Slide ()
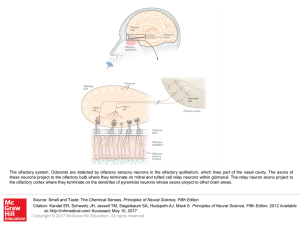
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
... The olfactory system. Odorants are detected by olfactory sensory neurons in the olfactory epithelium, which lines part of the nasal cavity. The axons of these neurons project to the olfactory bulb where they terminate on mitral and tufted cell relay neurons within glomeruli. The relay neuron axons p ...
A Review of the Neuron - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... into a code that is carried to the brain by a chain of neurons. Then systems of neurons in the brain interpret this information. The information is carried along axons and dendrites because of changes in electrical properties which we call action potential. An action potential is initiated when a me ...
... into a code that is carried to the brain by a chain of neurons. Then systems of neurons in the brain interpret this information. The information is carried along axons and dendrites because of changes in electrical properties which we call action potential. An action potential is initiated when a me ...
Unit 3A–Neural Processing and the Endocrine System
... neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord ...
... neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs neurotransmitter that influences movement, learning, attention, and emotion neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord ...
Chapter 9: Nervous System guide—Please complete these notes on
... outward 6. Action potential that results causes a bioelectric current that stimulates adjacent portions of membrane 7. Wave of action potentials travels axon as nerve impulse ...
... outward 6. Action potential that results causes a bioelectric current that stimulates adjacent portions of membrane 7. Wave of action potentials travels axon as nerve impulse ...
Nervous System Student Notes
... b. varies in length and diameter (larger diameter=faster conduction) c. axon collaterals: ___________________________________ d. axon terminals located _______________________________ ...
... b. varies in length and diameter (larger diameter=faster conduction) c. axon collaterals: ___________________________________ d. axon terminals located _______________________________ ...
Quiz - psychm5
... a. Some axons are only 0.1 millimeter long. b. Some axons stretch up to a meter in length throughout the nervous system. c. The human brain contains about three million miles of axons. d. All of these statements are true. ...
... a. Some axons are only 0.1 millimeter long. b. Some axons stretch up to a meter in length throughout the nervous system. c. The human brain contains about three million miles of axons. d. All of these statements are true. ...
Nervous System
... • Dendrites - receive incoming electrical stimulus – Neurons have hundreds of dendrites ...
... • Dendrites - receive incoming electrical stimulus – Neurons have hundreds of dendrites ...
Histology05-NerveTissue
... in conscious sensations, but others do not. However, they are not considered part of the autonomic nervous system, which is entirely ...
... in conscious sensations, but others do not. However, they are not considered part of the autonomic nervous system, which is entirely ...
Slide ()
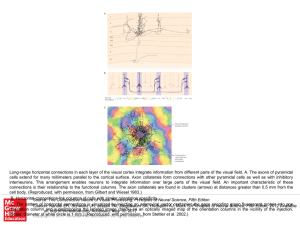
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
Ch11AB
... excite or inhibit other cells. The main function is the Axon is that it is the _______________________ of a neuron. The Axon generates and transmits nerve impulses called _______________ away from the neuronal cell body. (Slides 38-39) Molecules and organelles are moved along axons by motor molecule ...
... excite or inhibit other cells. The main function is the Axon is that it is the _______________________ of a neuron. The Axon generates and transmits nerve impulses called _______________ away from the neuronal cell body. (Slides 38-39) Molecules and organelles are moved along axons by motor molecule ...
Electrical Communication (Nervous System) ppt
... Axon- sends nerve impulses, coated in myelin sheath Axon Terminals- contact receptors of other cells Myelin- whitish, fatty material that insulates axon and speeds up signal transmission ◦ Schwann cells- cells wrapped around axon like a jelly roll, makes up myelin sheath ◦ Nodes of Ranvier- gaps bet ...
... Axon- sends nerve impulses, coated in myelin sheath Axon Terminals- contact receptors of other cells Myelin- whitish, fatty material that insulates axon and speeds up signal transmission ◦ Schwann cells- cells wrapped around axon like a jelly roll, makes up myelin sheath ◦ Nodes of Ranvier- gaps bet ...
