Cell respiration powerpoint animation
... electrons in the absence of O2, the cell must FERMENT the pyruvate. ...
... electrons in the absence of O2, the cell must FERMENT the pyruvate. ...
doc BIOC 311 Final Study Guide
... 1. Present in all eukaryotic cells – believed to have been an autotroph engulfed by phagocytosis that eventually entered symbiosis with the host (endosymbiotic theory). 2. Contain all necessary enzymes for the Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain (ETC) in addition to its own genome and ...
... 1. Present in all eukaryotic cells – believed to have been an autotroph engulfed by phagocytosis that eventually entered symbiosis with the host (endosymbiotic theory). 2. Contain all necessary enzymes for the Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport Chain (ETC) in addition to its own genome and ...
File - Jolyon Johnson
... • H+ then bonds with oxygen to make water or goes back to the intermembrane space • ADP and a phosphate in the matrix bond with the ATP synthase enzyme • The H+ gives ATP synthase the energy needed to bind the ADP and phosphate into ATP • ATP Synthase Video – Stop at 2:55 ...
... • H+ then bonds with oxygen to make water or goes back to the intermembrane space • ADP and a phosphate in the matrix bond with the ATP synthase enzyme • The H+ gives ATP synthase the energy needed to bind the ADP and phosphate into ATP • ATP Synthase Video – Stop at 2:55 ...
Test 1 Study Guide
... h. Lysosomes – “digestive system” i. Contains hydrolytic enzymes at low pH. Digests all classes of macromolecules. ii. Tay-Sach’s disease is genetic and is caused by missing digestive enzyme. The enzyme digests lipids. Lipids build up and kill cell. Death occurs in children i. Mitochondria – “powerh ...
... h. Lysosomes – “digestive system” i. Contains hydrolytic enzymes at low pH. Digests all classes of macromolecules. ii. Tay-Sach’s disease is genetic and is caused by missing digestive enzyme. The enzyme digests lipids. Lipids build up and kill cell. Death occurs in children i. Mitochondria – “powerh ...
Test 1 Study Guide Chapter 1 – Introduction
... h. Lysosomes – “digestive system” i. Contains hydrolytic enzymes at low pH. Digests all classes of macromolecules. ii. Tay-Sach’s disease is genetic and is caused by missing digestive enzyme. The enzyme digests lipids. Lipids build up and kill cell. Death occurs in children i. Mitochondria – “powerh ...
... h. Lysosomes – “digestive system” i. Contains hydrolytic enzymes at low pH. Digests all classes of macromolecules. ii. Tay-Sach’s disease is genetic and is caused by missing digestive enzyme. The enzyme digests lipids. Lipids build up and kill cell. Death occurs in children i. Mitochondria – “powerh ...
Coupling of electron and proton movement in
... Photosynthetic oxidation of two water molecules to molecular oxygen and four protons takes place at a manganese containing unit - the water oxidizing complex (WOC) - within the multimeric Photosystem II (PS II) complex that acts as a water-plastoquinone-oxidoreductase. The overall process comprises ...
... Photosynthetic oxidation of two water molecules to molecular oxygen and four protons takes place at a manganese containing unit - the water oxidizing complex (WOC) - within the multimeric Photosystem II (PS II) complex that acts as a water-plastoquinone-oxidoreductase. The overall process comprises ...
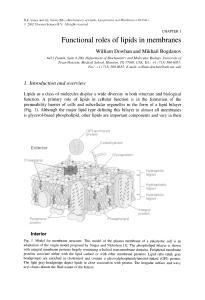
Functional Roles Of Lipids In membranes - IJS
... lipopolysaccharide structure is important to survival of Gram-negative bacteria in their natural environment. This structure is modified post-assembly in response to environment including host fluids, temperature, ionic properties, and antimicrobial agents [4]. In addition, both enteric and non-ente ...
... lipopolysaccharide structure is important to survival of Gram-negative bacteria in their natural environment. This structure is modified post-assembly in response to environment including host fluids, temperature, ionic properties, and antimicrobial agents [4]. In addition, both enteric and non-ente ...
Slide 1
... – Location: cristae of mitochondrion – Purpose: to generate a proton gradient that will be used to form ATP – What Happens?: Electrons are supplied by NADH & FADH2 , then ...
... – Location: cristae of mitochondrion – Purpose: to generate a proton gradient that will be used to form ATP – What Happens?: Electrons are supplied by NADH & FADH2 , then ...
Chapter 8 – an introduction to metabolism
... 14. Explain how enzyme structure determines enzyme specificity. 15. Explain the induced-fit model of enzyme function. 16. Describe the mechanisms by which enzymes lower activation energy. 17. Explain how substrate concentration affects the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. 18. Explain how temper ...
... 14. Explain how enzyme structure determines enzyme specificity. 15. Explain the induced-fit model of enzyme function. 16. Describe the mechanisms by which enzymes lower activation energy. 17. Explain how substrate concentration affects the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction. 18. Explain how temper ...
Cellular Respiration
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ...
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ...
Chapter 9
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ...
... respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen • Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ...
Cellular Respiration
... Cellular Respiration The process by which glucose molecules are broken down to release energy is cellular respiration. It is a series of chemical reactions that produces ATP. Most cellular processes use ATP for energy. ...
... Cellular Respiration The process by which glucose molecules are broken down to release energy is cellular respiration. It is a series of chemical reactions that produces ATP. Most cellular processes use ATP for energy. ...
