Slide ()
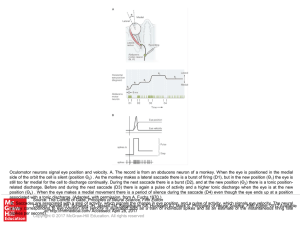
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 2.1 Locomotor behavior in hydra
... local interneurons, and ganglion cells are projection interneurons. Also note a second retinal local interneuron class, amacrine cells (f). Cajal pointed out that retinal neuronal cell bodies aggregate in three layers with synaptic neuropil zones in between, and illustrated a clear structural gradie ...
... local interneurons, and ganglion cells are projection interneurons. Also note a second retinal local interneuron class, amacrine cells (f). Cajal pointed out that retinal neuronal cell bodies aggregate in three layers with synaptic neuropil zones in between, and illustrated a clear structural gradie ...
Artificial Neural Networks : An Introduction
... Hebb Network • Hebb learning rule is the simpliest one • The learning in the brain is performed by the change in the synaptic gap • When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite cell B and repeatedly keep firing it, some growth process takes place in one or both cells • According to Hebb rule, we ...
... Hebb Network • Hebb learning rule is the simpliest one • The learning in the brain is performed by the change in the synaptic gap • When an axon of cell A is near enough to excite cell B and repeatedly keep firing it, some growth process takes place in one or both cells • According to Hebb rule, we ...
Tom`s JSNC2000 paper
... One of the goals of the ANIMAT project is to study information processing in vitro by providing a dissociated culture of neurons a body with which to behave, and a world in which to behave in. We have succeeded in our first major goal: to read activity from the culture in realtime, and to respond wi ...
... One of the goals of the ANIMAT project is to study information processing in vitro by providing a dissociated culture of neurons a body with which to behave, and a world in which to behave in. We have succeeded in our first major goal: to read activity from the culture in realtime, and to respond wi ...
rainfall-runoff modelling in batang layar and oya sub
... the complexity of the ANN’s structures is different from the structure of microprocessors therefore it needs to be emulated. time for processing a network is long. ...
... the complexity of the ANN’s structures is different from the structure of microprocessors therefore it needs to be emulated. time for processing a network is long. ...
Cellular Mechanisms of Learning and Memory
... in the target hippocampal neurons. This facilitation is called long-term potentiation (LTP). LTP can be studied in the intact animal, where it can last for days and even weeks. It can also be examined in slices of hippocampus and in cell culture for several hours. ...
... in the target hippocampal neurons. This facilitation is called long-term potentiation (LTP). LTP can be studied in the intact animal, where it can last for days and even weeks. It can also be examined in slices of hippocampus and in cell culture for several hours. ...
bioresources.com - NC State University
... between the input and output can be revealed without any assumptions or preliminary information from the ANN. The ANN, different from linear models, can also provide modelling in cases where the relations between the data of the handled problem is not linear, is uncertain, and may be indefinite (Zha ...
... between the input and output can be revealed without any assumptions or preliminary information from the ANN. The ANN, different from linear models, can also provide modelling in cases where the relations between the data of the handled problem is not linear, is uncertain, and may be indefinite (Zha ...
Brain(annotated)
... A more likely view is that the information is encoded in exact spike times (and also the strength of synaptic connections). Thus neurons are communicating by sending numbers (times) to each other, and interpreting that information via synaptic strengths. ...
... A more likely view is that the information is encoded in exact spike times (and also the strength of synaptic connections). Thus neurons are communicating by sending numbers (times) to each other, and interpreting that information via synaptic strengths. ...
Full Text - MECS Publisher
... attributes directly but these attributes need to be mapped to numerical values [4]. The mapping so done in this way produces an ordering in the values that any neural network takes into account while processing the data. Also, the final results that are generated by a neural network are continuous v ...
... attributes directly but these attributes need to be mapped to numerical values [4]. The mapping so done in this way produces an ordering in the values that any neural network takes into account while processing the data. Also, the final results that are generated by a neural network are continuous v ...
Artificial neural network
In machine learning and cognitive science, artificial neural networks (ANNs) are a family of statistical learning models inspired by biological neural networks (the central nervous systems of animals, in particular the brain) and are used to estimate or approximate functions that can depend on a large number of inputs and are generally unknown. Artificial neural networks are generally presented as systems of interconnected ""neurons"" which exchange messages between each other. The connections have numeric weights that can be tuned based on experience, making neural nets adaptive to inputs and capable of learning.For example, a neural network for handwriting recognition is defined by a set of input neurons which may be activated by the pixels of an input image. After being weighted and transformed by a function (determined by the network's designer), the activations of these neurons are then passed on to other neurons. This process is repeated until finally, an output neuron is activated. This determines which character was read.Like other machine learning methods - systems that learn from data - neural networks have been used to solve a wide variety of tasks that are hard to solve using ordinary rule-based programming, including computer vision and speech recognition.























