Cellular respiration guided notes completed
... The fluid matrix in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion contains the enzymes for the ...
... The fluid matrix in the inner membrane of the mitochondrion contains the enzymes for the ...
Cell Respiration Take Home Test 1. When cells break down food
... 1. When cells break down food molecules, energy a. is released all at once. b. is released entirely as body heat into the environment. c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic ...
... 1. When cells break down food molecules, energy a. is released all at once. b. is released entirely as body heat into the environment. c. is temporarily stored in ATP molecules while some is released as body heat. d. causes excitation of electrons in chlorophyll molecules. 2. The process of aerobic ...
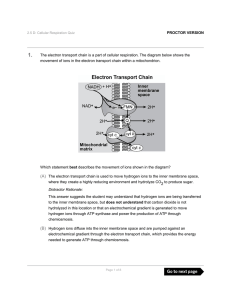
The electron transport chain is a part of cellular respiration. The
... inner membrane space via the electron transport chain to produce an electrochemical gradient, and that the ions then flow through ATP synthase to the mitochondrial matrix to power the production of ATP. ...
... inner membrane space via the electron transport chain to produce an electrochemical gradient, and that the ions then flow through ATP synthase to the mitochondrial matrix to power the production of ATP. ...
2. How we study biology • The scientific method requires controls
... activity (death) which is ultimately determined by genetic information. Consider plant forms that live to be 500 to 1,000 years old and humans who survive for 100 years to viruses who live only hours to weeks. ...
... activity (death) which is ultimately determined by genetic information. Consider plant forms that live to be 500 to 1,000 years old and humans who survive for 100 years to viruses who live only hours to weeks. ...
Cellular respiration - how cells make energy
... - like with glycolysis, we will not go into the details of the Krebs cycle. - Step 3: Electron chain. - Although some ATP's are produced by both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, we now need to deal with all the NADH's (and an FADH2 or two) - We already discussed the basics of this - we use chemiosmos ...
... - like with glycolysis, we will not go into the details of the Krebs cycle. - Step 3: Electron chain. - Although some ATP's are produced by both glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, we now need to deal with all the NADH's (and an FADH2 or two) - We already discussed the basics of this - we use chemiosmos ...
Energy Transfer Review notes
... The light reactions (in the thylakoids) split water, release O 2, produce ATP, and form NADPH The Calvin cycle (in the stroma) forms sugar from CO 2, using ATP and NADPH The light reactions convert solar energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH The thylakoids transform light into the chemical ...
... The light reactions (in the thylakoids) split water, release O 2, produce ATP, and form NADPH The Calvin cycle (in the stroma) forms sugar from CO 2, using ATP and NADPH The light reactions convert solar energy to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH The thylakoids transform light into the chemical ...
Shaping the Endoplasmic Reticulum into a Social Network
... In some family members[13_TD$IF], an APH is also the predicted N-terminal of the RHD. These RHDflanking elements provide additional stabilization. ER tubule formation does not solely rely on Rtns and Rtn-like proteins. In mammalian cells, tubules are constantly pulled out of the plane of ER membranes ...
... In some family members[13_TD$IF], an APH is also the predicted N-terminal of the RHD. These RHDflanking elements provide additional stabilization. ER tubule formation does not solely rely on Rtns and Rtn-like proteins. In mammalian cells, tubules are constantly pulled out of the plane of ER membranes ...
Chemiluminescent and Fluorescent Westerns
... on a membrane. The method relies on an enzyme-substrate reaction that emits light, which is traditionally detected on x-ray film. Chemiluminescent Westerns are widely used across a variety of laboratories, and many facilities provide the necessary darkroom and developer for documentation with x-ray ...
... on a membrane. The method relies on an enzyme-substrate reaction that emits light, which is traditionally detected on x-ray film. Chemiluminescent Westerns are widely used across a variety of laboratories, and many facilities provide the necessary darkroom and developer for documentation with x-ray ...
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration, Harvesting Chemical Energy
... ATP synthase is a protein complex that populates the inner membrane of the mitochondrion o It uses the movement of H+ ions in order to fuel the synthesis of ATP ATP Synthase is composed of four parts, each made up of multiple polypeptide o A rotor, knob, internal rob, and stator. Hydrogen ions flow ...
... ATP synthase is a protein complex that populates the inner membrane of the mitochondrion o It uses the movement of H+ ions in order to fuel the synthesis of ATP ATP Synthase is composed of four parts, each made up of multiple polypeptide o A rotor, knob, internal rob, and stator. Hydrogen ions flow ...
Chapter 9 – Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
... Using enzymes, cells can extract the potential energy stored in organic compounds during exergonic reactions. The energy taken out can be used to do work, and the rest is given off as heat. One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs ...