Psychology`s biological roots: neurons and neural communication
... Neurons influence each other through the release of neurotransmitters – chemical substances that carry signals across the synaptic cleft When the action potential reaches the end of the axon at its terminal button the neurotransmitters are released to travel across the synaptic cleft ...
... Neurons influence each other through the release of neurotransmitters – chemical substances that carry signals across the synaptic cleft When the action potential reaches the end of the axon at its terminal button the neurotransmitters are released to travel across the synaptic cleft ...
file - Athens Academy
... maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
... maintain our sanity, having an imbalance in this neurotransmitter plays a role in the development of Parkinson’s Disease. ...
SChapter 12
... ▫Propagation of Action Potentials- action potentials moving down axon. -Continuous propagation-Saltatory propagation▫Axon diameter affects propagation speed. -Type A fibers -Type B fibers -Type C fibers Synaptic Activity ▪Electric events of messages moving from one place to another are called nerve ...
... ▫Propagation of Action Potentials- action potentials moving down axon. -Continuous propagation-Saltatory propagation▫Axon diameter affects propagation speed. -Type A fibers -Type B fibers -Type C fibers Synaptic Activity ▪Electric events of messages moving from one place to another are called nerve ...
Unit VIII: Animal Structure and Function, Part II
... Propagation of the Action Potential Action potentials “travel” along an axon because they are selfpropagating • dominoes + neighboring region of the neuron will be depolarized • Access Excellence link ...
... Propagation of the Action Potential Action potentials “travel” along an axon because they are selfpropagating • dominoes + neighboring region of the neuron will be depolarized • Access Excellence link ...
Neuron
... Nissl bodies or Nissl substance—are composed of large aggregations of rough endoplasmic reticulum: are observed as basophilic clumps by light microscopy . extend into dendrites but not into axon and axon hillock. disintegrate as a result of injury to axon (chromatolysis). Golgi complex—are ...
... Nissl bodies or Nissl substance—are composed of large aggregations of rough endoplasmic reticulum: are observed as basophilic clumps by light microscopy . extend into dendrites but not into axon and axon hillock. disintegrate as a result of injury to axon (chromatolysis). Golgi complex—are ...
Nervous System and Senses - Avon Community School Corporation
... Flows through ventricles (spaces in brain), in the subarachnoid space, and through the central canal of the spinal ...
... Flows through ventricles (spaces in brain), in the subarachnoid space, and through the central canal of the spinal ...
Answers - Mosaiced.org
... however large. Therefore no action potentials can be generated. 92. No – skeletal muscle is an example of one that doesn’t 93. K+ channels remain open, so permeability to K+ is greater than at rest. Na+ channels are shut so difference can’t be offset. Greater –ve charge inside cell needed to oppose ...
... however large. Therefore no action potentials can be generated. 92. No – skeletal muscle is an example of one that doesn’t 93. K+ channels remain open, so permeability to K+ is greater than at rest. Na+ channels are shut so difference can’t be offset. Greater –ve charge inside cell needed to oppose ...
Document
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
Ch_09_Nervous_System_A_
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
... Actions/Effects: LSD alters the action of the neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine, triggering extreme changes in brain function. Physical effects include increased body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure. Psychological effects include perceptual and thought distortions ...
NERVES
... Dendrites- highly branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons Axon- a typically much longer extension that transmits signals to other cells Axon hillcock- conical region of an axon where it joins the cell body, typically the region where the signals that travel down the axon ar ...
... Dendrites- highly branched extensions that receive signals from other neurons Axon- a typically much longer extension that transmits signals to other cells Axon hillcock- conical region of an axon where it joins the cell body, typically the region where the signals that travel down the axon ar ...
The Nervous System
... b. motor neurons - carry messages from the CNS to muscle fibres and glands c. interneurons - carry messages within the CNS 6. Draw a diagram of a neuron to show its structure, and give the function of : a. dendrite(s) receive information and carry it towards the cell body, b. the axon conducts nerve ...
... b. motor neurons - carry messages from the CNS to muscle fibres and glands c. interneurons - carry messages within the CNS 6. Draw a diagram of a neuron to show its structure, and give the function of : a. dendrite(s) receive information and carry it towards the cell body, b. the axon conducts nerve ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.