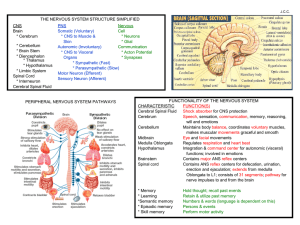
B6 – Brain and Mind Go to the BBC Bitesize website from the school
... Where are light receptor cells found in the eye? ____________________________________ What type of response is caused by simple reflexes? ________________________________ What is the benefit of simple reflex responses? ____________________________________ What is the disadvantage of only using refle ...
... Where are light receptor cells found in the eye? ____________________________________ What type of response is caused by simple reflexes? ________________________________ What is the benefit of simple reflex responses? ____________________________________ What is the disadvantage of only using refle ...
Document
... • Separates the capillaries in the brain from the nervous tissue • Capillary walls in the brain have no fenestrations; covered ...
... • Separates the capillaries in the brain from the nervous tissue • Capillary walls in the brain have no fenestrations; covered ...
Orexin-A, a peptide that can convince cancer cells to commit suicide
... different signals at the same time, a huge amount of receptors exist as well as several signalling pathways with different carriers. Orexin-A is one of these key-signals and its lock is called OX1-receptor. In case of cell suicide, researcher found out that the terminal molecule is p38. p38 is an en ...
... different signals at the same time, a huge amount of receptors exist as well as several signalling pathways with different carriers. Orexin-A is one of these key-signals and its lock is called OX1-receptor. In case of cell suicide, researcher found out that the terminal molecule is p38. p38 is an en ...
Lesson1 Powerpoint
... Sensory transduction Transforming external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
... Sensory transduction Transforming external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
Unit III Modules 9 to 13 Test Review
... Curare: an antagonist • Curare acts only at muscular synapses and NOT at the synapses of the central nervous system (curare does not cross the blood-brain barrier), • Thus, a victim of curare poisoning may be aware of what is happening until the very end. • The victim can feel the paralysis progres ...
... Curare: an antagonist • Curare acts only at muscular synapses and NOT at the synapses of the central nervous system (curare does not cross the blood-brain barrier), • Thus, a victim of curare poisoning may be aware of what is happening until the very end. • The victim can feel the paralysis progres ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functio ...
... called the involuntary nervous system. ___ 24. ____ neurons carry impulses from receptors to the spinal cord. 25. What are the two major division of the peripheral nervous system? ____&___ 26 Nervous system subdivision that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.____ 27.The __ is the basic functio ...
Document
... Sensory transduction Transforming external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
... Sensory transduction Transforming external physical forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
Physiology – Excitable Tissue – 11th May 2010
... 29. When skeletal muscle contracts, which of the following is true? a. calcium is released and this initiates contraction by binding Troponin T b. there is always a decrease in the length of the muscle c. if it is an isotonic contraction, work is done d. the initiating event is acetylcholine binding ...
... 29. When skeletal muscle contracts, which of the following is true? a. calcium is released and this initiates contraction by binding Troponin T b. there is always a decrease in the length of the muscle c. if it is an isotonic contraction, work is done d. the initiating event is acetylcholine binding ...
Mechanisms of Perception: Hearing, Touch, Smell, Taste & Attention
... Each type has its own unique structure, but they all basically work the same way Stimuli to the skin changes the chemistry of the receptor, which changes the permeability of the receptor cell membrane to ions, which sends a neural signal ...
... Each type has its own unique structure, but they all basically work the same way Stimuli to the skin changes the chemistry of the receptor, which changes the permeability of the receptor cell membrane to ions, which sends a neural signal ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... Cholinergic muscarinic receptors (M1-M8) Work via the second messenger system (IP3 and DAG) M1 – postsynaptic membranes; M2 – presynaptic membranes Agonist - muscarine Antagonist – - atropine,scopolamine M2), -pirenzepine (M1, M4) The effect of ACh binding: ...
... Cholinergic muscarinic receptors (M1-M8) Work via the second messenger system (IP3 and DAG) M1 – postsynaptic membranes; M2 – presynaptic membranes Agonist - muscarine Antagonist – - atropine,scopolamine M2), -pirenzepine (M1, M4) The effect of ACh binding: ...
summing-up - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... stimulus comes is called tropism: geotropism is the ability to orient in the direction of gravity; phototropism is the tendency to orient oneself according to light. ...
... stimulus comes is called tropism: geotropism is the ability to orient in the direction of gravity; phototropism is the tendency to orient oneself according to light. ...
Nervous system
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...