... Using enzymes, cells can extract the potential energy stored in organic compounds during exergonic reactions. The energy taken out can be used to do work, and the rest is given off as heat. One catabolic process is called fermentation which is a partial oxidation of organic molecules, and it occurs ...
respir532
... Electron Transport Chain: ________________ serves as the final OXYGEN electron acceptor of the electron transport chain. These electrons are at their lowest energy level. At the end of the electron transport chain, an enzyme combines the electrons with the hydrogen ions and oxygen to form water (H2 ...
... Electron Transport Chain: ________________ serves as the final OXYGEN electron acceptor of the electron transport chain. These electrons are at their lowest energy level. At the end of the electron transport chain, an enzyme combines the electrons with the hydrogen ions and oxygen to form water (H2 ...
Protein Biosynthesis
... to the newly exposed carboxy-terminal amino acid residue to establish an amide bond between the latter and the ethanolamine moiety of the glycolipid. 2. GPI assembly takes place entirely on the cytoplasmic side of the ER and followed by its translocation to the lumenal side, where attachment to the ...
... to the newly exposed carboxy-terminal amino acid residue to establish an amide bond between the latter and the ethanolamine moiety of the glycolipid. 2. GPI assembly takes place entirely on the cytoplasmic side of the ER and followed by its translocation to the lumenal side, where attachment to the ...
The Proton-Motive Force Overview Compartmentalization
... • Proton gradient across mitochondrial membrane ...
... • Proton gradient across mitochondrial membrane ...
8-3 The Reactions of Photosynthesis
... The two sets of photosynthetic reactions work together. • The light-dependent reactions trap sunlight energy in chemical form. • The Calvin cycle uses that chemical energy to produce stable, high-energy sugars from carbon dioxide and water. ...
... The two sets of photosynthetic reactions work together. • The light-dependent reactions trap sunlight energy in chemical form. • The Calvin cycle uses that chemical energy to produce stable, high-energy sugars from carbon dioxide and water. ...
Honors Biology Name Cells Notes, continued… PROKARYOTIC
... 2. Package refined proteins in vesicles that transport the proteins to different destinations based on the proteins functions a. Secretory Protein – (hormones like Insulin) packaged in secretory vesicle that fuses with cell membrane b. Lysosomes – enzymes for hydrolysis are packaged in a vesicle tha ...
... 2. Package refined proteins in vesicles that transport the proteins to different destinations based on the proteins functions a. Secretory Protein – (hormones like Insulin) packaged in secretory vesicle that fuses with cell membrane b. Lysosomes – enzymes for hydrolysis are packaged in a vesicle tha ...
6. protein folding
... pathways); they don't randomly search all possible conformations until they arrive at the most stable (lowest free energy) structure. • Proteins that don't (re)fold on their own, need "molecular chaperones" (which are also proteins) to keep them from slipping off the folding pathway or to help them ...
... pathways); they don't randomly search all possible conformations until they arrive at the most stable (lowest free energy) structure. • Proteins that don't (re)fold on their own, need "molecular chaperones" (which are also proteins) to keep them from slipping off the folding pathway or to help them ...
P Systems with Control Nuclei
... has one or more control points where active genes are copied and exported into the membrane region for transcription. The specific program (or mechanism) used to get the position of the control points for the active genes used in a next transcription step is left unspecified at this moment. (A simpl ...
... has one or more control points where active genes are copied and exported into the membrane region for transcription. The specific program (or mechanism) used to get the position of the control points for the active genes used in a next transcription step is left unspecified at this moment. (A simpl ...
unit 3 – photosynthesis and cellular respiration
... build new proteins. However, excess amino acids will be converted by enzymes to intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Before amino acids can enter these processes, deamination must take place – the amino groups must be removed. The nitrogen containing wastes are excreted in the form ...
... build new proteins. However, excess amino acids will be converted by enzymes to intermediates of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. Before amino acids can enter these processes, deamination must take place – the amino groups must be removed. The nitrogen containing wastes are excreted in the form ...
Study Guide - PEP 535 Exam#1
... What are the sources of protons during muscle contraction? What are the sources of proton buffering/utilization/removal in skeletal muscle? Is it correct to interpret lactate production as the cause of muscle acidosis? Why? Why does ATP hydrolysis release a proton? How would you explain the biochemi ...
... What are the sources of protons during muscle contraction? What are the sources of proton buffering/utilization/removal in skeletal muscle? Is it correct to interpret lactate production as the cause of muscle acidosis? Why? Why does ATP hydrolysis release a proton? How would you explain the biochemi ...
Thylakoid

A thylakoid is a membrane-bound compartment inside chloroplasts and cyanobacteria. They are the site of the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Thylakoids consist of a thylakoid membrane surrounding a thylakoid lumen. Chloroplast thylakoids frequently form stacks of disks referred to as grana (singular: granum). Grana are connected by intergranal or stroma thylakoids, which join granum stacks together as a single functional compartment.