Perfect Competition Chapter 11
... • The MC curve tells the competitive firm how much it should produce at a given price. • The firm can do no better than producing the quantity at which marginal cost equals price which in turn equals marginal revenue. ...
... • The MC curve tells the competitive firm how much it should produce at a given price. • The firm can do no better than producing the quantity at which marginal cost equals price which in turn equals marginal revenue. ...
aggregate demand, aggregate supply, and modern macroeconomics
... The slope of the indifference curve is the marginal rate of substitution – the rate at which one good must be added when the other is taken away in order to keep the individual indifferent between the two combinations. Indifference curves are downward sloping and bowed inward. ...
... The slope of the indifference curve is the marginal rate of substitution – the rate at which one good must be added when the other is taken away in order to keep the individual indifferent between the two combinations. Indifference curves are downward sloping and bowed inward. ...
Answers to Micro End-of-Chapter Questions 1
... d. Obviously, tenants like cheap rent, and since there are multiple tenants per building but only one owner, the votes go to the tenants. 7. a. The limitation of medallions likely increases the price of taxi medallions because it creates a monopoly position for medallion holders. There is no threat ...
... d. Obviously, tenants like cheap rent, and since there are multiple tenants per building but only one owner, the votes go to the tenants. 7. a. The limitation of medallions likely increases the price of taxi medallions because it creates a monopoly position for medallion holders. There is no threat ...
short-run supply curve - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... includes all costs—both explicit and implicit—associated with resources used by the firm. • Accounting profit is simply total revenue less all explicit costs incurred. – does not subtract the implicit costs. ...
... includes all costs—both explicit and implicit—associated with resources used by the firm. • Accounting profit is simply total revenue less all explicit costs incurred. – does not subtract the implicit costs. ...
Chapter 3 - LRedmond
... because it indicates that supply is inelastic. Thus, sellers will be slow to increase supply to take advantage of rising prices (ex. fruits and vegetables) B) A coefficient of 1.5 is good news for sellers because it indicates that supply is elastic. Thus sellers can quickly increase supply to take a ...
... because it indicates that supply is inelastic. Thus, sellers will be slow to increase supply to take advantage of rising prices (ex. fruits and vegetables) B) A coefficient of 1.5 is good news for sellers because it indicates that supply is elastic. Thus sellers can quickly increase supply to take a ...
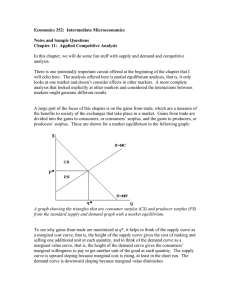
Economics 352
... Two diagram, side by side, demonstrating that the distribution of the burden of a tax depends on relative slopes of demand and supply curves. The first shows that when the demand curve is relatively steep the consumer will bear most of the burden of a tax. The second shows that when the supply curv ...
... Two diagram, side by side, demonstrating that the distribution of the burden of a tax depends on relative slopes of demand and supply curves. The first shows that when the demand curve is relatively steep the consumer will bear most of the burden of a tax. The second shows that when the supply curv ...
Price competition.
... Collusion by Repeated Interaction • Let us say that firms have a discount factor of B. • If each make 18 each period. How much is the present value? • The one period undercutting gains is close to 18. • The other firm can punish under-cutters by causing zero profit from then on. • A firm will not c ...
... Collusion by Repeated Interaction • Let us say that firms have a discount factor of B. • If each make 18 each period. How much is the present value? • The one period undercutting gains is close to 18. • The other firm can punish under-cutters by causing zero profit from then on. • A firm will not c ...
Supply and Demand - Technology Learner
... and is something that they want or need. A store’s small stock of avocadoes after bad weather in California severely damaged the crop is an example of a shortage. There are fewer avocadoes to meet customer demand, so their price is higher. Equilibrium An equilibrium situation is one in which supply ...
... and is something that they want or need. A store’s small stock of avocadoes after bad weather in California severely damaged the crop is an example of a shortage. There are fewer avocadoes to meet customer demand, so their price is higher. Equilibrium An equilibrium situation is one in which supply ...
Field 3Ce Final MS Ch04
... into the river. The wastewater is full of organic matter that arises from the process of converting wood to paper. This waste material gradually is converted to more benign materials by the natural assimilative capacity of the river water; however, before that happens, a number of people downstream ...
... into the river. The wastewater is full of organic matter that arises from the process of converting wood to paper. This waste material gradually is converted to more benign materials by the natural assimilative capacity of the river water; however, before that happens, a number of people downstream ...
Monopolistic Competition and Product Differentiation
... manufacturer can claim that its car is better than any other; this is not a statement that can be easily verified by the purchaser before purchase. However, Tiger Woods commands a very high fee for advertising. What the commercial therefore signals is something like “we can afford to pay Tiger Woods ...
... manufacturer can claim that its car is better than any other; this is not a statement that can be easily verified by the purchaser before purchase. However, Tiger Woods commands a very high fee for advertising. What the commercial therefore signals is something like “we can afford to pay Tiger Woods ...
Fall 2015 TEST 3 w/ solution
... 7. When Aishe's Bar-B-Que produces 10 pork sandwiches, the total cost is $5. When 11 pork sandwiches are produced, the total cost rises to $6. From this we know that the marginal cost of the eleventh pork sandwich: A) is equal to the average cost of 11 pork sandwiches. B) is greater than the averag ...
... 7. When Aishe's Bar-B-Que produces 10 pork sandwiches, the total cost is $5. When 11 pork sandwiches are produced, the total cost rises to $6. From this we know that the marginal cost of the eleventh pork sandwich: A) is equal to the average cost of 11 pork sandwiches. B) is greater than the averag ...
Valuing the Future: OMB's Refined Position
... the floor of the U.S. Senate, once in 2003, 108th Cong, 1st Sess, in 149 Cong Rec S 13598 (Oct 30, 2003), and again in 2005, Roll Call Vote No 148, 109th Cong, 1st Sess, in 151 Cong Rec S 7029 (Jun 22, 2005). Concerns about adverse economic impacts were cited by opponents in both floor debates. See, ...
... the floor of the U.S. Senate, once in 2003, 108th Cong, 1st Sess, in 149 Cong Rec S 13598 (Oct 30, 2003), and again in 2005, Roll Call Vote No 148, 109th Cong, 1st Sess, in 151 Cong Rec S 7029 (Jun 22, 2005). Concerns about adverse economic impacts were cited by opponents in both floor debates. See, ...