Economics 2010 (Morey section) - University of Colorado Boulder
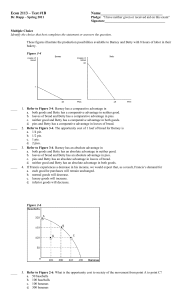
... 16. Chuck spends all his income on two goods: tacos and milkshakes. His income is $100, the price of tacos is $10, and the price of milkshakes is $2. Put tacos on the horizontal axis and milkshakes on the vertical axis. The opportunity cost of one taco equals ________ units of milkshakes. A) 5 B) 2 ...
... 16. Chuck spends all his income on two goods: tacos and milkshakes. His income is $100, the price of tacos is $10, and the price of milkshakes is $2. Put tacos on the horizontal axis and milkshakes on the vertical axis. The opportunity cost of one taco equals ________ units of milkshakes. A) 5 B) 2 ...
Macroeconomic Analysis Econ 6022 Level I
... 1. It is productive: it raises the amount of output that a worker can produce. 2. It is produced: Capital has itself been produced through the process of investment (private or public). 3. It is rival in its use: only a limited number of people can use a given piece of capital at one time. 4. It yie ...
... 1. It is productive: it raises the amount of output that a worker can produce. 2. It is produced: Capital has itself been produced through the process of investment (private or public). 3. It is rival in its use: only a limited number of people can use a given piece of capital at one time. 4. It yie ...
Supply
... supplier will offer at different prices. (Two variables, (factors), that can change are compared: #1 price & #2 quantities) • like the demand schedule, the supply schedule only reflects how the changes in PRICE affect the quantity produced. • Market supply schedule: A chart that lists how much of a ...
... supplier will offer at different prices. (Two variables, (factors), that can change are compared: #1 price & #2 quantities) • like the demand schedule, the supply schedule only reflects how the changes in PRICE affect the quantity produced. • Market supply schedule: A chart that lists how much of a ...
CH_5_Economics_Notes_Website
... 2. When government actions cause the supply of a good to increase, what happens to the supply curve for that good? (a) It shifts to the left. (b) It shifts to the right. (c) It reverses direction. (d) The supply curve is unaffected. ...
... 2. When government actions cause the supply of a good to increase, what happens to the supply curve for that good? (a) It shifts to the left. (b) It shifts to the right. (c) It reverses direction. (d) The supply curve is unaffected. ...
Supply
... 2. When government actions cause the supply of a good to increase, what happens to the supply curve for that good? (a) It shifts to the left. (b) It shifts to the right. (c) It reverses direction. (d) The supply curve is unaffected. ...
... 2. When government actions cause the supply of a good to increase, what happens to the supply curve for that good? (a) It shifts to the left. (b) It shifts to the right. (c) It reverses direction. (d) The supply curve is unaffected. ...
The Ohio State University Department of Economics Econ 501AjProf
... The height of the (inverse) supply curve at a particular quantity, X, is the price at which some …rm is willing to sell that unit of output. Since it also is the marginal cost of production for the …rm selling the output, the height up to the supply curve is society’s marginal cost of providing the ...
... The height of the (inverse) supply curve at a particular quantity, X, is the price at which some …rm is willing to sell that unit of output. Since it also is the marginal cost of production for the …rm selling the output, the height up to the supply curve is society’s marginal cost of providing the ...
Evidence from the Gravity Model Analysis
... country is derived by maximizing a constant elasticity of substitution (CES) utility function subject to income constraints in importing countries. On the other hand, the equation of trade supply is derived from the firm’s profit maximization procedure in the exporting country, with resource allocat ...
... country is derived by maximizing a constant elasticity of substitution (CES) utility function subject to income constraints in importing countries. On the other hand, the equation of trade supply is derived from the firm’s profit maximization procedure in the exporting country, with resource allocat ...
Elasticity of Supply
... Supply curve shows data from supply schedule in graph form Market supply curve shows data from market supply schedule ...
... Supply curve shows data from supply schedule in graph form Market supply curve shows data from market supply schedule ...
african trading blocs and economic growth
... gold rather than its citizens’ well-being, high living standards, and improved human development. Mercantilism’s building blocks include trade policies that support trade surpluses by promoting exports paid for in gold and restricting imports, government intervention in trade to ensure that countrie ...
