Chapter 4
... When does life begin? British Warnock Committee (1984) suggested experimentation on the human embryo within the first 14 days of its development. 1. Because before this time implantation in the uterus is not complete; 2. Because only after this time do the embryo cells lose their so-called ‘totip ...
... When does life begin? British Warnock Committee (1984) suggested experimentation on the human embryo within the first 14 days of its development. 1. Because before this time implantation in the uterus is not complete; 2. Because only after this time do the embryo cells lose their so-called ‘totip ...
Learning Flexible Neural Networks for Pattern Recognition
... continuing learning is not useful because the network is trapped at a minimum position as a cure we can teach the neurons activity function gradient like links weight. Among neurons activity functions sigmoid function (one_directed & two_directed) has the most application, therefore for studying the ...
... continuing learning is not useful because the network is trapped at a minimum position as a cure we can teach the neurons activity function gradient like links weight. Among neurons activity functions sigmoid function (one_directed & two_directed) has the most application, therefore for studying the ...
The Neuron: The Basic Unit of Communication Neuron: Basic
... muscles and causing the heart to beat more rapidly. 2. Drugs can mimic or block the effects of a neurotransmitter by fitting into receptor sites and preventing the neurotransmitter from acting. For example, the drug curare produces almost instant paralysis by blocking acetylcholine receptor sites on ...
... muscles and causing the heart to beat more rapidly. 2. Drugs can mimic or block the effects of a neurotransmitter by fitting into receptor sites and preventing the neurotransmitter from acting. For example, the drug curare produces almost instant paralysis by blocking acetylcholine receptor sites on ...
Chapter 12- CNS and epidermis
... activin) to signal dorsal portion of neural tube to become _____________ Notochord (then hinge cells) secretes ______ _________to signal ventral portion of neural tube to become motor neurons •Retinoic acid also plays a role ...
... activin) to signal dorsal portion of neural tube to become _____________ Notochord (then hinge cells) secretes ______ _________to signal ventral portion of neural tube to become motor neurons •Retinoic acid also plays a role ...
The explanatory power of Artificial Neural Networks
... that the starting point of any analysis consists in observations, and not in reality. Indeed what could be reality if it is not observable? In any situation, we have a (finite) set of observations, and we assume that these data represent reality. We could for example measure the tide at a specific c ...
... that the starting point of any analysis consists in observations, and not in reality. Indeed what could be reality if it is not observable? In any situation, we have a (finite) set of observations, and we assume that these data represent reality. We could for example measure the tide at a specific c ...
Neuroembryology of Neural Tube Defects
... Lateral walls of neural tube thicken, gradually reduce the size of the neural canal until only a small central canal remains. Differential thickening of the lateral walls produces a shallow longitudinal groove on each side = sulcus limitans. Dorsal part = alar plate (sensory) Ventral part = basal pl ...
... Lateral walls of neural tube thicken, gradually reduce the size of the neural canal until only a small central canal remains. Differential thickening of the lateral walls produces a shallow longitudinal groove on each side = sulcus limitans. Dorsal part = alar plate (sensory) Ventral part = basal pl ...
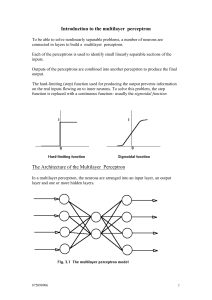
Introduction to the multilayer perceptron
... Remedies such as the "momentum term" add to computational cost Other remedies: using estimates of transfer functions using transfer functions with easy to compute derivatives using estimates of error values, eg., a single global error value for the hidden layer 3. Scaling problem Do not scale up wel ...
... Remedies such as the "momentum term" add to computational cost Other remedies: using estimates of transfer functions using transfer functions with easy to compute derivatives using estimates of error values, eg., a single global error value for the hidden layer 3. Scaling problem Do not scale up wel ...
Neural Networks
... Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. If w > 0, excitatory, else inhibitory. Excitatory weights are identical; inhibitory weights too. Each neuron has a fixed threshold for firing. That is if the net input to the neuron is greater than the threshold it fires. The threshold is set such th ...
... Neurons are connected by directed weighted paths. If w > 0, excitatory, else inhibitory. Excitatory weights are identical; inhibitory weights too. Each neuron has a fixed threshold for firing. That is if the net input to the neuron is greater than the threshold it fires. The threshold is set such th ...
Intelligent Systems - Teaching-WIKI
... • Recurrent networks have at least one feedback connection: – They have directed cycles with delays: they have internal states (like flip flops), can oscillate, etc. – The response to an input depends on the initial state which may depend on previous inputs. – This creates an internal state of the n ...
... • Recurrent networks have at least one feedback connection: – They have directed cycles with delays: they have internal states (like flip flops), can oscillate, etc. – The response to an input depends on the initial state which may depend on previous inputs. – This creates an internal state of the n ...
Artificial neural network
In machine learning and cognitive science, artificial neural networks (ANNs) are a family of statistical learning models inspired by biological neural networks (the central nervous systems of animals, in particular the brain) and are used to estimate or approximate functions that can depend on a large number of inputs and are generally unknown. Artificial neural networks are generally presented as systems of interconnected ""neurons"" which exchange messages between each other. The connections have numeric weights that can be tuned based on experience, making neural nets adaptive to inputs and capable of learning.For example, a neural network for handwriting recognition is defined by a set of input neurons which may be activated by the pixels of an input image. After being weighted and transformed by a function (determined by the network's designer), the activations of these neurons are then passed on to other neurons. This process is repeated until finally, an output neuron is activated. This determines which character was read.Like other machine learning methods - systems that learn from data - neural networks have been used to solve a wide variety of tasks that are hard to solve using ordinary rule-based programming, including computer vision and speech recognition.