Biochemistry of cell organelles
... triggers rotation of the whole F0 domain (how – still not clear). This in turn, leads to rotation of the subunit. But the subunit does not rotate the F1 domain because it fixed by the side-arm complex. Instead, rotation of the subunit distirb the shape of and subunits by such a way that they become ...
... triggers rotation of the whole F0 domain (how – still not clear). This in turn, leads to rotation of the subunit. But the subunit does not rotate the F1 domain because it fixed by the side-arm complex. Instead, rotation of the subunit distirb the shape of and subunits by such a way that they become ...
Eukaryotic Cells
... • Eukaryotic Cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles • The membrane is key! ...
... • Eukaryotic Cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles • The membrane is key! ...
Cell Membrane
... Semipermeable-regulates what enters and exits the cell Partitions the cell into different regions where different ...
... Semipermeable-regulates what enters and exits the cell Partitions the cell into different regions where different ...
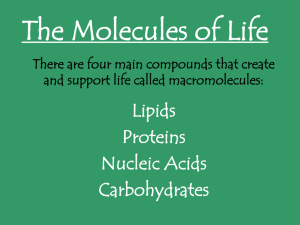
The Molecules of Life
... They are the fuel the body uses to sustain itself. The most important one to know is Glucose – a simple sugar that the body ‘burns’ to create its energy or ATP. ...
... They are the fuel the body uses to sustain itself. The most important one to know is Glucose – a simple sugar that the body ‘burns’ to create its energy or ATP. ...
2. What are the main properties that fats, proteins, and
... within the leaves. 31. What are the main products of the light-dependent reaction? Generally, the light-dependent reactions remove low energy electrons from water when chlorophyll absorbs energy; these electrons move down an electron transport system to produce ATP from ADP and (P); energized electr ...
... within the leaves. 31. What are the main products of the light-dependent reaction? Generally, the light-dependent reactions remove low energy electrons from water when chlorophyll absorbs energy; these electrons move down an electron transport system to produce ATP from ADP and (P); energized electr ...
Cell Physiology
... • electrons travel in pairs (2 e-) along the transport chain • each electron carrier becomes reduced when it receives an electron pair and oxidized again when it passes the electrons along to the next carrier • oxygen is the final electron acceptor – each oxygen atom accepts two electrons from cytoc ...
... • electrons travel in pairs (2 e-) along the transport chain • each electron carrier becomes reduced when it receives an electron pair and oxidized again when it passes the electrons along to the next carrier • oxygen is the final electron acceptor – each oxygen atom accepts two electrons from cytoc ...
File
... Transport by Carrier Proteins The plasma membrane stops the passage of most molecules into and out of the cell. However, biologically important molecules do pass. They do so because of carrier proteins that exist in the plasma membrane. • Carrier proteins are specific and each binds to specific mole ...
... Transport by Carrier Proteins The plasma membrane stops the passage of most molecules into and out of the cell. However, biologically important molecules do pass. They do so because of carrier proteins that exist in the plasma membrane. • Carrier proteins are specific and each binds to specific mole ...
Transport Across Cell Membrane
... Cell Membrane and Transport In bacteria, plants, and fungi cell membrane is surrounded by a non-living cell wall. But cell membrane is the real boundary. Most cell walls are permeable others are impermeable. Semi-permeable: Cell membranes allow some materials to pass through them and prevent others ...
... Cell Membrane and Transport In bacteria, plants, and fungi cell membrane is surrounded by a non-living cell wall. But cell membrane is the real boundary. Most cell walls are permeable others are impermeable. Semi-permeable: Cell membranes allow some materials to pass through them and prevent others ...
Lecture exam 1A
... D. only substrate-level phosphorylation utilizes a proton gradient to make ATP E. only oxidative phosphorylation involves an oxidation-reduction reaction 44. Chlorophyll a is found in A. PSI B. PSII C. Antenna complexes D. Only A and B are correct E. A, B and C are correct 45. All reaction center co ...
... D. only substrate-level phosphorylation utilizes a proton gradient to make ATP E. only oxidative phosphorylation involves an oxidation-reduction reaction 44. Chlorophyll a is found in A. PSI B. PSII C. Antenna complexes D. Only A and B are correct E. A, B and C are correct 45. All reaction center co ...
The Fluid Mosaic Model of the Cell Membrane
... of frozen plasma membranes from a variety of sources including vacuoles, nuclei, chloroplasts, mitochondria and bacteria to reveal proteins embedded within (Singer and Nicolson, 1972). Similarly, evidence had also emerged to support the existence of transmembrane proteins, proteins that traversed th ...
