Oxidation of Carbohydrate
... on availability of primary substrate • Mass action effect – Substrate availability affects metabolic rate – More available substrate = higher pathway activity – Excess of given substrate = cells rely on that energy substrate more than others ...
... on availability of primary substrate • Mass action effect – Substrate availability affects metabolic rate – More available substrate = higher pathway activity – Excess of given substrate = cells rely on that energy substrate more than others ...
Chapter 9 - Slothnet
... – Glycolysis (breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate) – The citric acid cycle (completes the breakdown of glucose) – Oxidative phosphorylation (accounts for most of the ATP synthesis) ...
... – Glycolysis (breaks down glucose into two molecules of pyruvate) – The citric acid cycle (completes the breakdown of glucose) – Oxidative phosphorylation (accounts for most of the ATP synthesis) ...
Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical Energy
... 2. State the reactants and products of glycolysis. ...
... 2. State the reactants and products of glycolysis. ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration Oxidation of Pyruvate Krebs Cycle
... reduces NAD → NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
... reduces NAD → NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration Kreb`s Cycle
... reduces NAD NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
... reduces NAD NADH (stores energy) produces acetyl CoA ...
Cells, Mitosis-Meiosis, Photosynthesis
... many living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic re ...
... many living things can also make ATP without oxygen. This is true of some plants and fungi and also of many bacteria. These organisms use aerobic respiration when oxygen is present, but when oxygen is in short supply, they use anaerobic respiration instead. Certain bacteria can only use anaerobic re ...
Universitat Autònoma SEPARACIÓ DE COMPOSTOS ANIÒNICS I NEUTRES AMB
... So, different liquid-liquid distribution experiments of these amino acids from aqueous solutions (at regulated pH) to organic solutions with or without the presence of the BPPPd(II) carrier were performed. It was monitored the amino acid concentration in both cases as well as the Pd(II) looses from ...
... So, different liquid-liquid distribution experiments of these amino acids from aqueous solutions (at regulated pH) to organic solutions with or without the presence of the BPPPd(II) carrier were performed. It was monitored the amino acid concentration in both cases as well as the Pd(II) looses from ...
Bioinformatics in Brief This week: DB for structures Structure
... Homologous Superfamily, HThis level groups together protein domains which are thought to share a common ancestor and can therefore be described as homologous. Similarities are identified first by sequence comparisons and subsequently by structure comparison using SSAP. the criteria: Sequence identit ...
... Homologous Superfamily, HThis level groups together protein domains which are thought to share a common ancestor and can therefore be described as homologous. Similarities are identified first by sequence comparisons and subsequently by structure comparison using SSAP. the criteria: Sequence identit ...
Cells and Energy
... plants obtain their chemical energy directly from plants. Animals that eat other animals, and bacteria and fungi that decompose other organisms, get their chemical energy indirectly from plants. When a wolf eats a rabbit, the tissues of the rabbit provide the wolf with a source of chemical energy. T ...
... plants obtain their chemical energy directly from plants. Animals that eat other animals, and bacteria and fungi that decompose other organisms, get their chemical energy indirectly from plants. When a wolf eats a rabbit, the tissues of the rabbit provide the wolf with a source of chemical energy. T ...
7.12. PROTEIN FOLDING AND MISFOLDING43
... usually long, un-branched and often twisted; the core of the organized structure is composed of β-sheets having strands positioned perpendicular to the fibril axis. The portion of a polypeptide chain that is incorporated into fibril core may vary substantially for different proteins; in some cases o ...
... usually long, un-branched and often twisted; the core of the organized structure is composed of β-sheets having strands positioned perpendicular to the fibril axis. The portion of a polypeptide chain that is incorporated into fibril core may vary substantially for different proteins; in some cases o ...
Chloroplast Tubules Visualized in Transplastomic Plants Expressing
... suggest that chloroplast tubules may be regulated developmentally and/or tissue-specifically and have functions related to photosynthesis and the intracellular signal transduction. Previously, the presence of tubular connections between etioplasts has been demonstrated in stomatal guard cells of Ara ...
... suggest that chloroplast tubules may be regulated developmentally and/or tissue-specifically and have functions related to photosynthesis and the intracellular signal transduction. Previously, the presence of tubular connections between etioplasts has been demonstrated in stomatal guard cells of Ara ...
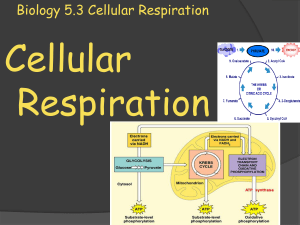
Biology 5.3 Cellular Respiration
... pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. In the second stage of cellular respiration, the pyruvate passes through either aerobic respiration (requires oxygen) or fermentation. When oxygen is not present, ferme ...
... pyruvate during glycolysis. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process (no oxygen required), and it results in a gain of two ATP molecules. In the second stage of cellular respiration, the pyruvate passes through either aerobic respiration (requires oxygen) or fermentation. When oxygen is not present, ferme ...
+ 2
... Definition - Oxidative Phosphorylation: The production of ATP using energy derived from oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions of an electron transport chain. Oxidative phosphorylation requires that the redox reactions occur within a membrane that separates two distinct compartments. ...
