Synaptic Transmisson
... 3. Block reuptake or block receptors 4. Produce more or less neurotransmitter 5. Prevent vesicles from releasing neurotransmitter ...
... 3. Block reuptake or block receptors 4. Produce more or less neurotransmitter 5. Prevent vesicles from releasing neurotransmitter ...
Mudpacking - Wellness Essentials, LLC
... injuries, broken bones, burns, falls, tattoos, piercings, deployed airbags, and any kind of scarcreating event including punctures, cuts, and surgeries. For example, an abdominal trauma from a c-section, appendectomy, car accident or sports injury may be sedating the digestive system and/or adrenal ...
... injuries, broken bones, burns, falls, tattoos, piercings, deployed airbags, and any kind of scarcreating event including punctures, cuts, and surgeries. For example, an abdominal trauma from a c-section, appendectomy, car accident or sports injury may be sedating the digestive system and/or adrenal ...
Lecture 7 Powerpoint file
... Neurons are Electrical • Importantly, we think the electrical signals are fundamental to brain function, so it makes sense that we should try to directly measure these signals – but how? ...
... Neurons are Electrical • Importantly, we think the electrical signals are fundamental to brain function, so it makes sense that we should try to directly measure these signals – but how? ...
9-Lecture1(updated)
... They are more neurons in human brain than they are bits in computers Human brain is evolving very slowly---computer memories are growing rapidly. There are a lot more neurons than we can reasonably model in modern digital computers, and they all fire in parallel NN running on a serial computer requi ...
... They are more neurons in human brain than they are bits in computers Human brain is evolving very slowly---computer memories are growing rapidly. There are a lot more neurons than we can reasonably model in modern digital computers, and they all fire in parallel NN running on a serial computer requi ...
Some text - (canvas.brown.edu).
... On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In the middle are different types of neurons. One is a sensory neuron, one is a motorneuron, and there is also one each of an excitatory and inhibitory interneuron. Excitatory neurot ...
... On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In the middle are different types of neurons. One is a sensory neuron, one is a motorneuron, and there is also one each of an excitatory and inhibitory interneuron. Excitatory neurot ...
Respiratory Regulation - Warner Pacific College
... When the lungs become inflated, stretch receptors activate a feedback that ”switches off” the respirator ramp and stop further inspiration ○ can also increase the rate of respiration Not activated until tidal volume increases Can appear to be a protective mechanism for preventing lung inflation ...
... When the lungs become inflated, stretch receptors activate a feedback that ”switches off” the respirator ramp and stop further inspiration ○ can also increase the rate of respiration Not activated until tidal volume increases Can appear to be a protective mechanism for preventing lung inflation ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 5.6 The voltage-clamp technique keeps the voltage across the membrane constant so that the amplitude and time course of ionic currents can be measured. In the two-electrode voltage-clamp technique, one electrode measures the voltage across the membrane while the other injects current into th ...
... FIGURE 5.6 The voltage-clamp technique keeps the voltage across the membrane constant so that the amplitude and time course of ionic currents can be measured. In the two-electrode voltage-clamp technique, one electrode measures the voltage across the membrane while the other injects current into th ...
Neurons Excitatory vs Inhibitory Neurons The Neuron and its Ions
... Inet = gN am3h(Vm − EN a) + gk n4(Vm − Ek ) + (Vm − El ) m, h, n: voltage gating variables with their own dynamics that determine when channels open and close • Bias weight ...
... Inet = gN am3h(Vm − EN a) + gk n4(Vm − Ek ) + (Vm − El ) m, h, n: voltage gating variables with their own dynamics that determine when channels open and close • Bias weight ...
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of
... Simulation 1 – Neurophysiological Properties of the Neuron You now have at least a working knowledge of action-potential generation in the squid giant axon. Early investigators of the mammalian brain imagined that the central nervous system (CNS) consisted of a complex interconnected network of neur ...
... Simulation 1 – Neurophysiological Properties of the Neuron You now have at least a working knowledge of action-potential generation in the squid giant axon. Early investigators of the mammalian brain imagined that the central nervous system (CNS) consisted of a complex interconnected network of neur ...
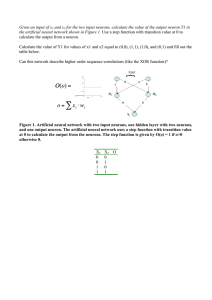
Given an input of x1 and x2 for the two input neurons, calculate the
... the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out the table below. Can this network describe higher order sequen ...
... the artificial neural network shown in Figure 1. Use a step function with transition value at 0 to calculate the output from a neuron. Calculate the value of Y1 for values of x1 and x2 equal to (0,0), (1,1), (1,0), and (0,1) and fill out the table below. Can this network describe higher order sequen ...
Cell Structure and Function
... together to perform a specific function. Each organ system has its own function but the systems work together and depend on one another. There are eleven different organ systems in the human body: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune, integumentary (skin), muscular, ner ...
... together to perform a specific function. Each organ system has its own function but the systems work together and depend on one another. There are eleven different organ systems in the human body: circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune, integumentary (skin), muscular, ner ...