... of frozen plasma membranes from a variety of sources including vacuoles, nuclei, chloroplasts, mitochondria and bacteria to reveal proteins embedded within (Singer and Nicolson, 1972). Similarly, evidence had also emerged to support the existence of transmembrane proteins, proteins that traversed th ...
Chapter 3 Exam
... separates two solutions. Solution A contains 0.9% NaCl and solution B contains 9.0 % NaCl. With respect to this system, which of the following statements would be true? A) water would move from solution A to solution B B) water would move from solution B to solution A C) Na+ would move from solution ...
... separates two solutions. Solution A contains 0.9% NaCl and solution B contains 9.0 % NaCl. With respect to this system, which of the following statements would be true? A) water would move from solution A to solution B B) water would move from solution B to solution A C) Na+ would move from solution ...
101 -- 2006
... __ 32. The Krebs cycle reduces molecules that then transfer electrons to the electron transport system. What are these reduced molecules? a) ATP and CO2 c) FADH2 and NADH e) NADH, FADH2, and ATP b) CO2 and FAD d) NADH and ATP __ 33. Muscle cells in oxygen deprivation convert pyruvate to _____ and in ...
... __ 32. The Krebs cycle reduces molecules that then transfer electrons to the electron transport system. What are these reduced molecules? a) ATP and CO2 c) FADH2 and NADH e) NADH, FADH2, and ATP b) CO2 and FAD d) NADH and ATP __ 33. Muscle cells in oxygen deprivation convert pyruvate to _____ and in ...
slide
... Where they are in contact with the aqueous environment, they have hydrophilic regions of amino acids. ...
... Where they are in contact with the aqueous environment, they have hydrophilic regions of amino acids. ...
Transport of molecules into a bacterial cell
... – What is the greediest electron hog we know? Molecular oxygen. – In Electron transport, electrons are passed to oxygen so that these metabolic processes can continue with more glucose. – Electron carriers in membrane are reversibly reduced, then reoxidized as they pass electrons (or Hs) to the next ...
... – What is the greediest electron hog we know? Molecular oxygen. – In Electron transport, electrons are passed to oxygen so that these metabolic processes can continue with more glucose. – Electron carriers in membrane are reversibly reduced, then reoxidized as they pass electrons (or Hs) to the next ...
Eukaryotic Organelles
... Proteins are assembled by ribosomes on the RER Vesicles transport proteins to the Golgi apparatus Golgi modify proteins and package them into new vesicles Vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane to release proteins outside the cell 5. Vesicles containing enzymes that remain inside the cell form lysos ...
... Proteins are assembled by ribosomes on the RER Vesicles transport proteins to the Golgi apparatus Golgi modify proteins and package them into new vesicles Vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane to release proteins outside the cell 5. Vesicles containing enzymes that remain inside the cell form lysos ...
Aquaporin IDI Prelab
... a. Why are the new water channels being developed referred to as biomimetic? ...
... a. Why are the new water channels being developed referred to as biomimetic? ...
What does a cell need?
... solutes, permeability of cell membranes is selective and regulated. • Permeability determined by transporter proteins. – Channels and carriers are solute specific – If no transporter, than that solute cannot cross membrane ...
... solutes, permeability of cell membranes is selective and regulated. • Permeability determined by transporter proteins. – Channels and carriers are solute specific – If no transporter, than that solute cannot cross membrane ...
unit II
... Understand the importance of the phospholipid, its structural formula, and it chemical characteristics that make it important to the plasma membrane Know the plasma membrane: its structure, percent lipid makeup, proteins present and their functions Know the mechanisms of molecular movement discussed ...
... Understand the importance of the phospholipid, its structural formula, and it chemical characteristics that make it important to the plasma membrane Know the plasma membrane: its structure, percent lipid makeup, proteins present and their functions Know the mechanisms of molecular movement discussed ...
Cell Physiology
... movement of particles and molecules from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration Cell use simple diffusion – the unassisted diffusion of solutes through the plasma membrane. These particles have to be ...
... movement of particles and molecules from an area of high concentration to areas of low concentration Cell use simple diffusion – the unassisted diffusion of solutes through the plasma membrane. These particles have to be ...
READ THIS!
... 16. For each diagram in Model 2, circle the side of the membrane where the ion or molecule would have originated (has higher concentration) in the normal function of a cell. 17. Which substances in Model 2 appear to be completely blocked by the membrane? Explain why. 18. Which substances in Model 2 ...
... 16. For each diagram in Model 2, circle the side of the membrane where the ion or molecule would have originated (has higher concentration) in the normal function of a cell. 17. Which substances in Model 2 appear to be completely blocked by the membrane? Explain why. 18. Which substances in Model 2 ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.