Exercise session 5
... M C = 2. Assume that the demand function for the product is de…ned as follows: p = 100 0:5 (q1 + q2 ) : If …rm 2 sets a quantity of q2 = 100, what’s the best response quantity for …rm 1. Solution: Residual demand curve facing …rm 1 is p = 100 0:5 (q1 + 100) = 50 0:5q1 : If the marginal cost of produ ...
... M C = 2. Assume that the demand function for the product is de…ned as follows: p = 100 0:5 (q1 + q2 ) : If …rm 2 sets a quantity of q2 = 100, what’s the best response quantity for …rm 1. Solution: Residual demand curve facing …rm 1 is p = 100 0:5 (q1 + 100) = 50 0:5q1 : If the marginal cost of produ ...
chap007Answers
... Briefly state the basic characteristics of pure competition. Strictly speaking, pure competition has probably never existed and probably never will. Then why study it? Pure competition has a very large number of firms; standardized products; no control over price: price takers; no obstacles to entry ...
... Briefly state the basic characteristics of pure competition. Strictly speaking, pure competition has probably never existed and probably never will. Then why study it? Pure competition has a very large number of firms; standardized products; no control over price: price takers; no obstacles to entry ...
Lecture 2 - Illinois State University
... • New resource deposits are discovered => increasing reserves • Changing price and technology can make more or less of the known reserves economically viable ...
... • New resource deposits are discovered => increasing reserves • Changing price and technology can make more or less of the known reserves economically viable ...
Review - Pareto E¢ ciency and Welfare Analysis Shih En Lu
... di¤erently about what "fair" means. However, both are desirable an e¢ cient outcome may be "worse" than a slightly ine¢ cient, but much fairer outcome. ECON 302 (SFU) ...
... di¤erently about what "fair" means. However, both are desirable an e¢ cient outcome may be "worse" than a slightly ine¢ cient, but much fairer outcome. ECON 302 (SFU) ...
Document
... payments rises. Some of the extra tax revenue raised will have to be used to fund increased social security payments rather than the public project the extra tax revenues are intended to fund. 2. Some public projects will, by their nature, cause a shift of the labour supply curve, and this may tend ...
... payments rises. Some of the extra tax revenue raised will have to be used to fund increased social security payments rather than the public project the extra tax revenues are intended to fund. 2. Some public projects will, by their nature, cause a shift of the labour supply curve, and this may tend ...
Chapter 7: Consumer Behavior - jb
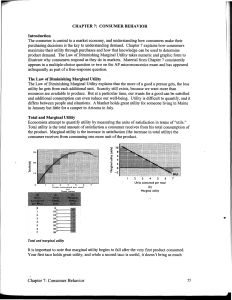
... product demand. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility takes numeric and graphic form to illustrate why consumers respond as they do in markets. Material from Chapter 7 consistently appears in a multiple-choice question or two on the AP microeconomics exam and has appeared infrequently as part of a ...
... product demand. The Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility takes numeric and graphic form to illustrate why consumers respond as they do in markets. Material from Chapter 7 consistently appears in a multiple-choice question or two on the AP microeconomics exam and has appeared infrequently as part of a ...
Module 3 Glossary Term Definition Advertising A form of non
... 1 – D: Land refers to the factors of production that are natural resources – water, wood, oil, etc. 2 – A: Capital resources are manmade tools (including buildings) created to make the business more efficient— financial, and physical. 3 – B: Entrepreneurial resources refer to the intelligence, imagi ...
... 1 – D: Land refers to the factors of production that are natural resources – water, wood, oil, etc. 2 – A: Capital resources are manmade tools (including buildings) created to make the business more efficient— financial, and physical. 3 – B: Entrepreneurial resources refer to the intelligence, imagi ...
Homework 3
... and corresponding prices, where qLH is the quantity allocated to an agent who declares L in period 1 and H in period 2. (a) Consider period t = 2. Fix the first period type, θ. Assume in period 2 that the lowtype’s (IR) constraint binds, the high type’s (IC) constraint binds and we can ignore the ot ...
... and corresponding prices, where qLH is the quantity allocated to an agent who declares L in period 1 and H in period 2. (a) Consider period t = 2. Fix the first period type, θ. Assume in period 2 that the lowtype’s (IR) constraint binds, the high type’s (IC) constraint binds and we can ignore the ot ...
Chapter 9
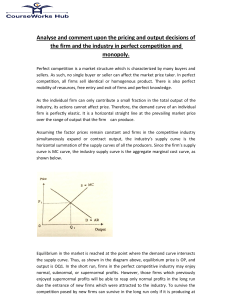
... b. Price discrimination takes place when a monopolist is faced with buyers that are widely different; therefore, the buyers' elasticity of demand for the product will be ...
... b. Price discrimination takes place when a monopolist is faced with buyers that are widely different; therefore, the buyers' elasticity of demand for the product will be ...
Economics 310 Handout 1 Professor Tom K
... An income-consumption curve is the combinations of products that are utility maximizing at different levels of income while holding all prices constant. Normal(superior) goods are goods where an increase in income would increase the demand for the goods. Inferior goods are goods where an increase in ...
... An income-consumption curve is the combinations of products that are utility maximizing at different levels of income while holding all prices constant. Normal(superior) goods are goods where an increase in income would increase the demand for the goods. Inferior goods are goods where an increase in ...
ECON 101 KONG Midterm 2 CMP Review Session
... 1. Tax on consumers, demand curve shifts down by per unit tax 2. Tax on producers, supply curve shifts up by per unit tax Big idea: consumers and producers want to be able to recreate their original condition before taxes Taxes create a NEW equilibrium that is NOT efficient Tax Incidence: how much o ...
... 1. Tax on consumers, demand curve shifts down by per unit tax 2. Tax on producers, supply curve shifts up by per unit tax Big idea: consumers and producers want to be able to recreate their original condition before taxes Taxes create a NEW equilibrium that is NOT efficient Tax Incidence: how much o ...
1 and 2, NRS 408.215
... (a) The roadway is scheduled for overlay or reconstruction within 2 years after the trenching is scheduled to begin; (b) The roadway is in such poor condition that a permanent patch of the pavement will not adversely affect the condition of the surface of the roadway; (c) The area is so congested wi ...
... (a) The roadway is scheduled for overlay or reconstruction within 2 years after the trenching is scheduled to begin; (b) The roadway is in such poor condition that a permanent patch of the pavement will not adversely affect the condition of the surface of the roadway; (c) The area is so congested wi ...