Title: 공학도를 위한 생물학 (2)
... And so this really short pathway, taste receptors in the tongue, to the muscles that control swallowing and ?[32:23] or spitting. So taht's a in short pathway, with a few neurons. Few neurons from sensory to the motor. As you move from sensory neuron, you get information very formed from sensory in ...
... And so this really short pathway, taste receptors in the tongue, to the muscles that control swallowing and ?[32:23] or spitting. So taht's a in short pathway, with a few neurons. Few neurons from sensory to the motor. As you move from sensory neuron, you get information very formed from sensory in ...
Bio 211 Lecture 18
... How does a neuron ‘know’ when to fire? Any one neuron receives many THOUSANDS of inputs from other neurons. Not all of these will make the neuron generate a nerve impulse. How does this work? ...
... How does a neuron ‘know’ when to fire? Any one neuron receives many THOUSANDS of inputs from other neurons. Not all of these will make the neuron generate a nerve impulse. How does this work? ...
neuroloc
... If the sound source is close to the right ear, then the LSO neurons on the left side of the brain • respond a lot • respond a little • don’t respond at all ...
... If the sound source is close to the right ear, then the LSO neurons on the left side of the brain • respond a lot • respond a little • don’t respond at all ...
Spinal Cord
... • Dorsal and ventral roots from same level combine spinal nerve, one on each side of spinal cord. ...
... • Dorsal and ventral roots from same level combine spinal nerve, one on each side of spinal cord. ...
Nerve Cell Communication - URMC
... branches. Hint: As the impulse travels along the axon, you should arrange the impulse card as shown in the diagram on the right. ...
... branches. Hint: As the impulse travels along the axon, you should arrange the impulse card as shown in the diagram on the right. ...
Arbib, 2008 - Semantic Scholar
... In putting parity at stage center in this account, we adhere to the view that the primary function of language is communication. Others have espoused the alternative view that language evolution could have obeyed an adaptive pressure for developing higher cognitive abilities and that verbal communic ...
... In putting parity at stage center in this account, we adhere to the view that the primary function of language is communication. Others have espoused the alternative view that language evolution could have obeyed an adaptive pressure for developing higher cognitive abilities and that verbal communic ...
Reflex Arc - TangHua2012-2013
... This ___________________________________________, along with of the large negative molecules, causes the ________________________________________________________. This situation is called _______________________________. -60mv When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, ______________________________wh ...
... This ___________________________________________, along with of the large negative molecules, causes the ________________________________________________________. This situation is called _______________________________. -60mv When the axon or dendrite is stimulated, ______________________________wh ...
REM-off
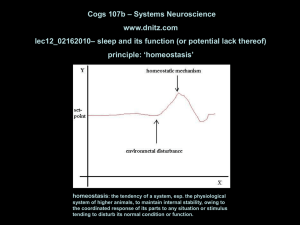
... amounts of overall sleep (especially REM sleep) as compared to animals, like horses, born relatively developed……but, if sleep is important for development, why does it persist into adulthood? ...
... amounts of overall sleep (especially REM sleep) as compared to animals, like horses, born relatively developed……but, if sleep is important for development, why does it persist into adulthood? ...
CPB748_JK Nervous
... • Overview: Command and Control Center • The human brain – Contains an estimated 100 billion nerve cells, or neurons ...
... • Overview: Command and Control Center • The human brain – Contains an estimated 100 billion nerve cells, or neurons ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... - long, to reach effector - travel from sympathetic chain ganglion via gray communicating ramus into spinal nerve or other sympathetic nerves to viscera - may contact several effectors (more divergence) ...
... - long, to reach effector - travel from sympathetic chain ganglion via gray communicating ramus into spinal nerve or other sympathetic nerves to viscera - may contact several effectors (more divergence) ...
USC Brain Project Specific Aims
... 11. The FARS model of control of grasping 1: Population coding 12. The FARS model of control of grasping 2: Sequence learning and the basal ganglia 13. The FARS model of control of grasping 3: Working Memory 21. The MNS1 Model 3: Modeling the Core Mirror Neuron Circuit 22. Control of eye movements [ ...
... 11. The FARS model of control of grasping 1: Population coding 12. The FARS model of control of grasping 2: Sequence learning and the basal ganglia 13. The FARS model of control of grasping 3: Working Memory 21. The MNS1 Model 3: Modeling the Core Mirror Neuron Circuit 22. Control of eye movements [ ...
Introduction
... to locate the brain regions where movements are processed to allow accurate pointing. They conclude that the supramarginal cortex, the posterior cingulate cortex of the left hemisphere, and the cerebellum are involved in the integration of visual feedback of hand movements and accurate pointing. In ...
... to locate the brain regions where movements are processed to allow accurate pointing. They conclude that the supramarginal cortex, the posterior cingulate cortex of the left hemisphere, and the cerebellum are involved in the integration of visual feedback of hand movements and accurate pointing. In ...
Autonomic vs. Somatic Nervous System
... Principal: Acetylcholine & norepinephrine N ttraditional ...
