neurons
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
ReflexArcLabBackgroundNotes
... Looking at this sequence of steps, this is what happens when something sharp touches you on your hand: The stimulus is touch, your pain receptor is the sensor that senses it and relays it to the nervous system (spinal cord and brain) which is the coordinator. The coordinator makes the decision of ho ...
... Looking at this sequence of steps, this is what happens when something sharp touches you on your hand: The stimulus is touch, your pain receptor is the sensor that senses it and relays it to the nervous system (spinal cord and brain) which is the coordinator. The coordinator makes the decision of ho ...
Individual olfactory sensory neurons project into more than one
... varied from preparation to preparation. In the example given in Figure 3 the axon bifurcated into two branches a and b that projected into the glomeruli G1 and G2 (Fig. 3A,B). Branch a bifurcated well before entering G1, sending both a1 and a2 towards G1. Note, however, that branch a2 shortly before ...
... varied from preparation to preparation. In the example given in Figure 3 the axon bifurcated into two branches a and b that projected into the glomeruli G1 and G2 (Fig. 3A,B). Branch a bifurcated well before entering G1, sending both a1 and a2 towards G1. Note, however, that branch a2 shortly before ...
The Nervous System
... • All neural functions involve communication of neurons with one another and with other cells – Neuroglia: supporting cells with various functions: ...
... • All neural functions involve communication of neurons with one another and with other cells – Neuroglia: supporting cells with various functions: ...
Chapter 7 The Nervous System - Mrs. heninger
... Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system to organs, muscles, & glands. The impulses “effect” (bring about) a motor response. ...
... Nerve fibers that carry impulses away from the central nervous system to organs, muscles, & glands. The impulses “effect” (bring about) a motor response. ...
Unit 2, the Brain
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
... Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched endings of an axon that transmit messages to other neurons. ...
The Nervous System - Blackwell Publishing
... are glial cells, which fall into several different classes, each with its own function. There are astrocytes, oligodendrocytes (in the central nervous system), microglia and ependymal cells. (The word ending -cyte means ‘cell’.) Glial cells were once thought of as the structural glue (that is what g ...
... are glial cells, which fall into several different classes, each with its own function. There are astrocytes, oligodendrocytes (in the central nervous system), microglia and ependymal cells. (The word ending -cyte means ‘cell’.) Glial cells were once thought of as the structural glue (that is what g ...
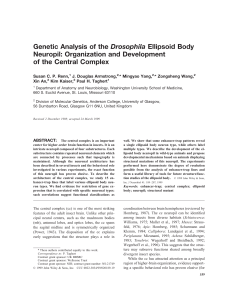
Genetic Analysis of the Drosophila Ellipsoid Body
... substructure contains repeated neuronal elements which are connected by processes such that topography is maintained. Although the neuronal architecture has been described in several insects and the behavioral role investigated in various experiments, the exact function of this neuropil has proven e ...
... substructure contains repeated neuronal elements which are connected by processes such that topography is maintained. Although the neuronal architecture has been described in several insects and the behavioral role investigated in various experiments, the exact function of this neuropil has proven e ...
Spike train propagation in the axon of a visual interneuron,... Locusta migratoria
... Action potentials, such as those seen in axons, are required to send information over long distances. Action potentials are required to threshold out the noise, which would otherwise accumulate in a graded potential over long distances by the random opening of voltage-gated channels (Laughlin 2001). ...
... Action potentials, such as those seen in axons, are required to send information over long distances. Action potentials are required to threshold out the noise, which would otherwise accumulate in a graded potential over long distances by the random opening of voltage-gated channels (Laughlin 2001). ...
I study the neural circuits that move bodies
... once. This is not the case in neurons; they're able to fire an AP every couple of milliseconds. But the VGSC chain-reaction only explains how a neuron is able to become depolarized. After they open, the neuron would be stuck at sodium's reversal potential because opening more sodium channels wouldn' ...
... once. This is not the case in neurons; they're able to fire an AP every couple of milliseconds. But the VGSC chain-reaction only explains how a neuron is able to become depolarized. After they open, the neuron would be stuck at sodium's reversal potential because opening more sodium channels wouldn' ...
