Astronomy Today 7th Edition Chaisson/McMillan
... collision at a critical time during formation. ...
... collision at a critical time during formation. ...
HW6 due - Yale Astronomy
... The probability for 1 star passing through a galaxy to collide with any 1 particular star from that galaxy is given by the ratio of the cross sectional area for a collision with the projected a ...
... The probability for 1 star passing through a galaxy to collide with any 1 particular star from that galaxy is given by the ratio of the cross sectional area for a collision with the projected a ...
Primordial planets, comets and moons foster life in the cosmos
... (1013 -1016 s), which is often termed the dark ages for ΛCDMHC (top) because this is the time required for the first star and the first planets to appear in this cosmology. The temperature of space has fallen to a few oK that will freeze any gas. The density has decreased by a billion. Any life aris ...
... (1013 -1016 s), which is often termed the dark ages for ΛCDMHC (top) because this is the time required for the first star and the first planets to appear in this cosmology. The temperature of space has fallen to a few oK that will freeze any gas. The density has decreased by a billion. Any life aris ...
Life in the galactic danger zone
... giant planets to inhibit these terrestrial planets. The danger posed by high metallicity environments in the work of Lineweaver is higher than that of our work.” So, if you believe Gowanlock, the higher metallicity coupled with the high density of stars near the galactic centre means that although m ...
... giant planets to inhibit these terrestrial planets. The danger posed by high metallicity environments in the work of Lineweaver is higher than that of our work.” So, if you believe Gowanlock, the higher metallicity coupled with the high density of stars near the galactic centre means that although m ...
Absorption efficiencies of antenna complexes in photosynthetic
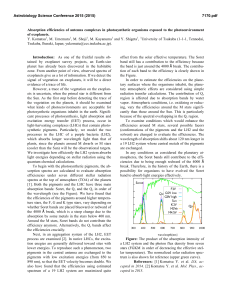
... light-harvesting complexes (LHCs) that contain photosynthetic pigments. Particularly, we model the two processes in the LHC of a purple bacteria (LH2), which absorbs longer wavelength light than that of plants, since the planets around M dwarfs or M stars (cooler than the Sun) will be the observatio ...
... light-harvesting complexes (LHCs) that contain photosynthetic pigments. Particularly, we model the two processes in the LHC of a purple bacteria (LH2), which absorbs longer wavelength light than that of plants, since the planets around M dwarfs or M stars (cooler than the Sun) will be the observatio ...
Comets-Asteroids-and
... and carbon. • The first one discovered (and the biggest) is named Ceres; it was discovered in 1801. • Asteroids range in size from tiny pebbles to about 578 miles (930 kilometers) in diameter (Ceres). ...
... and carbon. • The first one discovered (and the biggest) is named Ceres; it was discovered in 1801. • Asteroids range in size from tiny pebbles to about 578 miles (930 kilometers) in diameter (Ceres). ...
The star is born
... Presence of dust not recognized until ~1930. Produces dimming of light and reddening of light. Explained the existence of O stars that were red Amount of reddening related to amount of dimming, so correction for dust dimming could be made Dust surrounding stars can reflect the light of the stars and ...
... Presence of dust not recognized until ~1930. Produces dimming of light and reddening of light. Explained the existence of O stars that were red Amount of reddening related to amount of dimming, so correction for dust dimming could be made Dust surrounding stars can reflect the light of the stars and ...
15.6 Planets Beyond the Solar System
... Jupiter, but closer to star. Why didn’t our Jupiter migrate? Nearly all of these have been discovered using the radial velocity method. This method (and most other methods) miss planets far from their stars, so can’t tell how common systems like ours are. The detection of Earth-like planets is the “ ...
... Jupiter, but closer to star. Why didn’t our Jupiter migrate? Nearly all of these have been discovered using the radial velocity method. This method (and most other methods) miss planets far from their stars, so can’t tell how common systems like ours are. The detection of Earth-like planets is the “ ...
Powerpoint - BU Imaging Science
... • Successful nebular theory for formation of our solar system suggests that planetary systems are a natural consequence of star formation • Why didn’t you learn about extrasolar planets in elementary school? ...
... • Successful nebular theory for formation of our solar system suggests that planetary systems are a natural consequence of star formation • Why didn’t you learn about extrasolar planets in elementary school? ...
Searching for Baby Planets in a Star`s Dusty Rings
... examination of the relevant physics. The scale of the structures in the HD 163296 disk makes it a compelling target for follow-up work, not only with ALMA but also with infrared telescopes that might be able to directly image the widely separated putative protoplanets. More generally, ALMA’s great s ...
... examination of the relevant physics. The scale of the structures in the HD 163296 disk makes it a compelling target for follow-up work, not only with ALMA but also with infrared telescopes that might be able to directly image the widely separated putative protoplanets. More generally, ALMA’s great s ...
Here
... in the form of cold molecular gas. This gas has a temperature of only a few tens of Kelvin above absolute zero. The clouds are mostly molecular hydrogen but over 100 different molecules have been detected in these clouds, including water, silicon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, ammonia, ethanol and methan ...
... in the form of cold molecular gas. This gas has a temperature of only a few tens of Kelvin above absolute zero. The clouds are mostly molecular hydrogen but over 100 different molecules have been detected in these clouds, including water, silicon dioxide, sulphur dioxide, ammonia, ethanol and methan ...
