The Nervous System - Gordon State College
... system): part of the ANS that is responsible for reacting to stressful events and bodily arousal – parasympathetic division: part of the ANS that restores the body to normal functioning after arousal and is responsible for the day-to-day functioning of the organs and glands ...
... system): part of the ANS that is responsible for reacting to stressful events and bodily arousal – parasympathetic division: part of the ANS that restores the body to normal functioning after arousal and is responsible for the day-to-day functioning of the organs and glands ...
The Nervous System
... • If VM reaches threshold, Na+ channels open and Na+ influx ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the f ...
... • If VM reaches threshold, Na+ channels open and Na+ influx ensues, depolarizing the cell and causing the VM to increase. This is the rising phase of an AP. • Eventually, the Na+ channel will have inactivated and the K+ channels will be open. Now, K+ effluxes and repolarization occurs. This is the f ...
Attenuating GABAA Receptor Signaling in Dopamine Neurons
... may have disrupted the proper integration of information about reward probability at the level of DA neurons and increased the risk preference of β3-KO mice. ...
... may have disrupted the proper integration of information about reward probability at the level of DA neurons and increased the risk preference of β3-KO mice. ...
as a PDF - University of Sussex
... exposed to stimuli corresponding to a particular person, say Bill Clinton, and to very little else [18], [6]. They respond to the concept, and can be activated by pictures, voice or unique events. Obviously for most people such a cell would fire very infrequently. The alternative distributed represe ...
... exposed to stimuli corresponding to a particular person, say Bill Clinton, and to very little else [18], [6]. They respond to the concept, and can be activated by pictures, voice or unique events. Obviously for most people such a cell would fire very infrequently. The alternative distributed represe ...
Bio 12 - Test Review..
... The influx (flowing in) of Sodium ions causes the membrane to become _______ ...
... The influx (flowing in) of Sodium ions causes the membrane to become _______ ...
NVCC Bio 211 - gserianne.com
... glands, dendrites and neuronal cell bodies • General response method for cells ...
... glands, dendrites and neuronal cell bodies • General response method for cells ...
File - Perkins Science
... • Structural and functional units of the nervous system • General functions a.Respond to chemical and physical stimuli b.Conduct electrochemical impulses c.Release chemical regulators d.Enable perception of sensory stimuli, learning, memory, and control of muscles and glands ...
... • Structural and functional units of the nervous system • General functions a.Respond to chemical and physical stimuli b.Conduct electrochemical impulses c.Release chemical regulators d.Enable perception of sensory stimuli, learning, memory, and control of muscles and glands ...
Axon - Perkins Science
... • Structural and functional units of the nervous system • General functions a.Respond to chemical and physical stimuli b.Conduct electrochemical impulses c.Release chemical regulators d.Enable perception of sensory stimuli, learning, memory, and control of muscles and glands ...
... • Structural and functional units of the nervous system • General functions a.Respond to chemical and physical stimuli b.Conduct electrochemical impulses c.Release chemical regulators d.Enable perception of sensory stimuli, learning, memory, and control of muscles and glands ...
Neural Coding - Computing Science and Mathematics
... “decode” the signal from the neuron – Information coded in spikes fired by neuron in a 200 msec time window ...
... “decode” the signal from the neuron – Information coded in spikes fired by neuron in a 200 msec time window ...
Object recognition in clutter: selectivity and invariance
... Davide Zoccolan and James DiCarlo The problem: A major challenge of current theories of vision is to understand how the visual system performs object recognition in cluttered conditions, typical of natural visual scenes, where objects of interest do not appear in isolation but together with backgrou ...
... Davide Zoccolan and James DiCarlo The problem: A major challenge of current theories of vision is to understand how the visual system performs object recognition in cluttered conditions, typical of natural visual scenes, where objects of interest do not appear in isolation but together with backgrou ...
Introduction to Computational Neuroscience
... b. Single neurons. We know very well how point neurons work (think Hodgkin Huxley). Dendrites. Lots of potential for incredibly complex processing. My guess: all they do is make neurons bigger and reduce wiring length (see the work of Mitya Chklovskii). How much I would bet that that’: 20 p. ...
... b. Single neurons. We know very well how point neurons work (think Hodgkin Huxley). Dendrites. Lots of potential for incredibly complex processing. My guess: all they do is make neurons bigger and reduce wiring length (see the work of Mitya Chklovskii). How much I would bet that that’: 20 p. ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM: NEURAL TISSUE
... Neural Development and Growth • Stem cells differen8ate into neurons or glia (before birth) • Each neuronal daughter cell differen8ates and sends out processes that will be axons and dendrites • Growth cone ...
... Neural Development and Growth • Stem cells differen8ate into neurons or glia (before birth) • Each neuronal daughter cell differen8ates and sends out processes that will be axons and dendrites • Growth cone ...
31.1 Really Neurons
... The immune system of people with multiple sclerosis attacks myelin sheaths in the CNS. The myelin breaks down and scar tissue may result. How do you think this would affect the transmission of signals from the CNS? ...
... The immune system of people with multiple sclerosis attacks myelin sheaths in the CNS. The myelin breaks down and scar tissue may result. How do you think this would affect the transmission of signals from the CNS? ...