... gold rather than its citizens’ well-being, high living standards, and improved human development. Mercantilism’s building blocks include trade policies that support trade surpluses by promoting exports paid for in gold and restricting imports, government intervention in trade to ensure that countrie ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from... Bureau of Economic Research
... an attempt to apply to labor concepts similar to those used for capital stock. Aichian [1970] has extended this concept to a very general class of phenomena associated with "nonfull" employment of resources. In the case of capital, hours per machine is an appropriate measure to use, whereas in the c ...
... an attempt to apply to labor concepts similar to those used for capital stock. Aichian [1970] has extended this concept to a very general class of phenomena associated with "nonfull" employment of resources. In the case of capital, hours per machine is an appropriate measure to use, whereas in the c ...
Economics 102 Part III
... 10. What changes have been occurring recently in the regulation of public utilities? Why? 11. Explain how a company in monopolistic competition would determine the profit-maximizing quantity and price. Show the graph. 12. Explain what will result in monopolistic competition if a company is earning e ...
... 10. What changes have been occurring recently in the regulation of public utilities? Why? 11. Explain how a company in monopolistic competition would determine the profit-maximizing quantity and price. Show the graph. 12. Explain what will result in monopolistic competition if a company is earning e ...
Version A - University of Colorado Boulder
... 8. Karen consumes gasoline and other goods. A new excise tax on gasoline raises gas prices. However, the government pays Karen an income subsidy that is just enough for her to stay on her original (pre-tax) indifference curve. Her new optimal consumption bundle will have: A) less of other goods and ...
... 8. Karen consumes gasoline and other goods. A new excise tax on gasoline raises gas prices. However, the government pays Karen an income subsidy that is just enough for her to stay on her original (pre-tax) indifference curve. Her new optimal consumption bundle will have: A) less of other goods and ...
Competitive Market Behavior
... benefits received from consuming that last unit) is greater than the opportunity costs of producing an additional unit. Social welfare could be improved allocating resources to the production of this good and making it available to consumers. As production and sale of this good increases, the price ...
... benefits received from consuming that last unit) is greater than the opportunity costs of producing an additional unit. Social welfare could be improved allocating resources to the production of this good and making it available to consumers. As production and sale of this good increases, the price ...
Slide 1
... Market supply and market demand set the price Buyers and sellers takes price (P) as given Perfectly competitive firm can sell all it wants to sell at the market price Since the supplier is small, its output decision will not change market price Each firm must decide how much to supply (Q) Impe ...
... Market supply and market demand set the price Buyers and sellers takes price (P) as given Perfectly competitive firm can sell all it wants to sell at the market price Since the supplier is small, its output decision will not change market price Each firm must decide how much to supply (Q) Impe ...
Module 6 - Supply and Equilibrium
... Law of Supply • All other things equal, as price increases the quantity supplied rises • So there is an direct relationship between price and quantity supplied • Plotted on a graph, the law of supply infers an upward sloping supply curve • The law of diminishing returns causes the supply curves to b ...
... Law of Supply • All other things equal, as price increases the quantity supplied rises • So there is an direct relationship between price and quantity supplied • Plotted on a graph, the law of supply infers an upward sloping supply curve • The law of diminishing returns causes the supply curves to b ...
What is Microeconomics? - California State University, Bakersfield
... D constant and increase S? D constant and decrease S? D increase and S decreases by equal amounts? D decrease and S increases by equal amounts? D increases more than S decreases? D increases less than S decreases? ...
... D constant and increase S? D constant and decrease S? D increase and S decreases by equal amounts? D decrease and S increases by equal amounts? D increases more than S decreases? D increases less than S decreases? ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES ZEROS, QUALITY AND SPACE: Richard Baldwin
... volumes have not distinguished among these three factors. In this paper we show that focusing on how the number of traded goods and their prices differ as a function of trade costs and market size turns out to be very informative about the ability of trade theory to match trade data. We establish s ...
... volumes have not distinguished among these three factors. In this paper we show that focusing on how the number of traded goods and their prices differ as a function of trade costs and market size turns out to be very informative about the ability of trade theory to match trade data. We establish s ...
Second Midterm, Fall 2012 Version 1 with comments
... need to take it every day and the dose is 10 drops a day. If you take more the medicine is ineffective and if you take less it is ineffective. The medicine has no taste and no side effects. You choose to take the medicine in the proper dose. The government pays for it: there is socialized medicine. ...
