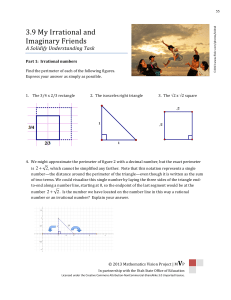
Rings and fields.
... Define the following equivalence relation on the set of polynomials R[x]: p(x) ∼ q(x) if x2 + 1 divides q(x) − p(x) 1. Check that this equivalence relation is compatible with both operations on polynomials. That means if p1 ∼ p2 and q1 ∼ q2 , then p1 + q1 ∼ p2 + q2 p1 q1 ∼ p2 q2 2. Check that the qu ...
... Define the following equivalence relation on the set of polynomials R[x]: p(x) ∼ q(x) if x2 + 1 divides q(x) − p(x) 1. Check that this equivalence relation is compatible with both operations on polynomials. That means if p1 ∼ p2 and q1 ∼ q2 , then p1 + q1 ∼ p2 + q2 p1 q1 ∼ p2 q2 2. Check that the qu ...
STRUCTURE THEOREMS OVER POLYNOMIAL RINGS 1
... Note that the proof in [8] only yields a structure theorem for p-groups, where p is the characteristic of k. An example of a module S for which the conditions of the theorem do not hold is given in [9] 4.4. Condition (1) of the theorem is independent of the ring R, so if, for given S, k and G, one o ...
... Note that the proof in [8] only yields a structure theorem for p-groups, where p is the characteristic of k. An example of a module S for which the conditions of the theorem do not hold is given in [9] 4.4. Condition (1) of the theorem is independent of the ring R, so if, for given S, k and G, one o ...
Solutions Chapters 1–5
... 8. The verification that End G is an abelian group under addition uses the fact that G is an abelian group. The additive identity is the zero function, and the additive inverse of f is given by (−f )(a) = −f (a). Multiplication is associative because composition of functions is associative. To establ ...
... 8. The verification that End G is an abelian group under addition uses the fact that G is an abelian group. The additive identity is the zero function, and the additive inverse of f is given by (−f )(a) = −f (a). Multiplication is associative because composition of functions is associative. To establ ...
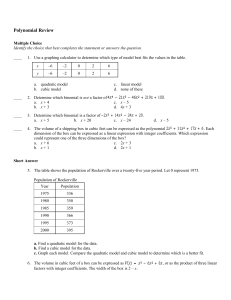
Chapter 9 Quadratic Equations and Functions
... • If the leading coefficient a is positive the parabola opens up, if it’s negative the parabola opens down. • The vertex is the lowest point of a parabola that opens up and the highest point of a parabola that opens down. • The line passing through the vertex that divides the parabola into two symme ...
... • If the leading coefficient a is positive the parabola opens up, if it’s negative the parabola opens down. • The vertex is the lowest point of a parabola that opens up and the highest point of a parabola that opens down. • The line passing through the vertex that divides the parabola into two symme ...
Equations in Quaternions
... where N(t, n) and T(t, n) are polynomialsin t and n with real coefficients. First we note that any rootxo of (1) has a trace toand a normnowhichsatisfy equations (6). This is apparent except whenf(ar, to,no) = 0, in which case equation (4) is meaningless. But in this case equation (3) implies that g ...
... where N(t, n) and T(t, n) are polynomialsin t and n with real coefficients. First we note that any rootxo of (1) has a trace toand a normnowhichsatisfy equations (6). This is apparent except whenf(ar, to,no) = 0, in which case equation (4) is meaningless. But in this case equation (3) implies that g ...