Add & Subtract Polynomials
... rational and student has no success irrational partial with real numbers to write success with number and real number expressions. simplify expres expressions. sions based on contextual situations. -identify parts of an expression as related to the context and to each part ...
... rational and student has no success irrational partial with real numbers to write success with number and real number expressions. simplify expres expressions. sions based on contextual situations. -identify parts of an expression as related to the context and to each part ...
x - ckw
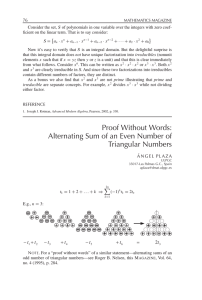
... No cubic or higher-degree polynomial is irreducible over the reals. Corollary 1.6: Any polynomial with real coefficients can be factored into linear and irreducible quadratic polynomials. This factorization is unique; any two factorizations have the same powers of the same factors. Example 1.7: Beca ...
... No cubic or higher-degree polynomial is irreducible over the reals. Corollary 1.6: Any polynomial with real coefficients can be factored into linear and irreducible quadratic polynomials. This factorization is unique; any two factorizations have the same powers of the same factors. Example 1.7: Beca ...