3 main tasks of neurons - Fleming County Schools
... function of the soma is to assess all messages the cell receives and pass on the appropriate information, at the appropriate time. ...
... function of the soma is to assess all messages the cell receives and pass on the appropriate information, at the appropriate time. ...
Fact sheet (PDF, 63.03 KB) (opens in a new window)
... which traditionally have been some of the most challenging cases for surgeons. Nervous injury, from trauma, disease or otherwise, is a major medical problem. Mature neurons do not undergo cell division and therefore it is very difficult to achieve successful rehabilitation after nerve injuries. It i ...
... which traditionally have been some of the most challenging cases for surgeons. Nervous injury, from trauma, disease or otherwise, is a major medical problem. Mature neurons do not undergo cell division and therefore it is very difficult to achieve successful rehabilitation after nerve injuries. It i ...
1749-7221-5-5-S2
... THIS PATIENT ARRIVED TO ME ONE YEAR AFTER AN INFECTED WOUND AT ELBOW WITH SEPTIC ARTHRITIS AND LOSS OF THE CUTANEOUS COVERING AND OF THE PROXIMAL 2/3 OF THE EXTENSOR MUSCLES OF WRIST AND HAND AFTER RECLAMATION OF THE SEPTIC LESION AND COVERAGE BY MEANS OF A FREE PARASCAPULAR FLAP, DIRECT NEUROTISATI ...
... THIS PATIENT ARRIVED TO ME ONE YEAR AFTER AN INFECTED WOUND AT ELBOW WITH SEPTIC ARTHRITIS AND LOSS OF THE CUTANEOUS COVERING AND OF THE PROXIMAL 2/3 OF THE EXTENSOR MUSCLES OF WRIST AND HAND AFTER RECLAMATION OF THE SEPTIC LESION AND COVERAGE BY MEANS OF A FREE PARASCAPULAR FLAP, DIRECT NEUROTISATI ...
Chapter 9 Nerves
... Integrative functions collect sensory information and make decisions that motor functions carry out ...
... Integrative functions collect sensory information and make decisions that motor functions carry out ...
power point for chap 11
... • Correspond to gap junctions found in other cell types • Contain intercellular protein channels ...
... • Correspond to gap junctions found in other cell types • Contain intercellular protein channels ...
Lesson 3 Brain Communication
... • They receive messages from other nerve cells and send it through the neuron. • The have DENDRITIC RECEPTORS on the ends: • Receivers on the end of each dendrite which catch the chemicals as they jump from the previous neuron. They then send the message down the dendrites. ...
... • They receive messages from other nerve cells and send it through the neuron. • The have DENDRITIC RECEPTORS on the ends: • Receivers on the end of each dendrite which catch the chemicals as they jump from the previous neuron. They then send the message down the dendrites. ...
Chapter 2 (The Brain) Study Guide 1. What is a neuron? What are
... 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? Endorphins? Acetylcholine? 5. Know each of the parts of the brain and their functions. 6. “Dendrite” comes from a greek word meaning __________? 7. What disorder has been associated with an excess of dopamine? Which disorder has been associated with a deficit of do ...
... 4. Effects of dopamine? Serotonin? Endorphins? Acetylcholine? 5. Know each of the parts of the brain and their functions. 6. “Dendrite” comes from a greek word meaning __________? 7. What disorder has been associated with an excess of dopamine? Which disorder has been associated with a deficit of do ...
Supporting Cells of the Nervous System
... Supporting Cells of the Nervous System Schwann cells structure: • They do all this by making a myelin sheath around many of the neuron processes in the PNS. They wrap themselves very tightly around the process of a neuron. • The cytoplasm and nucleus is squeezed to the surface of the wrapping calle ...
... Supporting Cells of the Nervous System Schwann cells structure: • They do all this by making a myelin sheath around many of the neuron processes in the PNS. They wrap themselves very tightly around the process of a neuron. • The cytoplasm and nucleus is squeezed to the surface of the wrapping calle ...