Slide 1 - Gatsby Computational Neuroscience Unit
... Dendrites. Lots of potential for incredibly complex processing. My guess: all they do is make neurons bigger and reduce wiring length (see the work of Mitya Chklovskii). How much I would bet that that’s true: 20 p. ...
... Dendrites. Lots of potential for incredibly complex processing. My guess: all they do is make neurons bigger and reduce wiring length (see the work of Mitya Chklovskii). How much I would bet that that’s true: 20 p. ...
Print this Page Presentation Abstract Program#/Poster#: 532.07/GG10
... which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation of normalization in the visual cortex is thought to involve inhibitory neurons t ...
... which the output is modulated by the summed local activity. In these models, the region of the sensory space that is pooled to produce suppression to a neuron is larger than that for summation. The neural implementation of normalization in the visual cortex is thought to involve inhibitory neurons t ...
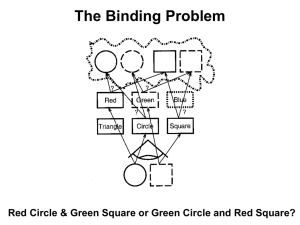
Optional extra slides on the Binding Problem
... This synchronization may boost temporal and spatial summation of EPSPs and IPSPs, and thus increase the chance to depolarize post-synaptic cell. ...
... This synchronization may boost temporal and spatial summation of EPSPs and IPSPs, and thus increase the chance to depolarize post-synaptic cell. ...
weiten6_PPT03
... you’ll see in this chapter and the remainder of the book, the effects of many phenomena— such as pain, drug use, and some diseases—can be explained in terms of how they alter one or more of these processes (usually at synapses releasing a specific Table of Contents neurotransmitter). ...
... you’ll see in this chapter and the remainder of the book, the effects of many phenomena— such as pain, drug use, and some diseases—can be explained in terms of how they alter one or more of these processes (usually at synapses releasing a specific Table of Contents neurotransmitter). ...
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding glial
... b) The neuron is negatively charged while the extra-cellular medium is positively charged c) The neuron predominantly contains negatively charged ions while the extra-cellular medium contains positively charged ...
... b) The neuron is negatively charged while the extra-cellular medium is positively charged c) The neuron predominantly contains negatively charged ions while the extra-cellular medium contains positively charged ...
Neurology
... if it carries impulse towards cell body and an axon if it carry impulses out of cell body. Axon is called nerve fiber and membrane covering the axon is called axolemma. In a myelinated axon axolemma is surrounded by myelin sheath called neurilemma, at regular interval there is myelin free gaps calle ...
... if it carries impulse towards cell body and an axon if it carry impulses out of cell body. Axon is called nerve fiber and membrane covering the axon is called axolemma. In a myelinated axon axolemma is surrounded by myelin sheath called neurilemma, at regular interval there is myelin free gaps calle ...
Introduction to electrophysiological recordings
... The presynaptic process of the axon releases neurotransmitters in the synaptic left that interact with postsynaptic membrane receptors that gate ion channels. For example, the glutamate (the most common neurotransmitter ~90%) opens postsynaptic Na+ channels. The influx of Na+ decreases the electrica ...
... The presynaptic process of the axon releases neurotransmitters in the synaptic left that interact with postsynaptic membrane receptors that gate ion channels. For example, the glutamate (the most common neurotransmitter ~90%) opens postsynaptic Na+ channels. The influx of Na+ decreases the electrica ...
Motor
... Activity of three neurons—one in M1, one in PM, and one in SMA—recorded as a monkey pressed three buttons in sequence. The sequence was first cued visually by lighting the buttons and was then cued internally. The M1 neuron showed similar activity whether the monkey performed from visual or int ...
... Activity of three neurons—one in M1, one in PM, and one in SMA—recorded as a monkey pressed three buttons in sequence. The sequence was first cued visually by lighting the buttons and was then cued internally. The M1 neuron showed similar activity whether the monkey performed from visual or int ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Sympathetic and Parasympathetic systems • Muscarinic receptors- found on the target organs and tissues supplied by the postganglionic neuron of the parasympathetic nervous system ...
... Sympathetic and Parasympathetic systems • Muscarinic receptors- found on the target organs and tissues supplied by the postganglionic neuron of the parasympathetic nervous system ...
Hearing the Call of Neurons PowerPoint
... many different shapes and sizes. A midget bipolar and ...
... many different shapes and sizes. A midget bipolar and ...
Key Transmitters - Sinauer Associates
... 11). Their voltage-dependence means that they act as coincidence detectors, only allowing current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors ...
... 11). Their voltage-dependence means that they act as coincidence detectors, only allowing current to pass when the neuron is simultaneously depolarized by, for example, highfrequency activation of AMPA channels, ongoing action potential activity, or co-activation of metabotropic glutamate receptors ...
APPLICATION OF AN EXPERT SYSTEM FOR ASSESSMENT OF …
... The brain has at least 1010 neurons, each connected to 104 others We are not attempting to build computer brains – extremely simplified versions of natural neural systems- rather we are aiming to discover the properties of models. The idea behind neural computing - by modeling the major features of ...
... The brain has at least 1010 neurons, each connected to 104 others We are not attempting to build computer brains – extremely simplified versions of natural neural systems- rather we are aiming to discover the properties of models. The idea behind neural computing - by modeling the major features of ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.