from tissues and sensory organs to the brain and spinal cord for processing ...
Nervous System WS (handed out after section exam)
... The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases because the myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing ion loss f ...
... The myelin sheath is responsible for saltatory conduction / transmission. This is where the electrical impulses jump from one node of Ranvier to the next node. This increases the speed of the nerve impulse. The speed increases because the myelin sheath acts as an insulator, preventing ion loss f ...
Vocal communication between male Xenopus laevis
... Some examples of background information include: How does a neuron receive information? What determines whether a neuron produces an action potential (and what is an action potential)? How does synaptic transmission work? For the most part, however, we will focus not on the individual neuron but on ...
... Some examples of background information include: How does a neuron receive information? What determines whether a neuron produces an action potential (and what is an action potential)? How does synaptic transmission work? For the most part, however, we will focus not on the individual neuron but on ...
Human Nervous System Central nervous system
... Accept nerve impulses from the CNS Transmit them to muscles or glands ...
... Accept nerve impulses from the CNS Transmit them to muscles or glands ...
packet - mybiologyclass
... 12. Solve a problem similar to the activity we did in “the brain and its functions.” Given parts of the brain and the areas of the body they govern, tell what might happen to the body if certain parts of the brain were damaged. (You will be given all of the information, you will just have to know ho ...
... 12. Solve a problem similar to the activity we did in “the brain and its functions.” Given parts of the brain and the areas of the body they govern, tell what might happen to the body if certain parts of the brain were damaged. (You will be given all of the information, you will just have to know ho ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... • But the voltage for producing O2(g) from solution is considerably higher than the standard potential, because of the high activation energy needed to form O2(g). • The voltage for this half cell seems to be closer to –1.5 V in reality. • The result then is the production of Cl2(g) and Cu(s). an ...
... • But the voltage for producing O2(g) from solution is considerably higher than the standard potential, because of the high activation energy needed to form O2(g). • The voltage for this half cell seems to be closer to –1.5 V in reality. • The result then is the production of Cl2(g) and Cu(s). an ...
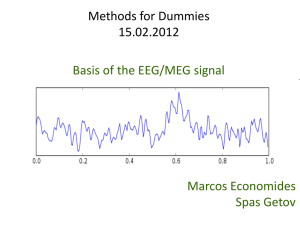
Electroencephalography
... and temporally – A single pyramidal cell may have more than 104 synapses distributed over its soma and dendritic surface. ...
... and temporally – A single pyramidal cell may have more than 104 synapses distributed over its soma and dendritic surface. ...
Central Auditory Pathways
... Neuron specialization The three major types of neurons, depending on their specialization: Sensory Neurons Motor Neurons Interneurons ...
... Neuron specialization The three major types of neurons, depending on their specialization: Sensory Neurons Motor Neurons Interneurons ...
LTP
... Typical LTP experiment: record from cell in hippocampus area CA1 (receives Schaffer collaterals from area CA3). In addition, stimulate two sets of input fibers. ...
... Typical LTP experiment: record from cell in hippocampus area CA1 (receives Schaffer collaterals from area CA3). In addition, stimulate two sets of input fibers. ...
Thalamus & Hypothalamus
... • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
... • Forms floor and lower walls of third ventricle • Contains various classes of peptidergic neuroendocrine cells which control endocrine function • Communicates with cortex via limbic system and also via direct projections ...
File
... Many action potentials are generated one after another along the cell membrane, causing a wave of depolarization (similar to falling dominos). When axons are myelinated, nerve impulses travel by saltatory conduction ...
... Many action potentials are generated one after another along the cell membrane, causing a wave of depolarization (similar to falling dominos). When axons are myelinated, nerve impulses travel by saltatory conduction ...
Self Assessment Chapter 11 - CM
... • Multipolar neurons – with a single axon and multiple dendrites, make up over 99% of all neurons ...
... • Multipolar neurons – with a single axon and multiple dendrites, make up over 99% of all neurons ...
NEURAL NETWORKS
... can perform the basic logic operations NOT, OR and AND. As any multivariable combinational function can be constructed using these operations, digital computer hardware of great complexity can be constructed using these simple neurons as building blocks. The above network has its knowledge pre-coded ...
... can perform the basic logic operations NOT, OR and AND. As any multivariable combinational function can be constructed using these operations, digital computer hardware of great complexity can be constructed using these simple neurons as building blocks. The above network has its knowledge pre-coded ...
48 0007-4888/05/14010048 © 2005 Springer Science+Business
... Even a slight decrease in GABAergic synaptic inhibition modifies the function of CNS. It remains unclear whether decreased inhibition is an obligatory component of hyperexcitability, typical of epilepsy. In some acute models of epilepsy and epileptiform status cell loss in epileptogenic zones correl ...
... Even a slight decrease in GABAergic synaptic inhibition modifies the function of CNS. It remains unclear whether decreased inhibition is an obligatory component of hyperexcitability, typical of epilepsy. In some acute models of epilepsy and epileptiform status cell loss in epileptogenic zones correl ...