Studies on Liver Plasma Membranes of Rats Fed
... Emmelot and Bos (13) reported that hepatoma plasma membranes had a lower density than normal liver plasma mem branes, but we have observed that membranes from livers of FAA-fed rats, as well as those from normal rats, floated be tween d 1.16 andd 1.18. However, a floating fraction(d< 1.16) was alway ...
... Emmelot and Bos (13) reported that hepatoma plasma membranes had a lower density than normal liver plasma mem branes, but we have observed that membranes from livers of FAA-fed rats, as well as those from normal rats, floated be tween d 1.16 andd 1.18. However, a floating fraction(d< 1.16) was alway ...
Kreb`s cycle - Secondary Education
... At five places in the cycle, a pair of high-energy electrons is accepted by electron carriers, changing NAD+ to NADH and FAD to FADH2. FAD (flavine adenine dinucleotide) and FADH2 are molecules similar to NAD+ and NADH, respectively. What happens to each of these Krebs cycle products? First, the car ...
... At five places in the cycle, a pair of high-energy electrons is accepted by electron carriers, changing NAD+ to NADH and FAD to FADH2. FAD (flavine adenine dinucleotide) and FADH2 are molecules similar to NAD+ and NADH, respectively. What happens to each of these Krebs cycle products? First, the car ...
Chapter 9 Cell Respiration
... Pyruvate + NADH lactate + NAD+ • Bacteria, fungi in cheese making • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate Pyruvate + NADH lactate + NAD+ • ATP when O2 is low. ...
... Pyruvate + NADH lactate + NAD+ • Bacteria, fungi in cheese making • Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate Pyruvate + NADH lactate + NAD+ • ATP when O2 is low. ...
Weekly Lesson Plans Teacher: Alicia Penfield Class: AP Biology
... Class: AP Biology, 3rd period Week of October 13 – 17 Monday Tuesday The students will… The students will… Explain metabolism and the Explain why photosynthesis role of matter and energy in is an anabolic reaction, and this process. its overall purpose. Distinguish exergonic and Summarize ea ...
... Class: AP Biology, 3rd period Week of October 13 – 17 Monday Tuesday The students will… The students will… Explain metabolism and the Explain why photosynthesis role of matter and energy in is an anabolic reaction, and this process. its overall purpose. Distinguish exergonic and Summarize ea ...
No Slide Title
... Primary active transport: ATP-dependent active transporters P-type Active cotransport of Na+ and K+ 25% of total energy consumption of a human at rest Inhibitors - ouabain and digitoxigenin (O+D = digitalis) ...
... Primary active transport: ATP-dependent active transporters P-type Active cotransport of Na+ and K+ 25% of total energy consumption of a human at rest Inhibitors - ouabain and digitoxigenin (O+D = digitalis) ...
Lecture 13: Fighting Entropy II: Respiration
... • In the presence of O2, pyruvate (generated by glycolysis) enters the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm • Prior to the start of the cycle, pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA, generating one molecule of NADH • The cycle then oxidizes acetyl CoA, generating 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per ...
... • In the presence of O2, pyruvate (generated by glycolysis) enters the mitochondrion from the cytoplasm • Prior to the start of the cycle, pyruvate is converted to acetyl CoA, generating one molecule of NADH • The cycle then oxidizes acetyl CoA, generating 1 ATP, 3 NADH, and 1 FADH2 per ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • The reactants in photosynthesis are the same as the products of cellular respiration. ...
... C6H12O6 + 6O2 6CO2 + 6H2O • The reactants in photosynthesis are the same as the products of cellular respiration. ...
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
... 2. Know the location where photosynthesis and respiration takes place in general and the specific location where the chemical reactions take place. (ie. Know what a biochemical pathway) 3. Know the names for the phases and what happens during each phase in photosynthesis and respiration. 4. Be able ...
... 2. Know the location where photosynthesis and respiration takes place in general and the specific location where the chemical reactions take place. (ie. Know what a biochemical pathway) 3. Know the names for the phases and what happens during each phase in photosynthesis and respiration. 4. Be able ...
Model Protocells from Single-Chain Lipids
... Membranes are important cellular constituents, allowing for processes such as ATP synthesis and neurochemical signal-transduction. Due to the long evolutionary history of cellular membranes, they are highly complex assemblies consisting primarily of double-chain lipids, sterols, and transmembrane sp ...
... Membranes are important cellular constituents, allowing for processes such as ATP synthesis and neurochemical signal-transduction. Due to the long evolutionary history of cellular membranes, they are highly complex assemblies consisting primarily of double-chain lipids, sterols, and transmembrane sp ...
File
... Pyruvate. Products of Glycolysis: 1. Net gain of 2 ATP (2 “spent”, 4 made) 2. NADH 3. 2 Pyruvate ...
... Pyruvate. Products of Glycolysis: 1. Net gain of 2 ATP (2 “spent”, 4 made) 2. NADH 3. 2 Pyruvate ...
Ch18.doc
... 2. Note that the question says “excess of pure lactate dehydrogenase and NADH”. This is important because alanine-transaminase will produce pyruvate which as soon as it is produced will be reduced to lactic acid using NADH. NADH has a strong absorbance at 340 nm, so the rate of decrease in 340 nm ab ...
... 2. Note that the question says “excess of pure lactate dehydrogenase and NADH”. This is important because alanine-transaminase will produce pyruvate which as soon as it is produced will be reduced to lactic acid using NADH. NADH has a strong absorbance at 340 nm, so the rate of decrease in 340 nm ab ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.