Chapter 10
... • Radioactive material in chondrules allows dating back to when they first condensed from the solar nebula • Some chondrules contain ancient dust grains that have survived from before the Solar System’s birth! ...
... • Radioactive material in chondrules allows dating back to when they first condensed from the solar nebula • Some chondrules contain ancient dust grains that have survived from before the Solar System’s birth! ...
Our Solar System and Beyond
... • Indirect: Measurements of stellar properties revealing the effects of orbiting planets ...
... • Indirect: Measurements of stellar properties revealing the effects of orbiting planets ...
Document
... In a Galaxy (The Milky Way) a long time ago (1990) I did some simulations. I new that active stars had polar spots and I asked the question: „What would the RV and bisector variations look like for a star with a polar spot viewed nearly pole on. My results (from memory): 1. The RV curve is nearly s ...
... In a Galaxy (The Milky Way) a long time ago (1990) I did some simulations. I new that active stars had polar spots and I asked the question: „What would the RV and bisector variations look like for a star with a polar spot viewed nearly pole on. My results (from memory): 1. The RV curve is nearly s ...
Masers and high mass star formation Claire Chandler
... • Radiation pressure acting on dust grains can become large enough to reverse the infall of matter: – Fgrav = GM*m/r2 – Frad = Ls/4pr2c – Above 10 Msun radiation pressure could reverse infall ...
... • Radiation pressure acting on dust grains can become large enough to reverse the infall of matter: – Fgrav = GM*m/r2 – Frad = Ls/4pr2c – Above 10 Msun radiation pressure could reverse infall ...
slides - Relativity Group
... • A 10-km asteroid would produce the explosion equivalent of several billion nuclear bombs • Initial destruction by high temperatures, blast, and acid rain would be followed by months of darkness and intense cold as the Sun’s light is blotted out by clouds of dust • Further evidence of the impact is ...
... • A 10-km asteroid would produce the explosion equivalent of several billion nuclear bombs • Initial destruction by high temperatures, blast, and acid rain would be followed by months of darkness and intense cold as the Sun’s light is blotted out by clouds of dust • Further evidence of the impact is ...
Presentation
... “Is Earth unique, and if not, how many Earth-size planets might there be in our galaxy, orbiting their parent stars at just the right distances to have liquid water on their surfaces?” “What are the distributions in planet size, in planet orbits, and the types of stars hosting planets”? (modified fr ...
... “Is Earth unique, and if not, how many Earth-size planets might there be in our galaxy, orbiting their parent stars at just the right distances to have liquid water on their surfaces?” “What are the distributions in planet size, in planet orbits, and the types of stars hosting planets”? (modified fr ...
geol0810 homework 1: early solar system history
... energy released by the decay of a 26Al atom to a 26Mg atom provided a potent source of heat during the first few million years of Solar System history. The radioactive decay of 26Al to form 26Mg releases so much heat that asteroid-sized bodies would have melted (and thus allow for differentiation) i ...
... energy released by the decay of a 26Al atom to a 26Mg atom provided a potent source of heat during the first few million years of Solar System history. The radioactive decay of 26Al to form 26Mg releases so much heat that asteroid-sized bodies would have melted (and thus allow for differentiation) i ...
powerpoint - High Energy Physics at Wayne State
... To understand how stars are born, we begin by learning about the raw material from which they are made. Interstellar matter: gas and dust that lies in the ...
... To understand how stars are born, we begin by learning about the raw material from which they are made. Interstellar matter: gas and dust that lies in the ...
Nebular theory
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
... Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at least 4 observations. Look for similarities, difference ...
EXOPLANETS The search for planets beyond our solar system
... Understanding stars and planets The extraordinary range of worlds found have already got theorists re-working their ideas about the evolution of planetary systems. How do monster planets end up orbiting so closely to their star? Planetary systems are thought to condense from the dust disc that surro ...
... Understanding stars and planets The extraordinary range of worlds found have already got theorists re-working their ideas about the evolution of planetary systems. How do monster planets end up orbiting so closely to their star? Planetary systems are thought to condense from the dust disc that surro ...
rtf
... Abstract: Mechanisms of interstellar panspermia have recently been identified whereby life, wherever it has originated, will disperse throughout the habitable zone of the Galaxy within a few billion years. This re-opens the question of where life originated. The interiors of comets, during their aqu ...
... Abstract: Mechanisms of interstellar panspermia have recently been identified whereby life, wherever it has originated, will disperse throughout the habitable zone of the Galaxy within a few billion years. This re-opens the question of where life originated. The interiors of comets, during their aqu ...
Formation of the Solar System
... • Note: terrestrial planets all closer to the Sun Apr 24, 2006 ...
... • Note: terrestrial planets all closer to the Sun Apr 24, 2006 ...
AST 150: Radioactive Dating Game Activity
... and ants intelligent? Furthermore, single-‐celled life existed on Earth very early, and multicellular life took 2.5 billion years to form. Maybe the development of complex life, let alone intelligent life, ...
... and ants intelligent? Furthermore, single-‐celled life existed on Earth very early, and multicellular life took 2.5 billion years to form. Maybe the development of complex life, let alone intelligent life, ...