The Nervous System
... Parkinson’s Disease – affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. Neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms ...
... Parkinson’s Disease – affects nerve cells, or neurons, in a part of the brain that controls muscle movement. Neurons that make a chemical called dopamine die or do not work properly. Dopamine normally sends signals that help coordinate your movements. No one knows what damages these cells. Symptoms ...
Introduction_to_nerv..
... Organisation of the nervous system The sensory neurons (nerve cells) which transmit this information and the receptors form the sensory system. The processing and integration of this information is performed by the CNS. The final function whereby information is transmitted to effectors, which act u ...
... Organisation of the nervous system The sensory neurons (nerve cells) which transmit this information and the receptors form the sensory system. The processing and integration of this information is performed by the CNS. The final function whereby information is transmitted to effectors, which act u ...
Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other
... Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other somatic cells By Balogh Olivér ...
... Unique features of neurons, which distinguish them from other somatic cells By Balogh Olivér ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... • Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from another neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium-Na) which mix with negative ions (Chloride-Cl) that is already inside the axon (thus Neur ...
... • Dendrites receive neurotransmitter from another neuron across the synapse. • Reached its threshold- then fires based on the all-or-none response. • Opens up a portal in axon, and lets in positive ions (Sodium-Na) which mix with negative ions (Chloride-Cl) that is already inside the axon (thus Neur ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... 23.Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by endoneurium, a delicate layer of loose connective tissue that also encloses the fiber’s associated myelin or neurilemma sheath. Groups of fibers are bound into bundles called: ...
... 23.Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by endoneurium, a delicate layer of loose connective tissue that also encloses the fiber’s associated myelin or neurilemma sheath. Groups of fibers are bound into bundles called: ...
Name
... pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and mo ...
... pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS _____ 5. Neuron, serving as part of the conduction pathway between sensory and mo ...
Neurons
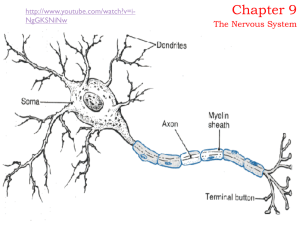
... Dendrites are treelike extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body. These tiny protrusions receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma. Dendrites are also covered with synapses. Dendrite Characteristics ...
... Dendrites are treelike extensions at the beginning of a neuron that help increase the surface area of the cell body. These tiny protrusions receive information from other neurons and transmit electrical stimulation to the soma. Dendrites are also covered with synapses. Dendrite Characteristics ...
The Nervous System
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
Chapter 11 Worksheet 2 The action potential: Fill in the blanks. The
... The action potential: Fill in the blanks. The dendrites receive signals from messenger molecules released from adjacent neurons called _________________________________. These molecules bind to receptors that act as ______________ gated ion channels. When these channels open they allow ions to flow ...
... The action potential: Fill in the blanks. The dendrites receive signals from messenger molecules released from adjacent neurons called _________________________________. These molecules bind to receptors that act as ______________ gated ion channels. When these channels open they allow ions to flow ...
Nervous Tissue - Northland Community & Technical College
... consists of cranial and spinal nerves that contain both sensory and motor fibers connects CNS to muscles, glands & all sensory ...
... consists of cranial and spinal nerves that contain both sensory and motor fibers connects CNS to muscles, glands & all sensory ...
Histology of the Peripheral Nervous System
... axons of small diameter are usually unmyelinated in CNS; not embedded in oligodendrocytes in PNS; enveloped within simple grooves of the Schwann cells A single axon or a group of axons may be enclosed in a single invagination of the Schwann cell surface. ...
... axons of small diameter are usually unmyelinated in CNS; not embedded in oligodendrocytes in PNS; enveloped within simple grooves of the Schwann cells A single axon or a group of axons may be enclosed in a single invagination of the Schwann cell surface. ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.