Chapter 2: The Brain and Behavior
... gap to affect the next neuron. The size of the gap is exaggerated here; it is actually only about one millionth of an inch. Some transmitter molecules excite the next neuron, and some inhibit its activity. ...
... gap to affect the next neuron. The size of the gap is exaggerated here; it is actually only about one millionth of an inch. Some transmitter molecules excite the next neuron, and some inhibit its activity. ...
Chapter 2: The Brain and Behavior
... gap to affect the next neuron. The size of the gap is exaggerated here; it is actually only about one millionth of an inch. Some transmitter molecules excite the next neuron, and some inhibit its activity. ...
... gap to affect the next neuron. The size of the gap is exaggerated here; it is actually only about one millionth of an inch. Some transmitter molecules excite the next neuron, and some inhibit its activity. ...
Key Transmitters - Sinauer Associates
... current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (see below). The consequent entry of Ca2+ ions then induces a variety of downstream effect ...
... current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors (see below). The consequent entry of Ca2+ ions then induces a variety of downstream effect ...
Slide 1
... auditory nerve terminates at the large endbulbs of Held that synapse onto spherical bushy cells (see Fig. 25.18A). Bushy cells project bilaterally such that a single MSO receives input from both sides. Bushy cell inputs form delay lines such that ITD is mapped along the MSO. Data suggest that the de ...
... auditory nerve terminates at the large endbulbs of Held that synapse onto spherical bushy cells (see Fig. 25.18A). Bushy cells project bilaterally such that a single MSO receives input from both sides. Bushy cell inputs form delay lines such that ITD is mapped along the MSO. Data suggest that the de ...
Lecture 3 NS_2015
... Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft (20-30 nm thick). Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and the activated receptors trigger some postsynaptic eve ...
... Step 5: The transmitter is released into the extracellular space in quantized amounts and diffuses passively across the synaptic cleft (20-30 nm thick). Step 6: Some of the transmitter molecules bind to receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, and the activated receptors trigger some postsynaptic eve ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology 242
... current, leakage channels, voltage-gated ion channels, chemically-gated ion channels, polarized, depolarized, repolarized, hyperpolarized, graded potential, action potential, threshold stimulus, absolute refractory period, relative refractory period, propagation, All-or-None Principle, continuous co ...
... current, leakage channels, voltage-gated ion channels, chemically-gated ion channels, polarized, depolarized, repolarized, hyperpolarized, graded potential, action potential, threshold stimulus, absolute refractory period, relative refractory period, propagation, All-or-None Principle, continuous co ...
Chapter 2 Power Point: The Biological Perspective
... • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - area of neurons running down ...
... • Visual association cortex – identifies and makes sense of visual information. • Parietal lobes - sections of the brain located at the top and back of each cerebral hemisphere containing the centers for touch, taste, and temperature sensations. • Somatosensory cortex - area of neurons running down ...
Touch is complicated
... Proprioceptor = sensory receptors involved in proprioceptive signaling that reside in deeper structures such as the muscles, tendons, and joints: Important to the motor system in guiding movement through the environment ...
... Proprioceptor = sensory receptors involved in proprioceptive signaling that reside in deeper structures such as the muscles, tendons, and joints: Important to the motor system in guiding movement through the environment ...
Morphological and Functional Types of Neurons
... Figure 5. A and B, Camera lucida drawings of retrogradely labeled type 1 cells. Note large soma, tufted branching of primary dendrites, and thick axons. Bar. 100 pm. C and D, Camera lucida drawings of retrogradely labeled type II cells. In comparison with A, type II cells have smaller somata, thinne ...
... Figure 5. A and B, Camera lucida drawings of retrogradely labeled type 1 cells. Note large soma, tufted branching of primary dendrites, and thick axons. Bar. 100 pm. C and D, Camera lucida drawings of retrogradely labeled type II cells. In comparison with A, type II cells have smaller somata, thinne ...
formalin as a peripheral noxious stimulus causes a biphasic
... 60 minutes post formalin injection (n=4). As shown in this figure, the activity of the LPGi neurons exhibit a first peak, ...
