Oceanic lithosphere-asthenosphere boundary from - HAL
... errors are thus obtained by the calculation of the standard deviation of the stacked samples of the complete catalog. The compatibility of the merged phase velocity data set is assessed by comparison with individual data sets and it reflects the weighting of the data set relative errors. As an exampl ...
... errors are thus obtained by the calculation of the standard deviation of the stacked samples of the complete catalog. The compatibility of the merged phase velocity data set is assessed by comparison with individual data sets and it reflects the weighting of the data set relative errors. As an exampl ...
Persistent organic pollutants in ocean sediments from the North
... Examining the presence of POPs in the deep ocean environment will therefore help to understand important sinks for these chemicals and aid hemispheric/global mass balances now that chemical production for some chemicals (e.g., PCBs) has effectively ceased. Recent work in a trans Arctic Ocean assessm ...
... Examining the presence of POPs in the deep ocean environment will therefore help to understand important sinks for these chemicals and aid hemispheric/global mass balances now that chemical production for some chemicals (e.g., PCBs) has effectively ceased. Recent work in a trans Arctic Ocean assessm ...
Plate Tectonics: The Unifying Theory
... Features of Mid Ocean Ridges • Central rift valley (width is inversely proportional to the rate of spreading) • Shallow-focus earthquakes • Almost exclusively basalt ...
... Features of Mid Ocean Ridges • Central rift valley (width is inversely proportional to the rate of spreading) • Shallow-focus earthquakes • Almost exclusively basalt ...
3 Types of Metamorphism
... • Rocks are metamorphosed over large areas that are the size of many states or even several countries ...
... • Rocks are metamorphosed over large areas that are the size of many states or even several countries ...
What is heat?
... mountains and pulling apart the ridges/rifts. The ocean-atmosphere is also a heat engine. • In the last 4 Ga, the earth’s cooling has been about 100 ° C per Billion years. • The earth is predicted to reach thermal equilibrium with space in about 10 Ga. ...
... mountains and pulling apart the ridges/rifts. The ocean-atmosphere is also a heat engine. • In the last 4 Ga, the earth’s cooling has been about 100 ° C per Billion years. • The earth is predicted to reach thermal equilibrium with space in about 10 Ga. ...
Tidal characteristics along the Western and Northern Coasts
... stations. The cotidal lines in Figure 4 & 5 represent HWI and are the average time interval between the Moon’s transit over the Greenwich meridian and the time of high water at any location. The estimated cotidal lines shown pass through locations having the same co-tidal hour. A slow tide progressi ...
... stations. The cotidal lines in Figure 4 & 5 represent HWI and are the average time interval between the Moon’s transit over the Greenwich meridian and the time of high water at any location. The estimated cotidal lines shown pass through locations having the same co-tidal hour. A slow tide progressi ...
Marine Geology: Exploring the New Frontiers of the Ocean (The
... drift.Together these two theories became united as the plate tectonic revolution. This sets the stage for succeeding chapters on the mid-ocean ridges, deep-sea trenches, and submarine volcanoes. Ocean circulation is responsible for much of the world’s climate. Mild foggy winters in London are caused ...
... drift.Together these two theories became united as the plate tectonic revolution. This sets the stage for succeeding chapters on the mid-ocean ridges, deep-sea trenches, and submarine volcanoes. Ocean circulation is responsible for much of the world’s climate. Mild foggy winters in London are caused ...
Moored observations of upper-ocean response to the monsoons in
... evolution of the upper-ocean temperature, salinity, and velocity fields in the Arabian Sea. The focus was on the region of strong forcing, off the coast of Oman, close to the axis of the Findlater Jet. We hoped to discriminate between upper-ocean variability introduced by mesoscale ocean features and ...
... evolution of the upper-ocean temperature, salinity, and velocity fields in the Arabian Sea. The focus was on the region of strong forcing, off the coast of Oman, close to the axis of the Findlater Jet. We hoped to discriminate between upper-ocean variability introduced by mesoscale ocean features and ...
Issue 2 - INDEEP
... a very small fraction of the oceans, mostly in polar regions, will face the opposing effects of increases in oxygen or productivity, and almost nowhere will there be cooling or pH increase. The biological responses to such biogeochemical changes could be considerable since marine habitats and hotspo ...
... a very small fraction of the oceans, mostly in polar regions, will face the opposing effects of increases in oxygen or productivity, and almost nowhere will there be cooling or pH increase. The biological responses to such biogeochemical changes could be considerable since marine habitats and hotspo ...
