Section A.6 Notes Page 1 A.6 Solving Equations
... Notice that numbers are large on this one. We must see if there is a common factor first. We find that each number is divisible by 2, so we can factor out a 2: 2(2 x 2 − 19 x + 35) = 0 Now we can factor what is inside the parenthesis. This doesn’t ask for an intercept, but just to solve for x. ...
... Notice that numbers are large on this one. We must see if there is a common factor first. We find that each number is divisible by 2, so we can factor out a 2: 2(2 x 2 − 19 x + 35) = 0 Now we can factor what is inside the parenthesis. This doesn’t ask for an intercept, but just to solve for x. ...
1.4 The Complex Numbers.
... is continuous and differentiable, with derivative f 0 (x) = nxn−1 . Since f (0) = 0 and limx→+∞ f (x) = +∞, the intermediate value theorem tells us that the graph of f crosses the line y = r somewhere, say at the point (s, r). This means f (s) = r, or in other words sn = r. But now we ask: “Why does ...
... is continuous and differentiable, with derivative f 0 (x) = nxn−1 . Since f (0) = 0 and limx→+∞ f (x) = +∞, the intermediate value theorem tells us that the graph of f crosses the line y = r somewhere, say at the point (s, r). This means f (s) = r, or in other words sn = r. But now we ask: “Why does ...
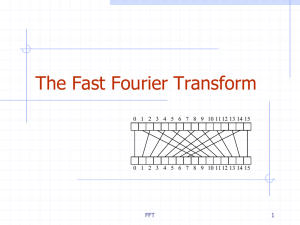
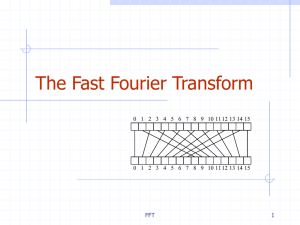
FFT - Personal Web Pages
... Find the (2n-1)-degree polynomial that goes through the points {(x0,p(x0)q(x0)), (x1,p(x1)q(x1)), …, (x2n-1,p(x2n-1)q(x2n-1))}. ...
... Find the (2n-1)-degree polynomial that goes through the points {(x0,p(x0)q(x0)), (x1,p(x1)q(x1)), …, (x2n-1,p(x2n-1)q(x2n-1))}. ...











![arXiv:math/9802122v1 [math.CO] 27 Feb 1998](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013469206_1-76e512f42e60a4643a93990b56cee184-300x300.png)