... 60 minutes post formalin injection (n=4). As shown in this figure, the activity of the LPGi neurons exhibit a first peak, ...
Spinal Cord Reflexes
... activation of reflexes. For example, alternating activation of Ia stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with ...
... activation of reflexes. For example, alternating activation of Ia stretch reflex in flexors and extensors of limb, and FRA reflex with ...
Synapse Jeopardy
... • The place where one neuron connects to another. It includes the nerve terminal of the first neuron, the place on the second neuron with receptors, and the space between them. Click here to reveal the correct concept ...
... • The place where one neuron connects to another. It includes the nerve terminal of the first neuron, the place on the second neuron with receptors, and the space between them. Click here to reveal the correct concept ...
somatosensation
... « Take Home Message » • The transduction by mechanoreceptors (sense of touch) involves “stretch-sensitive” ion (sodium) channels on the membrane of the touch receptors • A mechanical deformation of the skin opens the channels and sodium enters into the « nerve » terminal, inducing a depolarization, ...
... « Take Home Message » • The transduction by mechanoreceptors (sense of touch) involves “stretch-sensitive” ion (sodium) channels on the membrane of the touch receptors • A mechanical deformation of the skin opens the channels and sodium enters into the « nerve » terminal, inducing a depolarization, ...
Micro Muscle: Muscle signal response and myosin activity
... Muscle fibers begin to contract when they receive signals from the nervous system to do so. Many different aspects of physiology interact to allow this to take place. Recall from the nervous system is made up of networks of nervous tissue. This nervous tissue is made of cells called neurons that can ...
... Muscle fibers begin to contract when they receive signals from the nervous system to do so. Many different aspects of physiology interact to allow this to take place. Recall from the nervous system is made up of networks of nervous tissue. This nervous tissue is made of cells called neurons that can ...
BIOL 218 F 2012 MTX 4 Q NS 121121
... Body of the cell hosting the majority of the organelles Brain and spinal cord Bundle of axons Specialized / dedicated neurons that carry action potentials to effectors Carry action potentials to the CNS CNS center with discrete regions Elements of the CNS and PNS that manage homeostasis Ascending an ...
... Body of the cell hosting the majority of the organelles Brain and spinal cord Bundle of axons Specialized / dedicated neurons that carry action potentials to effectors Carry action potentials to the CNS CNS center with discrete regions Elements of the CNS and PNS that manage homeostasis Ascending an ...
Axon
An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), also known as a nerve fibre, is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, that typically conducts electrical impulses away from the neuron's cell body. The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles and glands. In certain sensory neurons (pseudounipolar neurons), such as those for touch and warmth, the electrical impulse travels along an axon from the periphery to the cell body, and from the cell body to the spinal cord along another branch of the same axon. Axon dysfunction causes many inherited and acquired neurological disorders which can affect both the peripheral and central neurons.An axon is one of two types of protoplasmic protrusions that extrude from the cell body of a neuron, the other type being dendrites. Axons are distinguished from dendrites by several features, including shape (dendrites often taper while axons usually maintain a constant radius), length (dendrites are restricted to a small region around the cell body while axons can be much longer), and function (dendrites usually receive signals while axons usually transmit them). All of these rules have exceptions, however.Some types of neurons have no axon and transmit signals from their dendrites. No neuron ever has more than one axon; however in invertebrates such as insects or leeches the axon sometimes consists of several regions that function more or less independently of each other. Most axons branch, in some cases very profusely.Axons make contact with other cells—usually other neurons but sometimes muscle or gland cells—at junctions called synapses. At a synapse, the membrane of the axon closely adjoins the membrane of the target cell, and special molecular structures serve to transmit electrical or electrochemical signals across the gap. Some synaptic junctions appear partway along an axon as it extends—these are called en passant (""in passing"") synapses. Other synapses appear as terminals at the ends of axonal branches. A single axon, with all its branches taken together, can innervate multiple parts of the brain and generate thousands of synaptic terminals.