... Principal: Acetylcholine & norepinephrine N ttraditional ...
cranial nerves & pns
... trunks (used by the sympathetic nervous system). Not all ganglia are located in the sympathetic trunks. Some are not; and it is possible for a preganglionic fiber to go right through, making no synaptic junction there at all, joining instead with ganglia located in front of the vertebrae. For the pa ...
... trunks (used by the sympathetic nervous system). Not all ganglia are located in the sympathetic trunks. Some are not; and it is possible for a preganglionic fiber to go right through, making no synaptic junction there at all, joining instead with ganglia located in front of the vertebrae. For the pa ...
An Evolutionary Framework for Replicating Neurophysiological Data
... match electrophysiological data [8, 14–16]. However, in order to better understand the mechanisms underlying neurological circuits and to verify theoretical models of cognition, it is important that they are able to match neurological data in terms of neuronal firing rates as well as population func ...
... match electrophysiological data [8, 14–16]. However, in order to better understand the mechanisms underlying neurological circuits and to verify theoretical models of cognition, it is important that they are able to match neurological data in terms of neuronal firing rates as well as population func ...
Neural computations that underlie decisions about sensory stimuli
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
... light, with some values being more likely than others when light is present (see Box 1). How do you use the value from the detector to decide if the light was present? This problem consists of deciding which hypothesis – light is present (h1) or light is absent (h2) – is most likely to be true given ...
Deep Learning - UCF Computer Science
... • Some (a half of) neurons in a fully connected layer become inactive whose outputs will not participate in the forward pass and backpropagation. • Every time a neural network with reduced complexity is generated to process the input signals forwards, or updated by backpropagation. ...
... • Some (a half of) neurons in a fully connected layer become inactive whose outputs will not participate in the forward pass and backpropagation. • Every time a neural network with reduced complexity is generated to process the input signals forwards, or updated by backpropagation. ...
The Languages of Neurons: An Analysis of Coding Mechanisms by
... pulse trains sent to the CNS were found to elicit the same behavioral avoidance response as the cell-generated S/P word trains, underscoring the functional significance of temporal S/P coding [21]. These results also suggest that knowledge of specific neuronal codes might be a useful adjunct in trea ...
... pulse trains sent to the CNS were found to elicit the same behavioral avoidance response as the cell-generated S/P word trains, underscoring the functional significance of temporal S/P coding [21]. These results also suggest that knowledge of specific neuronal codes might be a useful adjunct in trea ...
Startup: CST Prep Nervous System
... • Action Potential – A.K.A. a nerve impulse – A rapid reversal of charges, from negative to positive along the neruon - from Dentrites to Axon Terminals. ...
... • Action Potential – A.K.A. a nerve impulse – A rapid reversal of charges, from negative to positive along the neruon - from Dentrites to Axon Terminals. ...
The Cells of the Nervous System Lab
... Of the ~190 billion cells in the human brain , about half of them neurons while the other half is comprised of glia, ependymal, and endothelial cells (Azevedo et al., 2009). Neurons vary enormously in size, shape, and function. The shape of a neuron determines its connections with other cells and th ...
... Of the ~190 billion cells in the human brain , about half of them neurons while the other half is comprised of glia, ependymal, and endothelial cells (Azevedo et al., 2009). Neurons vary enormously in size, shape, and function. The shape of a neuron determines its connections with other cells and th ...
Symbolic Reasoning in Spiking Neurons:
... The basal ganglia is generally believed by both neuroscientists (e.g. Redgrave et al., 1999) and cognitive scientists (e.g. Anderson et al., 2004) to be responsible for action selection. That is, given a wide variety of possible options as to what to do next, a single one must be chosen. This can be ...
... The basal ganglia is generally believed by both neuroscientists (e.g. Redgrave et al., 1999) and cognitive scientists (e.g. Anderson et al., 2004) to be responsible for action selection. That is, given a wide variety of possible options as to what to do next, a single one must be chosen. This can be ...
The Art and Science of Research Grant Writing
... nigrostriatal DAergic (70,71) and PHDA neurons (72) seem to be inhibited by D2/3–type DA (auto)receptors. There are data, however, indicating that TIDA neurons can be influenced by both D1 and D2 receptors, but the responses are different from that seen in nigrostriatal DAergic neurons (73). D2 rece ...
... nigrostriatal DAergic (70,71) and PHDA neurons (72) seem to be inhibited by D2/3–type DA (auto)receptors. There are data, however, indicating that TIDA neurons can be influenced by both D1 and D2 receptors, but the responses are different from that seen in nigrostriatal DAergic neurons (73). D2 rece ...
Graded Potentials
... Chapter 12: Nervous Tissue Objectives Describe the anatomical and functional divisions of the nervous system. Sketch and label the structure of a typical neuron, describe the functions of each component, and classify neurons on the basis of their structure and function. Describe the locations ...
... Chapter 12: Nervous Tissue Objectives Describe the anatomical and functional divisions of the nervous system. Sketch and label the structure of a typical neuron, describe the functions of each component, and classify neurons on the basis of their structure and function. Describe the locations ...
9.14 Lecture 16: Descending Pathways and Evolution Notes
... because of disorientation; he veered from course, bumped into obstacles ...
... because of disorientation; he veered from course, bumped into obstacles ...