... Medulla Oblongata lies within the midbrain between the pons and spinal cord,it forms the brainstem. The medulla controls heart rate, breathing swallowing, coughing and vomiting. The midbrain and the pons relay messages between the medulla oblongata and the cerebrum. ...
The Nervous System - Kirchner-WHS
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
... system is the function of everything. ► It sends signals notify the brain to react to the situation. ► Reflexes, movement, muscles, everything! ...
Aging of the Nervous System: Structural Changes
... From the beginning of the 20th Century until the 1990s, it was stated that neurons DID NOT proliferate. The fact that they COULD NOT proliferate did not exclude the possibility of proliferation under “specific conditions.” In fact, the CNS has a considerable regenerative potential depending on ...
... From the beginning of the 20th Century until the 1990s, it was stated that neurons DID NOT proliferate. The fact that they COULD NOT proliferate did not exclude the possibility of proliferation under “specific conditions.” In fact, the CNS has a considerable regenerative potential depending on ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint Notes
... called the _____________________________________________. ________________________(chemicals) released from the sending neuron _________________________________and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing it to generate an action potential. ...
... called the _____________________________________________. ________________________(chemicals) released from the sending neuron _________________________________and bind to receptor sites on the receiving neuron, thereby influencing it to generate an action potential. ...
CNS Brain * Cerebrum * Cerebellum * Brain Stem * Diencephalon
... makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Contains major ANS reflex centers Spinal cord Contains AN ...
... makes muscular movements graceful and smooth Midbrain Eye and facial movements Medulla Oblongata Regulates respiration and heart beat Hypothalamus Integration & command center for autonomic (visceral) functions; involved in emotions Brainstem Contains major ANS reflex centers Spinal cord Contains AN ...
Slide 1
... L03: Explain what it means for a neuron to “fire” an action potential, describing how the neuron’s structure makes this possible. L04: Explain the process by which neurons communicate with each other, allowing the nervous system to integrate complex information. L05: Differentiate the roles played b ...
... L03: Explain what it means for a neuron to “fire” an action potential, describing how the neuron’s structure makes this possible. L04: Explain the process by which neurons communicate with each other, allowing the nervous system to integrate complex information. L05: Differentiate the roles played b ...
Parkinson disease
... nucleus of the thalamus, which sends excitatory projections to the motor cortex, thus leading to hypokinesia. •The mechanism by which the brain cells in Parkinson's are lost may consist of an abnormal accumulation of the protein alpha-synuclein bound to ubiquitin in the damaged cells. The alpha-synu ...
... nucleus of the thalamus, which sends excitatory projections to the motor cortex, thus leading to hypokinesia. •The mechanism by which the brain cells in Parkinson's are lost may consist of an abnormal accumulation of the protein alpha-synuclein bound to ubiquitin in the damaged cells. The alpha-synu ...
Biology 621 - Chapter 12 Midterm Exam Review
... 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the organs they control. 32What two ions are moved across a neuron’s membra ...
... 29. Within the spinal cord, motor and sensory neurons are connected byinterneurons 30. The 2 divisions of the autonomic nervous system sympathetic ¶sympathetic 31 The above two divisions have a(n) antagonistic effects on the organs they control. 32What two ions are moved across a neuron’s membra ...
nervous system 2012 - Junction Hill C
... to other cells by a fiber called an axon. Axons can be very short or quite long. You have some really long axons that extend almost 1 meter from your lower back to your toes ...
... to other cells by a fiber called an axon. Axons can be very short or quite long. You have some really long axons that extend almost 1 meter from your lower back to your toes ...
Nervous System
... your ear sense this movement and sends messages to the peripheral nervous system, which then controls your body and makes sure you do not lose your balance. ...
... your ear sense this movement and sends messages to the peripheral nervous system, which then controls your body and makes sure you do not lose your balance. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - An overview of - e
... The corpus callosum is the most important landmark in the brain. It is a bridge of axons that joins the two hemispheres and allows communication between them. Corpus Callosum ...
... The corpus callosum is the most important landmark in the brain. It is a bridge of axons that joins the two hemispheres and allows communication between them. Corpus Callosum ...
Molecular neuroscience

Molecular neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that observes concepts in molecular biology applied to the nervous systems of animals. The scope of this subject primarily pertains to a reductionist view of neuroscience, considering topics such as molecular neuroanatomy, mechanisms of molecular signaling in the nervous system, the effects of genetics on neuronal development, and the molecular basis for neuroplasticity and neurodegenerative diseases. As with molecular biology, molecular neuroscience is a relatively new field that is considerably dynamic.