File
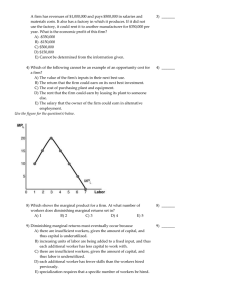
... in her market, based on relationships between consumers’ spending habits and current cappuccino prices. d. The market supply schedule would help Lily determine the lowest possible price she should ask for a cappuccino, based on the current year-end sales at the top-selling coffee shops in her area. ...
... in her market, based on relationships between consumers’ spending habits and current cappuccino prices. d. The market supply schedule would help Lily determine the lowest possible price she should ask for a cappuccino, based on the current year-end sales at the top-selling coffee shops in her area. ...
Choice, Change, Challenge, and Opportunity
... Different decisions appear to activate different areas of the brain. Some decisions are made In the pre-frontal cortex where memories are stored and data analyzed and might be deemed rational. In the hippocampus where memories of anxiety and fear are stored and might be deemed irrational. © 2010 Pea ...
... Different decisions appear to activate different areas of the brain. Some decisions are made In the pre-frontal cortex where memories are stored and data analyzed and might be deemed rational. In the hippocampus where memories of anxiety and fear are stored and might be deemed irrational. © 2010 Pea ...
Assignment Guide
... 2) Explain why the marginal revenue curve for a monopolist lies below the demand curve when plotted on a graph. 3) Calculate marginal revenue from a schedule of output and total revenue, and plot marginal revenue and price. 4) Explain why a monopoly firm should never operate on the inelastic portion ...
... 2) Explain why the marginal revenue curve for a monopolist lies below the demand curve when plotted on a graph. 3) Calculate marginal revenue from a schedule of output and total revenue, and plot marginal revenue and price. 4) Explain why a monopoly firm should never operate on the inelastic portion ...
Lecture 04.2b
... • Marginal cost curve will cut the average cost curve at its lowest point. • In a perfectly competitive market a firm's profit maximizing price would be above the price at which the average cost curve cuts the marginal cost curve. – If the marginal revenue is above the average total cost price the f ...
... • Marginal cost curve will cut the average cost curve at its lowest point. • In a perfectly competitive market a firm's profit maximizing price would be above the price at which the average cost curve cuts the marginal cost curve. – If the marginal revenue is above the average total cost price the f ...
Document
... To get the process going, suppose you start off spending your entire budget of $40 on pizza 5 pizzas per week at a total utility of 142. If you give up one pizza, you free up enough money to rent 2 videos. Would total utility increase from this reallocation? You give up 12 units of utility – the m ...
... To get the process going, suppose you start off spending your entire budget of $40 on pizza 5 pizzas per week at a total utility of 142. If you give up one pizza, you free up enough money to rent 2 videos. Would total utility increase from this reallocation? You give up 12 units of utility – the m ...
Example: PPC (Production Possibilities Curve)
... causes higher judgments should unemployment, be therefore it should be eliminated ...
... causes higher judgments should unemployment, be therefore it should be eliminated ...
AP Microecnomics
... • Messy and illegible….really messy and really illegible….graphs • Use proper terms • Track answer format to question format • Answer questions in any order ...
... • Messy and illegible….really messy and really illegible….graphs • Use proper terms • Track answer format to question format • Answer questions in any order ...
Shifts of the Supply Curve
... different. • When marginal product is decreasing but still positive, hiring additional workers causes total out to ...
... different. • When marginal product is decreasing but still positive, hiring additional workers causes total out to ...
Choice, Change, Challenge, and Opportunity
... Different decisions appear to activate different areas of the brain. Some decisions are made In the pre-frontal cortex where memories are stored and data analyzed and might be deemed rational. In the hippocampus where memories of anxiety and fear are stored and might be deemed irrational. © 2010 Pea ...
... Different decisions appear to activate different areas of the brain. Some decisions are made In the pre-frontal cortex where memories are stored and data analyzed and might be deemed rational. In the hippocampus where memories of anxiety and fear are stored and might be deemed irrational. © 2010 Pea ...
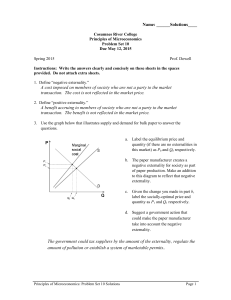
Problem Set 10 Solutions
... the skills generate a greater marginal revenue product of labor (MRPL) and consequently command a higher wage in the labor market. b. Human Capital Increased human capital increases a persons marginal product and hence their MRPL, resulting in a higher wage. c. Working Conditions For jobs with undes ...
... the skills generate a greater marginal revenue product of labor (MRPL) and consequently command a higher wage in the labor market. b. Human Capital Increased human capital increases a persons marginal product and hence their MRPL, resulting in a higher wage. c. Working Conditions For jobs with undes ...
Economics 101 L
... a) Is a firm in a competitive industry considered a price taker or a price setter? Explain what this means. Price taker. This means that the firm does not have any power to set the price for the good in the market. Whatever price the market determines is the price that the firm must charge. b) Is a ...
... a) Is a firm in a competitive industry considered a price taker or a price setter? Explain what this means. Price taker. This means that the firm does not have any power to set the price for the good in the market. Whatever price the market determines is the price that the firm must charge. b) Is a ...