Basics of associative algebras
... case. Let R be a ring, commutative or not. A subset I of R is a two-sided ideal (of R or in R) if (i) I is a group under addition, (ii) RI ⇢ I, and (iii) IR ⇢ I. If we only require that I satisfy (i) and (ii), we say I is a left ideal of R. Similarly, if we only require I satisfy (i) and (iii), we s ...
... case. Let R be a ring, commutative or not. A subset I of R is a two-sided ideal (of R or in R) if (i) I is a group under addition, (ii) RI ⇢ I, and (iii) IR ⇢ I. If we only require that I satisfy (i) and (ii), we say I is a left ideal of R. Similarly, if we only require I satisfy (i) and (iii), we s ...
Families of elliptic curves of high rank with nontrivial torsion group
... Let P ∈ K[X] be the polynomial P (X) = i=1 (X − Xi ) = X 4 + c3 X 3 + c2 X 2 + c1 X + c0 . It may be written in a unique form as P = Q2 − R with Q and R in K[X] such that Q(X) = X 2 + d1 X + d0 and R(X) = r1 X + r2 , where d1 , d0 , r1 , r2 ∈ Q. Indeed, we obtain the equality by setting d1 = c3 /2, ...
... Let P ∈ K[X] be the polynomial P (X) = i=1 (X − Xi ) = X 4 + c3 X 3 + c2 X 2 + c1 X + c0 . It may be written in a unique form as P = Q2 − R with Q and R in K[X] such that Q(X) = X 2 + d1 X + d0 and R(X) = r1 X + r2 , where d1 , d0 , r1 , r2 ∈ Q. Indeed, we obtain the equality by setting d1 = c3 /2, ...
Elements of Modern Algebra
... number systems. At the same time, in many cases we wish to examine how certain properties are consequences of other, known properties. This sort of examination deepens our understanding of the system. As we proceed, we shall be careful to distinguish between the properties we have assumed and made a ...
... number systems. At the same time, in many cases we wish to examine how certain properties are consequences of other, known properties. This sort of examination deepens our understanding of the system. As we proceed, we shall be careful to distinguish between the properties we have assumed and made a ...
Universal enveloping algebras and some applications in physics
... definitions are reviewed. Indeed, physicists may be unfamiliar with the dailylife terminology of mathematicians and translation rules might prove to be useful in order to have access to the mathematical literature. Each definition is particularized to the finite-dimensional case to gain some intuiti ...
... definitions are reviewed. Indeed, physicists may be unfamiliar with the dailylife terminology of mathematicians and translation rules might prove to be useful in order to have access to the mathematical literature. Each definition is particularized to the finite-dimensional case to gain some intuiti ...
THE CONGRUENT NUMBER PROBLEM 1. Introduction
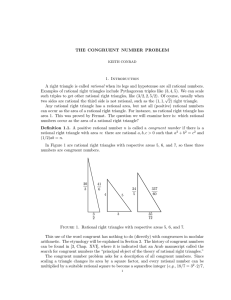
... congruent number eventually shows up in the last column, e.g., the triangle (175, 288, 337) with area 25200 = 7 · 602 occurs at k = 16 and ` = 9. Alas, the table is not systematic in the appearance of the last column: we can’t tell by building the table when any particular number should occur, if at ...
... congruent number eventually shows up in the last column, e.g., the triangle (175, 288, 337) with area 25200 = 7 · 602 occurs at k = 16 and ` = 9. Alas, the table is not systematic in the appearance of the last column: we can’t tell by building the table when any particular number should occur, if at ...