Common Core Learning Standards GRADE 7 Mathematics
... measures of the opposite interior angle by drawing the triangle. ...
... measures of the opposite interior angle by drawing the triangle. ...
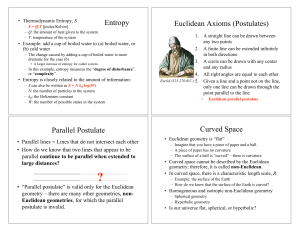
Geometry Grade Level: 9 (with Recommendation), 10, 11, 12 Length
... 12. Make formal geometric constructions, including those representing Montana American Indians, with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisec ...
... 12. Make formal geometric constructions, including those representing Montana American Indians, with a variety of tools and methods (compass and straightedge, string, reflective devices, paper folding, dynamic geometric software, etc.). Copying a segment; copying an angle; bisecting a segment; bisec ...
Inscribed Angle
... Ex 3 - Find the mTAP, given that OT = 80° and OP = 110°. If you add TO and OP, you get 190°. ...
... Ex 3 - Find the mTAP, given that OT = 80° and OP = 110°. If you add TO and OP, you get 190°. ...
GEOM_U4_BLM_Final
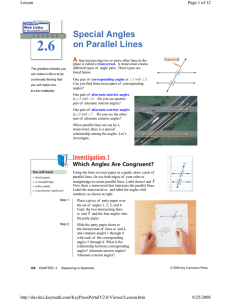
... Notice there are two reflections. Lines m and n are parallel. The resulting image has the same orientation as the pre-image, but has been moved to the right by 10 cm. A question to think about: does the distance of the translation have any relationship to the distance between the parallel lines? A t ...
... Notice there are two reflections. Lines m and n are parallel. The resulting image has the same orientation as the pre-image, but has been moved to the right by 10 cm. A question to think about: does the distance of the translation have any relationship to the distance between the parallel lines? A t ...
Special Angles on Parallel Lines
... The Geometer’s Sketchpad® can repeat a recursive rule on a figure using a command called Iterate. Using Iterate, you can create the initial stages of fascinating geometric figures called fractals. Fractals are self-similar, meaning that if you zoom in on a part of the figure, it looks like the whole ...
... The Geometer’s Sketchpad® can repeat a recursive rule on a figure using a command called Iterate. Using Iterate, you can create the initial stages of fascinating geometric figures called fractals. Fractals are self-similar, meaning that if you zoom in on a part of the figure, it looks like the whole ...
Sine and Cosine Laws
... 5. At a provincial park, there is a sign, a reception area, and a picnic area. The reception area is 350 m away from the picnic area, the picnic area is 475 m away from the sign. From the picnic area, the angle between the 2 lines of sight for the reception area and the sign is 64°. How far apart is ...
... 5. At a provincial park, there is a sign, a reception area, and a picnic area. The reception area is 350 m away from the picnic area, the picnic area is 475 m away from the sign. From the picnic area, the angle between the 2 lines of sight for the reception area and the sign is 64°. How far apart is ...
Euler angles
The Euler angles are three angles introduced by Leonhard Euler to describe the orientation of a rigid body. To describe such an orientation in 3-dimensional Euclidean space three parameters are required. They can be given in several ways, Euler angles being one of them; see charts on SO(3) for others. Euler angles are also used to describe the orientation of a frame of reference (typically, a coordinate system or basis) relative to another. They are typically denoted as α, β, γ, or φ, θ, ψ.Euler angles represent a sequence of three elemental rotations, i.e. rotations about the axes of a coordinate system. For instance, a first rotation about z by an angle α, a second rotation about x by an angle β, and a last rotation again about z, by an angle γ. These rotations start from a known standard orientation. In physics, this standard initial orientation is typically represented by a motionless (fixed, global, or world) coordinate system; in linear algebra, by a standard basis.Any orientation can be achieved by composing three elemental rotations. The elemental rotations can either occur about the axes of the fixed coordinate system (extrinsic rotations) or about the axes of a rotating coordinate system, which is initially aligned with the fixed one, and modifies its orientation after each elemental rotation (intrinsic rotations). The rotating coordinate system may be imagined to be rigidly attached to a rigid body. In this case, it is sometimes called a local coordinate system. Without considering the possibility of using two different conventions for the definition of the rotation axes (intrinsic or extrinsic), there exist twelve possible sequences of rotation axes, divided in two groups: Proper Euler angles (z-x-z, x-y-x, y-z-y, z-y-z, x-z-x, y-x-y) Tait–Bryan angles (x-y-z, y-z-x, z-x-y, x-z-y, z-y-x, y-x-z). Tait–Bryan angles are also called Cardan angles; nautical angles; heading, elevation, and bank; or yaw, pitch, and roll. Sometimes, both kinds of sequences are called ""Euler angles"". In that case, the sequences of the first group are called proper or classic Euler angles.