... need to take it every day and the dose is 10 drops a day. If you take more the medicine is ineffective and if you take less it is ineffective. The medicine has no taste and no side effects. You choose to take the medicine in the proper dose. The government pays for it: there is socialized medicine. ...
Document
... Toyland? a. The opportunity cost of an additional 100 dolls is 50 fire trucks. b. The opportunity cost of an additional 100 dolls is 100 fire trucks. c. Toyland’s production possibilities frontier is a straight, downward-sloping line. d. The opportunity cost of an additional 100 dolls increases as m ...
... Toyland? a. The opportunity cost of an additional 100 dolls is 50 fire trucks. b. The opportunity cost of an additional 100 dolls is 100 fire trucks. c. Toyland’s production possibilities frontier is a straight, downward-sloping line. d. The opportunity cost of an additional 100 dolls increases as m ...
Ahliman Abbasov Microeconomics (Qrup 1023-1024)
... 40. Define Minimum Wage, show and discuss its relationship with Unemployment. 41. Define Rent Control, identify between short-run and long-run Rent Control. 42. Discuss and explain the term Equilibrium without Trade. 43. Discuss and explain the term World Price and Comparative Advantage. 44. Discuss ...
... 40. Define Minimum Wage, show and discuss its relationship with Unemployment. 41. Define Rent Control, identify between short-run and long-run Rent Control. 42. Discuss and explain the term Equilibrium without Trade. 43. Discuss and explain the term World Price and Comparative Advantage. 44. Discuss ...
Answers: When demand rises, do prices rise too?
... The marginal cost curve, labelled MC on Figure 1, shows how the monopolist’s total costs change as it increases its output by one unit. As in the supply and demand model, this is often horizontal or upwards sloping. In Figure 1, we allow it to be upwards sloping, signifying that the monopolist find ...
... The marginal cost curve, labelled MC on Figure 1, shows how the monopolist’s total costs change as it increases its output by one unit. As in the supply and demand model, this is often horizontal or upwards sloping. In Figure 1, we allow it to be upwards sloping, signifying that the monopolist find ...
Lecture_Ch05 - Princeton High School
... It boils down to this: • in the short run, the quantity of at least one input is fixed, whereas in the long run the quantities of all inputs are variable. • The inputs with fixed quantities in the short run are called fixed inputs. In the long run, even fixed inputs ...
... It boils down to this: • in the short run, the quantity of at least one input is fixed, whereas in the long run the quantities of all inputs are variable. • The inputs with fixed quantities in the short run are called fixed inputs. In the long run, even fixed inputs ...
Decision-making and Demand and Supply
... • The demand curve is created assuming ceteris paribus, so it maps only the relationship between P and QD. • The demand function shows all the determinants of demand. All the factors other than P, such a PR and Y, are shift factors. ...
... • The demand curve is created assuming ceteris paribus, so it maps only the relationship between P and QD. • The demand function shows all the determinants of demand. All the factors other than P, such a PR and Y, are shift factors. ...
Assignment Guide: Unit II
... 4) Differentiate between a change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied. ...
... 4) Differentiate between a change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied. ...
capacity-utilization-and-unemployment
... – More leisure is always better (as well as more consumption goods). – Leisure is a normal good. ...
... – More leisure is always better (as well as more consumption goods). – Leisure is a normal good. ...
Comparative advantage

The theory of comparative advantage is an economic theory about the work gains from trade for individuals, firms, or nations that arise from differences in their factor endowments or technological progress. In an economic model, an agent has a comparative advantage over another in producing a particular good if he can produce that good at a lower relative opportunity cost or autarky price, i.e. at a lower relative marginal cost prior to trade. One does not compare the monetary costs of production or even the resource costs (labor needed per unit of output) of production. Instead, one must compare the opportunity costs of producing goods across countries. The closely related law or principle of comparative advantage holds that under free trade, an agent will produce more of and consume less of a good for which he has a comparative advantage.David Ricardo developed the classical theory of comparative advantage in 1817 to explain why countries engage in international trade even when one country's workers are more efficient at producing every single good than workers in other countries. He demonstrated that if two countries capable of producing two commodities engage in the free market, then each country will increase its overall consumption by exporting the good for which it has a comparative advantage while importing the other good, provided that there exist differences in labor productivity between both countries. Widely regarded as one of the most powerful yet counter-intuitive insights in economics, Ricardo's theory implies that comparative advantage rather than absolute advantage is responsible for much of international trade.