Plate Tectonics: GL209 Prof. John Tarney Lecture 3: Wilson Cycle 1
... America, projected down to 30 km -- based largely on gravity and magnetic evidence, plus some seismic profiles -- and some extrapolation from land geology based on deep drill holes. The critical point is the huge thicknesses of Mesozoic and Tertiary sediments, here shown as almost 15 km, but in othe ...
... America, projected down to 30 km -- based largely on gravity and magnetic evidence, plus some seismic profiles -- and some extrapolation from land geology based on deep drill holes. The critical point is the huge thicknesses of Mesozoic and Tertiary sediments, here shown as almost 15 km, but in othe ...
Ocean Drilling Program Scientific Results Volume 120
... in mid-Cretaceous time, was marked by a further disintegration and reorganization of the Gondwana fragments into four plates: Seychelles/Greater India and Africa/Madagascar broke up, as did Australia (including Broken Ridge and the Northern Kerguelen Plateau) and Antarctica (including the Southern K ...
... in mid-Cretaceous time, was marked by a further disintegration and reorganization of the Gondwana fragments into four plates: Seychelles/Greater India and Africa/Madagascar broke up, as did Australia (including Broken Ridge and the Northern Kerguelen Plateau) and Antarctica (including the Southern K ...
Geology/Earth Science - Northern Michigan University
... affecting its salinity. Analyze the movements of ocean water. Includes circulation of ocean water; ocean tides and waves; the effects of ocean movements; and vertical movement of ocean water. Analyze the structure and topography of the ocean floor. Includes the main divisions, characteristics, struc ...
... affecting its salinity. Analyze the movements of ocean water. Includes circulation of ocean water; ocean tides and waves; the effects of ocean movements; and vertical movement of ocean water. Analyze the structure and topography of the ocean floor. Includes the main divisions, characteristics, struc ...
Chapter 36 F Open Ocean Deep Sea
... structure from diatoms to picoplankton, and reduce export efficiency, driving biotic changes over major regions of the abyss, such as the equatorial Pacific (Smith et al., 2008). However the effects of climate change, including ocean warming, on biodiversity are likely to vary regionally and among s ...
... structure from diatoms to picoplankton, and reduce export efficiency, driving biotic changes over major regions of the abyss, such as the equatorial Pacific (Smith et al., 2008). However the effects of climate change, including ocean warming, on biodiversity are likely to vary regionally and among s ...
exhanges.naobook
... and the subtropical Atlantic, and swings from one phase to another produce large changes in the mean wind speed and direction over the Atlantic, the heat and moisture transport between the Atlantic and the neighboring continents, and the intensity and number of storms, their paths, and their associa ...
... and the subtropical Atlantic, and swings from one phase to another produce large changes in the mean wind speed and direction over the Atlantic, the heat and moisture transport between the Atlantic and the neighboring continents, and the intensity and number of storms, their paths, and their associa ...
CHAPTER 24 Polar and Alpine Environments
... Pleistocene glaciations, and (d) the large inter-annual instability of the terrestrial tundra environment. Climatic stresses restrict arctic plant species to those which have successfully adapted to low temperatures and physiological drought. The Arctic Ocean is young geologically, being only 4 mill ...
... Pleistocene glaciations, and (d) the large inter-annual instability of the terrestrial tundra environment. Climatic stresses restrict arctic plant species to those which have successfully adapted to low temperatures and physiological drought. The Arctic Ocean is young geologically, being only 4 mill ...
Apparent optical properties of the Canadian
... their derivative products (Morel and Prieur, 1977), whereas for turbid case-2 waters they are not. Case-1 waters do not require an extensive set of spectral bands for high-quality data products, which rely primarily on the blue-green visible (VIS) wavelengths. Although Arctic AOPs were recognized as ...
... their derivative products (Morel and Prieur, 1977), whereas for turbid case-2 waters they are not. Case-1 waters do not require an extensive set of spectral bands for high-quality data products, which rely primarily on the blue-green visible (VIS) wavelengths. Although Arctic AOPs were recognized as ...
Cordilleran foreland vs hinterland deformation: Thermal controls of
... undeformed during late Mesozoic to early Tertiary tectonics. Shortening occurred primarily in overlying sedimentary thrust sheets, mediated by high pore fluid pressures, i.e., thinned skin tectonics. In contrast, Cordillera hinterland shortening deformation (and subsequent extension mainly in the so ...
