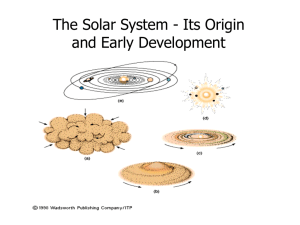
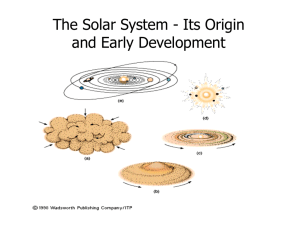
The formation of stars and planets
... as comets. Biggest KBOs: Pluto-Charon, Sedna, Quauar, unnamed new object. • Oort cloud: nearly spherical swarm of comets, originally formed in outer solar system, then kicked out by Jupiter, but still marginally bound to solar system. ...
... as comets. Biggest KBOs: Pluto-Charon, Sedna, Quauar, unnamed new object. • Oort cloud: nearly spherical swarm of comets, originally formed in outer solar system, then kicked out by Jupiter, but still marginally bound to solar system. ...
Exoplanet Discovery
... planets (astroseismology) and atmospheric composition – what will we find? ...
... planets (astroseismology) and atmospheric composition – what will we find? ...
ppt
... planet's size, distance from star, and orbital period. With velocity measurements, could then get planet's mass and hence density (rocky, gas giant?) *Massive planet like Jupiter that is very close to the star ...
... planet's size, distance from star, and orbital period. With velocity measurements, could then get planet's mass and hence density (rocky, gas giant?) *Massive planet like Jupiter that is very close to the star ...
Lecture (Powerpoint)
... gas cloud or disk, increase in gravitational attraction to that region... Unstable ...
... gas cloud or disk, increase in gravitational attraction to that region... Unstable ...
α Centauri: a double star - University of Canterbury
... An example of planet formation in a circumstellar disk around α CenB. The disk is initially populated by 600 lunar-mass planetary embryos in nearly circular orbits. The radius of each circle is proportional to the size of the object. After 200 Myr four planets have formed. One planet has about the m ...
... An example of planet formation in a circumstellar disk around α CenB. The disk is initially populated by 600 lunar-mass planetary embryos in nearly circular orbits. The radius of each circle is proportional to the size of the object. After 200 Myr four planets have formed. One planet has about the m ...
ph709-09
... cannot be positively ruled out by theoretical models due to uncertainties affecting cloud properties and cloud cover. Highly reflective clouds covering at least 75% of the day side of the planet could indeed prevent the water reservoir from being entirely vaporized. Planet “d”. Irradiation condition ...
... cannot be positively ruled out by theoretical models due to uncertainties affecting cloud properties and cloud cover. Highly reflective clouds covering at least 75% of the day side of the planet could indeed prevent the water reservoir from being entirely vaporized. Planet “d”. Irradiation condition ...
SES4U ~ The Formation of Our Solar Systemstudentcopy
... than the H and He gas. What happens next is uncertain. – One possibility is that the thin disk of dust is gravitationally unstable, leading to the formation of roughly 1 kilometer size objects known as planetesimals. – Another possibility is that the flow in the disk is turbulent, so that the dust c ...
... than the H and He gas. What happens next is uncertain. – One possibility is that the thin disk of dust is gravitationally unstable, leading to the formation of roughly 1 kilometer size objects known as planetesimals. – Another possibility is that the flow in the disk is turbulent, so that the dust c ...
Comparative Planetology
... shaken up the universe by suggesting that Pluto is not necessarily a planet at all but just a lump of ice. The startling suggestion comes from scientists at the Rose Center for Earth and Space, which opened last year at the American Museum of Natural History in New York. ...
... shaken up the universe by suggesting that Pluto is not necessarily a planet at all but just a lump of ice. The startling suggestion comes from scientists at the Rose Center for Earth and Space, which opened last year at the American Museum of Natural History in New York. ...
Number of planets - Associazione Astrofili "Crab Nebula"
... The Working Group on Extrasolar Planets (WGESP) of the IAU defines as an extrasolar planet (shortened exoplanet) “…a body whose mass lies below the threshold value for the onset of deuterium thermo-nuclear fusion (which is about 13 Jupiter masses [MJ] for a typical solar composition) and at the same ...
... The Working Group on Extrasolar Planets (WGESP) of the IAU defines as an extrasolar planet (shortened exoplanet) “…a body whose mass lies below the threshold value for the onset of deuterium thermo-nuclear fusion (which is about 13 Jupiter masses [MJ] for a typical solar composition) and at the same ...
Level 1 Solar system, Planets, Sun, Asteroid belt, Kuipler belt and
... 2. Our solar system is made up of the sun and everything that travels around it. This includes eight planets and their natural satellites such as Earth's moon; dwarf planets such as Pluto and Ceres; asteroids; comets and meteoroids 3. The sun is the center of our solar system. It contains almost all ...
... 2. Our solar system is made up of the sun and everything that travels around it. This includes eight planets and their natural satellites such as Earth's moon; dwarf planets such as Pluto and Ceres; asteroids; comets and meteoroids 3. The sun is the center of our solar system. It contains almost all ...
Light of Distant Stars - Glasgow Science Centre
... Jeremiah Horrocks was an English astronomer who lived in the 17th century. He wrote about the first observed transit of Venus. Here is his account of the event, as taken from his book Venus in Sole Visa: When the time of the observation approached, I retired to my apartment, and having closed the wi ...
... Jeremiah Horrocks was an English astronomer who lived in the 17th century. He wrote about the first observed transit of Venus. Here is his account of the event, as taken from his book Venus in Sole Visa: When the time of the observation approached, I retired to my apartment, and having closed the wi ...
Pocket Solar System
... Notes to the presenter Making the Pocket Solar System model Refer to the illustrated instruction sheet to guide participants through the following steps: 1. Put the Sun at one end of the paper and the Kuiper belt at the other end. 2. Fold the paper in half and make sure you crease it firmly. Un ...
... Notes to the presenter Making the Pocket Solar System model Refer to the illustrated instruction sheet to guide participants through the following steps: 1. Put the Sun at one end of the paper and the Kuiper belt at the other end. 2. Fold the paper in half and make sure you crease it firmly. Un ...
Origin and Nature of Planetary Systems
... We have included a model for another system. For the string model, we used the same scale as the previous systems, 1 meter = 100,000,000 kilometers. However, we have also enlarged the model to 1 meter = 10,000,000 kilometers so that we can show the smaller bodies to scale. What is this system (ans ...
... We have included a model for another system. For the string model, we used the same scale as the previous systems, 1 meter = 100,000,000 kilometers. However, we have also enlarged the model to 1 meter = 10,000,000 kilometers so that we can show the smaller bodies to scale. What is this system (ans ...
oct81
... why do you think all the terrestrial planets have smaller masses than the Jovian planets? 98% hydrogen and helium 1.4% hydrogen compounds – CH4, NH3, H2O ...
... why do you think all the terrestrial planets have smaller masses than the Jovian planets? 98% hydrogen and helium 1.4% hydrogen compounds – CH4, NH3, H2O ...
A report of the SEEDS Direct Imaging Survey
... super-earths around late M stars – Planet formation around M stars • TMT era / SEIT: ~2024• WFIRST: early 2020s- ...
... super-earths around late M stars – Planet formation around M stars • TMT era / SEIT: ~2024• WFIRST: early 2020s- ...
Unit 5
... Earth revolves around the Sun in and year and rotates on its axis in a 24-hour day. They have related this rotation of Earth to day and night while recognizing that the movements of the sun, moon, and stars are connected. SC.5.E.5.1: (DOK 1) Recognize that a galaxy consists of gas, dust, and many st ...
... Earth revolves around the Sun in and year and rotates on its axis in a 24-hour day. They have related this rotation of Earth to day and night while recognizing that the movements of the sun, moon, and stars are connected. SC.5.E.5.1: (DOK 1) Recognize that a galaxy consists of gas, dust, and many st ...
Solar System Formation
... Comets are sometimes called dirty snowballs or "icy mudballs". They are a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust that for some reason didn't get incorporated into planets when the solar system was formed. This makes them very interesting as samples of the early history of the solar s ...
... Comets are sometimes called dirty snowballs or "icy mudballs". They are a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust that for some reason didn't get incorporated into planets when the solar system was formed. This makes them very interesting as samples of the early history of the solar s ...
Solar System - eNetLearning
... Comets are sometimes called dirty snowballs or "icy mudballs". They are a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust that for some reason didn't get incorporated into planets when the solar system was formed. This makes them very interesting as samples of the early history of the solar s ...
... Comets are sometimes called dirty snowballs or "icy mudballs". They are a mixture of ices (both water and frozen gases) and dust that for some reason didn't get incorporated into planets when the solar system was formed. This makes them very interesting as samples of the early history of the solar s ...