... Definition - Oxidative Phosphorylation: The production of ATP using energy derived from oxidation/reduction (redox) reactions of an electron transport chain. Oxidative phosphorylation requires that the redox reactions occur within a membrane that separates two distinct compartments. ...
13 Copy of EAR final2012-09-15 05:175.8 MB
... The semicircular ducts has the same configuration but smaller than the semicircular canals. They are arranged at right angle to each other so the three plans are represented ...
... The semicircular ducts has the same configuration but smaller than the semicircular canals. They are arranged at right angle to each other so the three plans are represented ...
Text - Enlighten - University of Glasgow
... impermeant solutes, mostly of protein, their osmotic coefficients, charge and dependence on pH. Quantitative data, including buffering constants, are available for each of the major solutes or can be estimated for endogenous buffer systems (Tsien and Tsien, 1990; Grabov and Blatt, 1997; Tiffert and L ...
... impermeant solutes, mostly of protein, their osmotic coefficients, charge and dependence on pH. Quantitative data, including buffering constants, are available for each of the major solutes or can be estimated for endogenous buffer systems (Tsien and Tsien, 1990; Grabov and Blatt, 1997; Tiffert and L ...
actin filament-membrane attachment: are membrane particles
... technique of freeze fracture. We have used this technique to determine whether membrane particles are involved in the attachment of actin filaments to the membrane. If particles are involved, the attachment of the actin filaments to membranes is by integral membrane proteins or proteins situated at ...
... technique of freeze fracture. We have used this technique to determine whether membrane particles are involved in the attachment of actin filaments to the membrane. If particles are involved, the attachment of the actin filaments to membranes is by integral membrane proteins or proteins situated at ...
Chapter 3
... are passed along a series of carriers to drive phosphorylation of ADP to ATP – H+ from NADH and FADH are accepted by O2 to form water – H2O (neutral) ...
... are passed along a series of carriers to drive phosphorylation of ADP to ATP – H+ from NADH and FADH are accepted by O2 to form water – H2O (neutral) ...
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP directly • It breaks the large free-energy drop from food to O2 int ...
... • Electrons are transferred from NADH or FADH2 to the electron transport chain • Electrons are passed through a number of proteins including cytochromes (each with an iron atom) to O2 • The electron transport chain generates no ATP directly • It breaks the large free-energy drop from food to O2 int ...
Red Blood Cell Glycophorins
... present at 5 to 9 x lo5 copies per cell, while the less similarities in genomic organization, it appears that the abundant GPB, GPC, and GPD are present at 0.8 to 3 x genes for GPA and GPB arose from a common ancestral lo5, 0.5 to 1 X 105, and 0.2 x lo5 copies per cell, gene through homologous recom ...
... present at 5 to 9 x lo5 copies per cell, while the less similarities in genomic organization, it appears that the abundant GPB, GPC, and GPD are present at 0.8 to 3 x genes for GPA and GPB arose from a common ancestral lo5, 0.5 to 1 X 105, and 0.2 x lo5 copies per cell, gene through homologous recom ...
α-Hemolysin pore formation into a supported
... been studied as a model of ionic channel and protein self-assembly in phospholipid bilayers. The QCM-D technology is a sensitive technique to study molecular interactions on surfaces, SPB in particular. The working principle of the QCM-D technique is based on the piezoelectric properties of quartz. ...
... been studied as a model of ionic channel and protein self-assembly in phospholipid bilayers. The QCM-D technology is a sensitive technique to study molecular interactions on surfaces, SPB in particular. The working principle of the QCM-D technique is based on the piezoelectric properties of quartz. ...
Red blood cell glycophorins
... present at 5 to 9 x lo5 copies per cell, while the less similarities in genomic organization, it appears that the abundant GPB, GPC, and GPD are present at 0.8 to 3 x genes for GPA and GPB arose from a common ancestral lo5, 0.5 to 1 X 105, and 0.2 x lo5 copies per cell, gene through homologous recom ...
... present at 5 to 9 x lo5 copies per cell, while the less similarities in genomic organization, it appears that the abundant GPB, GPC, and GPD are present at 0.8 to 3 x genes for GPA and GPB arose from a common ancestral lo5, 0.5 to 1 X 105, and 0.2 x lo5 copies per cell, gene through homologous recom ...
REVIEWS
... downstream organelles in the secretory pathway do not generally support protein folding13. Furthermore, ER QC ensures that proteins are not dispatched to terminal compartments when they are still incompletely folded and therefore potentially damaging to the cell. For example, it is essential that no ...
... downstream organelles in the secretory pathway do not generally support protein folding13. Furthermore, ER QC ensures that proteins are not dispatched to terminal compartments when they are still incompletely folded and therefore potentially damaging to the cell. For example, it is essential that no ...
Focus Issue on Plastid Biology Update Novel
... From here most electrons are transferred by the enzyme ferredoxin-NADP-oxido-reductase (FNR) to NADP+ generating NADPH + H+. By this means the electrons cross a redox potential difference of about 1.13 V in total which is strong enough to fuel all subsequent redox-dependent reactions in the cell. T ...
... From here most electrons are transferred by the enzyme ferredoxin-NADP-oxido-reductase (FNR) to NADP+ generating NADPH + H+. By this means the electrons cross a redox potential difference of about 1.13 V in total which is strong enough to fuel all subsequent redox-dependent reactions in the cell. T ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.