The Languages of Neurons: An Analysis of Coding Mechanisms by
... expensive process, calculated as using 2.2 × 109 adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules per spike [9], it has been proposed that AP’s are generated only when required for specific tasks and that neurons are electro-physiologically inactive most of the time 2.2. Neuronal language formats While inform ...
... expensive process, calculated as using 2.2 × 109 adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules per spike [9], it has been proposed that AP’s are generated only when required for specific tasks and that neurons are electro-physiologically inactive most of the time 2.2. Neuronal language formats While inform ...
Brain development
... • (5) In development: genes that code for modules are expressed and modules develop according to these instructions “The grammar genes would be stretches of DNA that code for proteins… that guide, attract, or glue neurons together into networks that… are necessary to compute the solution to some gra ...
... • (5) In development: genes that code for modules are expressed and modules develop according to these instructions “The grammar genes would be stretches of DNA that code for proteins… that guide, attract, or glue neurons together into networks that… are necessary to compute the solution to some gra ...
Worksheet - Nervous System I Lecture Notes Page
... must open then close in sequence along the entire length of the cell membrane. This results in a relative ________________ (slower/faster) rate of conduction. In contract, myelinated neurons are capable of ___________________________(continuous/saltatory) conduction. In this type of conduction only ...
... must open then close in sequence along the entire length of the cell membrane. This results in a relative ________________ (slower/faster) rate of conduction. In contract, myelinated neurons are capable of ___________________________(continuous/saltatory) conduction. In this type of conduction only ...
Neurons eat glutamate to stay alive
... in culture, the effects in rat brain slices were less pronounced. However, as Divakaruni et al. (2017) explain, many other cell types may be masking the effects. Nonetheless, it would also be interesting to test such metabolic flexibility in vivo by infusing 13C-labeled glutamate to determine its in ...
... in culture, the effects in rat brain slices were less pronounced. However, as Divakaruni et al. (2017) explain, many other cell types may be masking the effects. Nonetheless, it would also be interesting to test such metabolic flexibility in vivo by infusing 13C-labeled glutamate to determine its in ...
2301 - Ch. 4.2
... chemicals released by mast cells stimulate nerve endings that produce the sensation of pain. ...
... chemicals released by mast cells stimulate nerve endings that produce the sensation of pain. ...
Principles of Electrical Currents
... a dispersive pad, usually located proximal to the treatment area – Bipolar: two electrodes of equal size, both are over or near the treatment site – Water immersion - used for irregularly shaped areas – Probes: one hand-held active lead • advantages: can locate and treat small triggers • disadvantag ...
... a dispersive pad, usually located proximal to the treatment area – Bipolar: two electrodes of equal size, both are over or near the treatment site – Water immersion - used for irregularly shaped areas – Probes: one hand-held active lead • advantages: can locate and treat small triggers • disadvantag ...
doc GIT
... Lecture 01 – March 22th 2006 GIT role in homeostasis The main reason that systems fct the way they ...
... Lecture 01 – March 22th 2006 GIT role in homeostasis The main reason that systems fct the way they ...
Darwin VII after - Ohio University
... robot series simulate other brain regions. All are run by brain-like neuronal nets with thousands of "neurons." Such models help to test out our detailed models of the brain at the level of cell assemblies. (With thanks to Dr. Jeff Krichmar, The Neurosciences Institute, San Diego, www.nsi.edu). To a ...
... robot series simulate other brain regions. All are run by brain-like neuronal nets with thousands of "neurons." Such models help to test out our detailed models of the brain at the level of cell assemblies. (With thanks to Dr. Jeff Krichmar, The Neurosciences Institute, San Diego, www.nsi.edu). To a ...
Ch03
... • Signals from the retina travel through the optic nerve to the – Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) – Primary visual receiving area in the occipital lobe (the striate cortex or area V1) – And then through two pathways to the temporal lobe and the parietal lobe ...
... • Signals from the retina travel through the optic nerve to the – Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) – Primary visual receiving area in the occipital lobe (the striate cortex or area V1) – And then through two pathways to the temporal lobe and the parietal lobe ...
Implementation of an Educational Wireless Biopotential
... The goal of the project was to implement a system to record electroencephalography biopotential measurements, and to send them wirelessly to a cloud storage service. Moreover, the application should allow the user to view and manage the recorded data using a browser. The application was planned to b ...
... The goal of the project was to implement a system to record electroencephalography biopotential measurements, and to send them wirelessly to a cloud storage service. Moreover, the application should allow the user to view and manage the recorded data using a browser. The application was planned to b ...
Perception
... *important property of neurons because it enables them to transmit signals over long distances 2.)Action potential remains the same size no matter what the intensity of the stimulus is *increasing intensity changes the rate of firing (not the size of the action potentials) Limit to increasing late ...
... *important property of neurons because it enables them to transmit signals over long distances 2.)Action potential remains the same size no matter what the intensity of the stimulus is *increasing intensity changes the rate of firing (not the size of the action potentials) Limit to increasing late ...