What theory best explains the features of our
... twice Mars distance) • Also very different in composition: mostly H/He; no solid surface. • Gigantic for a planet: 300 Earth mass; >1,000 Earth volume. • Many moons, rings… Great Red Spot ...
... twice Mars distance) • Also very different in composition: mostly H/He; no solid surface. • Gigantic for a planet: 300 Earth mass; >1,000 Earth volume. • Many moons, rings… Great Red Spot ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... same straight line (2D according to the 2D picture and the 2D surface, though they are in 3D space, or 4D as Einstein said) and then the star is in b or b’ position, there the probability depends on the planet’s angle with it’s axis and the star of which the planet is moving around. ...
... same straight line (2D according to the 2D picture and the 2D surface, though they are in 3D space, or 4D as Einstein said) and then the star is in b or b’ position, there the probability depends on the planet’s angle with it’s axis and the star of which the planet is moving around. ...
PLANETS
... The COROT instrument makes it possible, with a method called stellar seismology, to probe the inner structure of the stars, as well as to detect many extrasolar planets, by observing the periodic micro-eclipses occurring when these bodies transit in front of their parent star. Its objective is doubl ...
... The COROT instrument makes it possible, with a method called stellar seismology, to probe the inner structure of the stars, as well as to detect many extrasolar planets, by observing the periodic micro-eclipses occurring when these bodies transit in front of their parent star. Its objective is doubl ...
Chapter 15
... into the “hot Jupiter” category, making other planetary systems look quite different from our own. Until we are able to observe much smaller planets at much larger distances from their parent stars, we will not know just how unusual our own system is – or if it is unusual at all. ...
... into the “hot Jupiter” category, making other planetary systems look quite different from our own. Until we are able to observe much smaller planets at much larger distances from their parent stars, we will not know just how unusual our own system is – or if it is unusual at all. ...
Celestial Objects
... Earth has only one moon (called the Moon). Some planets, including Jupiter and Saturn, have dozens of moons. ...
... Earth has only one moon (called the Moon). Some planets, including Jupiter and Saturn, have dozens of moons. ...
Planet

A planet (from Ancient Greek ἀστήρ πλανήτης (astēr planētēs), or πλάνης ἀστήρ (plánēs astēr), meaning ""wandering star"") is an astronomical object orbiting a star, brown dwarf, or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science, mythology, and religion. Several planets in the Solar System can be seen with the naked eye. These were regarded by many early cultures as divine, or as emissaries of deities. As scientific knowledge advanced, human perception of the planets changed, incorporating a number of disparate objects. In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially adopted a resolution defining planets within the Solar System. This definition is controversial because it excludes many objects of planetary mass based on where or what they orbit. Although eight of the planetary bodies discovered before 1950 remain ""planets"" under the modern definition, some celestial bodies, such as Ceres, Pallas, Juno, Vesta (each an object in the solar asteroid belt), and Pluto (the first trans-Neptunian object discovered), that were once considered planets by the scientific community are no longer viewed as such.The planets were thought by Ptolemy to orbit Earth in deferent and epicycle motions. Although the idea that the planets orbited the Sun had been suggested many times, it was not until the 17th century that this view was supported by evidence from the first telescopic astronomical observations, performed by Galileo Galilei. By careful analysis of the observation data, Johannes Kepler found the planets' orbits were not circular but elliptical. As observational tools improved, astronomers saw that, like Earth, the planets rotated around tilted axes, and some shared such features as ice caps and seasons. Since the dawn of the Space Age, close observation by space probes has found that Earth and the other planets share characteristics such as volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology.Planets are generally divided into two main types: large low-density giant planets, and smaller rocky terrestrials. Under IAU definitions, there are eight planets in the Solar System. In order of increasing distance from the Sun, they are the four terrestrials, Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars, then the four giant planets, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Six of the planets are orbited by one or more natural satellites.More than a thousand planets around other stars (""extrasolar planets"" or ""exoplanets"") have been discovered in the Milky Way: as of 1 October 2015, 1968 known extrasolar planets in 1248 planetary systems (including 490 multiple planetary systems), ranging in size from just above the size of the Moon to gas giants about twice as large as Jupiter. On December 20, 2011, the Kepler Space Telescope team reported the discovery of the first Earth-sized extrasolar planets, Kepler-20e and Kepler-20f, orbiting a Sun-like star, Kepler-20. A 2012 study, analyzing gravitational microlensing data, estimates an average of at least 1.6 bound planets for every star in the Milky Way.Around one in five Sun-like stars is thought to have an Earth-sized planet in its habitable zone.