Direct-sum decompositions over one-dimensional Cohen-Macaulay rings
... M one can form the monoid +(M ) consisting of isomorphism classes of modules that are direct summands of direct sums of finitely many copies of M . This is always a finitely generated Krull monoid [24], and the main result of [24] is that every finitely generated Krull monoid arises in this way. In ...
... M one can form the monoid +(M ) consisting of isomorphism classes of modules that are direct summands of direct sums of finitely many copies of M . This is always a finitely generated Krull monoid [24], and the main result of [24] is that every finitely generated Krull monoid arises in this way. In ...
COMPUTING THE SMITH FORMS OF INTEGER MATRICES AND
... has been steadily improved in the past four decades. A group of algorithms for computing the Smith forms is available now. The best asymptotic algorithm may not always yield the best practical run time. In spite of their different asymptotic complexities, different algorithms are favorable to differ ...
... has been steadily improved in the past four decades. A group of algorithms for computing the Smith forms is available now. The best asymptotic algorithm may not always yield the best practical run time. In spite of their different asymptotic complexities, different algorithms are favorable to differ ...
Explicit product ensembles for separable quantum states
... The state of a quantum system composed of N subsystems is separable if it can be written as a classical mixture or classical ensemble of tensor product states. Although it is straightforward to decide whether a pure state is separable, the same question is in general unsolved for mixed states. A sim ...
... The state of a quantum system composed of N subsystems is separable if it can be written as a classical mixture or classical ensemble of tensor product states. Although it is straightforward to decide whether a pure state is separable, the same question is in general unsolved for mixed states. A sim ...
CLASS NUMBER DIVISIBILITY OF QUADRATIC FUNCTION
... function fields F whose ideal class numbers are divisible by a given positive integer g. In [3], using the Friesen’s result, Chakraborty and Mukhopadhyay ...
... function fields F whose ideal class numbers are divisible by a given positive integer g. In [3], using the Friesen’s result, Chakraborty and Mukhopadhyay ...
Abstracts of Papers
... ring A[X1 , · · · , Xn ] and let q = Q ∩ A; the relative height of Q, denoted here by ²Q , is the maximal length of the chains of prime ideals of A[X1 , · · · , Xn ] between q[X1 , · · · , Xn ] and Q. The main result of the present paper is a characterization of quasi-Prfer rings by means of the not ...
... ring A[X1 , · · · , Xn ] and let q = Q ∩ A; the relative height of Q, denoted here by ²Q , is the maximal length of the chains of prime ideals of A[X1 , · · · , Xn ] between q[X1 , · · · , Xn ] and Q. The main result of the present paper is a characterization of quasi-Prfer rings by means of the not ...
solutions - UCLA Department of Mathematics
... is true. So, the contrapositive must also be true: for all creatures c, if ∼ F (c) then ∼ P (c). That is, we know that (iv) is true. To summarize so far, we know that (i) and (iv) are true, but we cannot be certain about the truth of (ii) and (iii). We now examine (v). Consider the implication: if P ...
... is true. So, the contrapositive must also be true: for all creatures c, if ∼ F (c) then ∼ P (c). That is, we know that (iv) is true. To summarize so far, we know that (i) and (iv) are true, but we cannot be certain about the truth of (ii) and (iii). We now examine (v). Consider the implication: if P ...
Leonardo Pisano Fibonacci (c.1175 - c.1240)
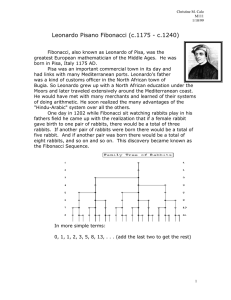
... Another example of the Fibonacci numbers is by starting with two small squares of size 1 next to each other. Then drawing a square of size 2 (=1+1). Now draw a new square - touching both a unit square and the latest square of side 2 - so having sides 3 units long; and then another touching both the ...
... Another example of the Fibonacci numbers is by starting with two small squares of size 1 next to each other. Then drawing a square of size 2 (=1+1). Now draw a new square - touching both a unit square and the latest square of side 2 - so having sides 3 units long; and then another touching both the ...