... undeformed during late Mesozoic to early Tertiary tectonics. Shortening occurred primarily in overlying sedimentary thrust sheets, mediated by high pore fluid pressures, i.e., thinned skin tectonics. In contrast, Cordillera hinterland shortening deformation (and subsequent extension mainly in the so ...
A proposed biogeography of the deep ocean floor
... but that these endemic species must have a shared history of ‘‘having long been isolated by some combination of unique ecological conditions and barriers to dispersal . . .’’ (p. 375). However, as noted by Lomolino et al., most biogeographic units have not been analyzed to show they consist of assem ...
... but that these endemic species must have a shared history of ‘‘having long been isolated by some combination of unique ecological conditions and barriers to dispersal . . .’’ (p. 375). However, as noted by Lomolino et al., most biogeographic units have not been analyzed to show they consist of assem ...
brochure Archienviron 2 - Archean Environment: The habitat of early
... crust would have been low: temperatures in the shallow interior of Archean oceanic crust may have been lower than those in modern crust, not higher as is commonly assumed. Archean volcanic rocks were more magnesian than their modern counterparts and Archean ocean water more reducing. How did these d ...
... crust would have been low: temperatures in the shallow interior of Archean oceanic crust may have been lower than those in modern crust, not higher as is commonly assumed. Archean volcanic rocks were more magnesian than their modern counterparts and Archean ocean water more reducing. How did these d ...
Conservation on the High Seas – drift algae habitat as an open
... documented as regularly undergoing this transformation into pelagic habitat (e.g. Hirosaki 1960, Kingsford and Choat 1985). However, one genus of brown algae – Sargassum – has taken this role to the next step. In the Atlantic, two species of Sargassum, S. natans and S. fluitans, have become holopela ...
... documented as regularly undergoing this transformation into pelagic habitat (e.g. Hirosaki 1960, Kingsford and Choat 1985). However, one genus of brown algae – Sargassum – has taken this role to the next step. In the Atlantic, two species of Sargassum, S. natans and S. fluitans, have become holopela ...
How Waves Reveal Internal Structure of the Earth.
... automobile leaving Americus will get to some destination? That will depend, of course, on 1) how far away the destination is, and 2) on how fast the car is driven – distance and speed. It’s the same with waves. Distance and speed dictate how far they travel. If the distance is known the only variabl ...
... automobile leaving Americus will get to some destination? That will depend, of course, on 1) how far away the destination is, and 2) on how fast the car is driven – distance and speed. It’s the same with waves. Distance and speed dictate how far they travel. If the distance is known the only variabl ...
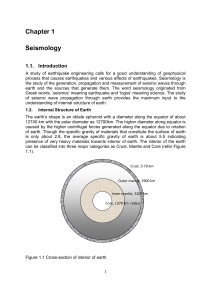
Chapter 1
... asthenosphere, extends down to about 700 km depth. The rigid lithospheric shell is broken into several irregularly shaped major plates and a large number of minor or secondary plates. The lithospheric plates are not stationary, on the contrary, they float in a complex pattern, with a velocity of som ...
... asthenosphere, extends down to about 700 km depth. The rigid lithospheric shell is broken into several irregularly shaped major plates and a large number of minor or secondary plates. The lithospheric plates are not stationary, on the contrary, they float in a complex pattern, with a velocity of som ...
Gravity, refraction, heat flow overview
... The Bouguer anomaly subtracts out the mass of the mountains; thus the Bouguer anomaly should be just the root term, 2πG(ρc - ρm)R. Note that for isostatically compensated mountains, this is equal to -2πGρcE, or about -112 mGal for each kilometer of elevation. This tends to be much larger than effect ...
... The Bouguer anomaly subtracts out the mass of the mountains; thus the Bouguer anomaly should be just the root term, 2πG(ρc - ρm)R. Note that for isostatically compensated mountains, this is equal to -2πGρcE, or about -112 mGal for each kilometer of elevation. This tends to be much larger than effect ...
Developed in Consultation with Florida Educators
... Erosion and Deposition Rock that has been broken down can be eroded. Erosion is the movement of rock and soil by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Erosion can be fast or slow. For example, land is eroded quickly when hurricane waves carry away large amounts of sand from a beach. Gravity can quickly carr ...
... Erosion and Deposition Rock that has been broken down can be eroded. Erosion is the movement of rock and soil by wind, water, ice, or gravity. Erosion can be fast or slow. For example, land is eroded quickly when hurricane waves carry away large amounts of sand from a beach. Gravity can quickly carr ...
Physical oceanography

Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanographies.