Synapses - Franklin College
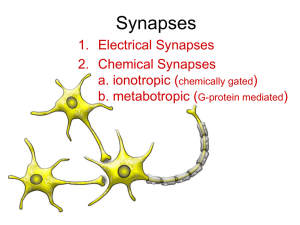
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
... Two neurons releasing neurotransmitters that act on a third neuron. The first two neurons could be in the Central Nervous System, and the third might be a motor neuron leading out to a muscle or gland. Schwann Cells form a myelin sheath Around the axon of motor neurons Neurons ...
Document
... • Stimulation causes cell membrane to open briefly • Positively charged sodium ions flow in • Shift in electrical charge travels along neuron • The Action Potential • All – or – none law ...
... • Stimulation causes cell membrane to open briefly • Positively charged sodium ions flow in • Shift in electrical charge travels along neuron • The Action Potential • All – or – none law ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
... FUN FACTS ABOUT YOUR BRAIN - the human Central Nervous System (CNS) weighs approximately __ pounds; largest existing brain is approximately __ lbs (sperm whale) - there are approximately ___________ neurons in the CNS; that’s 100 000 000 000 !!!!!!! - each of these neurons makes between _________ __ ...
Chapter 2: Introduction to Physiology of Perception
... • Electrical signals are generated when such ions ...
... • Electrical signals are generated when such ions ...
Single Unit Recording
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
... electrode introduced into the brain of a living animal will detect electrical activity that is generated by the neurons adjacent to the electrode tip. If the electrode is a microelectrode, with a tip size of 3 to 10 micrometers, the electrode will often isolate the activity of a single neuron. The a ...
Structure of the Brain PowerPoint Notes
... place segment by segment as they move down the length of the axon • ____________________ – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon Sending information – ___________________________ ...
... place segment by segment as they move down the length of the axon • ____________________ – if an action potential starts at the beginning of the axon, the action potential will continue at the same speed segment to segment to the very end of the axon Sending information – ___________________________ ...
Neuron death - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. discuss the mechanisms involved in neuron death. 2. discuss the process and goals of synaptic rearrangement. 3. discuss neurodevelopment in infancy through to adolescence. ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. discuss the mechanisms involved in neuron death. 2. discuss the process and goals of synaptic rearrangement. 3. discuss neurodevelopment in infancy through to adolescence. ...
The Reflex Arc
... C. Receptor – a specialized nerve tissue that is sensitive to a specific stimulus. 1. Receptors may be nerve endings in the skin which may be sensitive to temperature changes. 2. Receptors may be complex organs such as the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, s ...
... C. Receptor – a specialized nerve tissue that is sensitive to a specific stimulus. 1. Receptors may be nerve endings in the skin which may be sensitive to temperature changes. 2. Receptors may be complex organs such as the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, s ...
the nervous system
... the neuron membranes • The space between neurons is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters carry impulses across the synapse ...
... the neuron membranes • The space between neurons is called the synapse • Neurotransmitters carry impulses across the synapse ...
The Nervous System - Riverside Preparatory High School
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ ...
... m/s. Another conducts at the rate of 1 m/s. Which neuron has a myelinated axon? 2. List the following in order: A. K+ channels open and K+ floods out of cell B. Membrane is polarized (resting potential) C. Neurotransmitters are released from vesicles into synaptic cleft D. Na+ channels open and Na+ ...
Chapter 2
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
... • Action potential occurs when the membrane potential rapidly shifts from -70 to +40 mV – Ion channels open in the membrane, allowing sodium ions to enter the axon – Sodium entry shifts the membrane potential toward a ...
and peripheral nerves, and is composed of cells called neurons that
... concentration gradients and the membrane potential. Nerve impulses have a domino effect. An action potential in one part of the neuron causes another action potential in the adjacent part and so on. This is due to the diffusion of sodium ions between the region of the action potential and the restin ...
... concentration gradients and the membrane potential. Nerve impulses have a domino effect. An action potential in one part of the neuron causes another action potential in the adjacent part and so on. This is due to the diffusion of sodium ions between the region of the action potential and the restin ...
Previous lecture
... A. Inhibitory synapses on dendrites do a good job of inhibiting EPSPs on nearby spines B. Inhibitory synapses on cell bodies and initial segments ...
... A. Inhibitory synapses on dendrites do a good job of inhibiting EPSPs on nearby spines B. Inhibitory synapses on cell bodies and initial segments ...
The Function & Anatomy of Neurons What is a Neuron?
... peripheral to the central nervous system (unipolar). Association- Carry impulses between neurons within the central nervous system(multipolar). Motor(Efferent)- Carry impulses from the central nervous system to any part of the body capable of responding. (most are multipolar). ...
... peripheral to the central nervous system (unipolar). Association- Carry impulses between neurons within the central nervous system(multipolar). Motor(Efferent)- Carry impulses from the central nervous system to any part of the body capable of responding. (most are multipolar). ...
Neuroanatomy
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
Slide 1
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
... and allows positively charged ions into the axon. This overwhelming positive charge causes an electrical charge to form (an action potential). At 120 meters per second, the action potential travels to the terminal buttons via the axon. ...
fleming_Oct
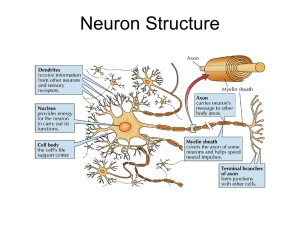
... dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The neuron shown here is a motor neuron. Motor neurons originate in the brain or spinal cord and send their axons to the muscles or glands of the body. ...
... dendrites and soma to the branching ends of the axon. The neuron shown here is a motor neuron. Motor neurons originate in the brain or spinal cord and send their axons to the muscles or glands of the body. ...
(580.422) Lecture 7, Synaptic Transmission
... Glutamate receptors require further comment. NMDA-type glutamate receptors are conditionally activated, depending on the presence of glutamate AND depolarization of the postsynaptic terminal. The depolarization is necessary to relieve a block of the NMDA receptor channel by Mg++ ions. ...
... Glutamate receptors require further comment. NMDA-type glutamate receptors are conditionally activated, depending on the presence of glutamate AND depolarization of the postsynaptic terminal. The depolarization is necessary to relieve a block of the NMDA receptor channel by Mg++ ions. ...
Peripheral nervous system
... 3. Na+ channels open and sodium floods into the cell in one section of the axon 4. The Na+ channels in that area close but the region down the axon gets positive enough to reach threshold Na+ channels open and sodium rushes in… this continues down the axon 5. The K+ channels open and potassium dif ...
... 3. Na+ channels open and sodium floods into the cell in one section of the axon 4. The Na+ channels in that area close but the region down the axon gets positive enough to reach threshold Na+ channels open and sodium rushes in… this continues down the axon 5. The K+ channels open and potassium dif ...
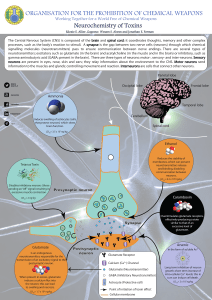
Working Together for a World Free of Chemical Weapons
... Glutamate Is an endogenous neurotransmitter, responsible for the transmission of an excitatory signal to the postsynaptic neuron. ...
... Glutamate Is an endogenous neurotransmitter, responsible for the transmission of an excitatory signal to the postsynaptic neuron. ...
Human Vision: Electrophysiology and Psychophysics
... Uptil now we have discussed the conditions of a neuron at rest. But the neuron is in a network and the information processing capacities of the neuron lie in its capacity to communicate with the other neurons. ...
... Uptil now we have discussed the conditions of a neuron at rest. But the neuron is in a network and the information processing capacities of the neuron lie in its capacity to communicate with the other neurons. ...
Nonsynaptic plasticity
Nonsynaptic plasticity is a form of neuroplasticity that involves modification of ion channel function in the axon, dendrites, and cell body that results in specific changes in the integration of excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs). Nonsynaptic plasticity is a modification of the intrinsic excitability of the neuron. It interacts with synaptic plasticity, but it is considered a separate entity from synaptic plasticity. Intrinsic modification of the electrical properties of neurons plays a role in many aspects of plasticity from homeostatic plasticity to learning and memory itself. Nonsynaptic plasticity affects synaptic integration, subthreshold propagation, spike generation, and other fundamental mechanisms of neurons at the cellular level. These individual neuronal alterations can result in changes in higher brain function, especially learning and memory. However, as an emerging field in neuroscience, much of the knowledge about nonsynaptic plasticity is uncertain and still requires further investigation to better define its role in brain function and behavior.