Inhibitory Control of Hippocampal Inhibitory Neurons
... fire, pyramidal cells are inhibited and these pyramidal cells are allowed to fire again when they do not get inhibiting signals. A single perisomatic neuron (baskell cell or axo-axonic cell) innervates around a thousand pyramidal cells. On the other hand, these inhibitory cells are orchestrated by i ...
... fire, pyramidal cells are inhibited and these pyramidal cells are allowed to fire again when they do not get inhibiting signals. A single perisomatic neuron (baskell cell or axo-axonic cell) innervates around a thousand pyramidal cells. On the other hand, these inhibitory cells are orchestrated by i ...
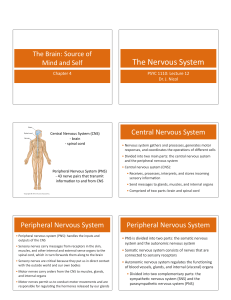
The Nervous System
... muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spinal cord, which in turn forwards them along to the brain • Sensory nerves are criJcal because they put us in direct contact with the ...
... muscles, and other internal and external sense organs to the spinal cord, which in turn forwards them along to the brain • Sensory nerves are criJcal because they put us in direct contact with the ...
Chapter Three - New Providence School District
... A nenron passes its message on to another neuron by releasing a chemical messenger into the gap or that separates it from other neurons, The sending neuron, called the releases a chemical messenger into the synaptic cleft, which then excites the neuron. ...
... A nenron passes its message on to another neuron by releasing a chemical messenger into the gap or that separates it from other neurons, The sending neuron, called the releases a chemical messenger into the synaptic cleft, which then excites the neuron. ...
Wallin_Back_to_School_with_the_Thinking_Maps
... • Dendrite: Gathers chemicals in brain fluid. It is continually looking to make connections with other neurons. The dendrite REACHES to other neurons to make connections as it SLURPS up information! BUMP! • Cell Body: Converts chemicals into an electrical charge. They ...
... • Dendrite: Gathers chemicals in brain fluid. It is continually looking to make connections with other neurons. The dendrite REACHES to other neurons to make connections as it SLURPS up information! BUMP! • Cell Body: Converts chemicals into an electrical charge. They ...
Brain Maps – The Sensory Homunculus
... Today you will explore brain mapping in a very personal way. Each of you will create your own individual homunculus. To do this, you first will make a tool to measure the density of touch receptors on your skin. Then, you will use this tool to estimate the receptor density on various regions of your ...
... Today you will explore brain mapping in a very personal way. Each of you will create your own individual homunculus. To do this, you first will make a tool to measure the density of touch receptors on your skin. Then, you will use this tool to estimate the receptor density on various regions of your ...
Release of Acetylcholine: Signal at nerve terminal causes CA2+
... affinity, Na+- dependant, ATP requiring process. It is co-transported with Na+, and ATP is required to “pump” Na+ cations out of the neurones. This is a rate-limiting step for acetylcholine by: choline acetyl transferase. - Acetyl COA comes from citrate cleavage into acetyl COA + OX.A.A. It reacts ...
... affinity, Na+- dependant, ATP requiring process. It is co-transported with Na+, and ATP is required to “pump” Na+ cations out of the neurones. This is a rate-limiting step for acetylcholine by: choline acetyl transferase. - Acetyl COA comes from citrate cleavage into acetyl COA + OX.A.A. It reacts ...
Brain Maps – The Sensory Homunculus
... Today you will explore brain mapping in a very personal way. Each of you will create your own individual homunculus. To do this, you first will make a tool to measure the density of touch receptors on your skin. Then, you will use this tool to estimate the receptor density on various regions of your ...
... Today you will explore brain mapping in a very personal way. Each of you will create your own individual homunculus. To do this, you first will make a tool to measure the density of touch receptors on your skin. Then, you will use this tool to estimate the receptor density on various regions of your ...
Neural Basis of the Ventriloquist
... ElectroEncephaloGraphy (EEG) Neurons use electrical potentials to communicate Multiple, aligned, synchronously-firing neurons produce enough voltage change to be read by electrodes on the scalp. ...
... ElectroEncephaloGraphy (EEG) Neurons use electrical potentials to communicate Multiple, aligned, synchronously-firing neurons produce enough voltage change to be read by electrodes on the scalp. ...
The Auditory System
... (b) secondary somatosensory cortex (SII): Bilateral processing. (d) somatosensory association cortex (posterior parietal lobe): Vision and touch, as illustrated by “asomatognosia.” ...
... (b) secondary somatosensory cortex (SII): Bilateral processing. (d) somatosensory association cortex (posterior parietal lobe): Vision and touch, as illustrated by “asomatognosia.” ...
ES145 - Systems Analysis & Physiology
... He found that stimulation of points in the temporal lobe produced vivid childhood memories, or pieces of old musical tunes. A 21 year old man reported: “It was like standing in the doorway at [my] high school. I heard my mother talking on the phone, telling my aunt to come over that night.” Another ...
... He found that stimulation of points in the temporal lobe produced vivid childhood memories, or pieces of old musical tunes. A 21 year old man reported: “It was like standing in the doorway at [my] high school. I heard my mother talking on the phone, telling my aunt to come over that night.” Another ...
In The Name of Allah The Most Beneficent The
... Neuromuscular System (Peripheral Nerves, come from the spinal cord to control the muscles of the limbs) The junction between the peripheral nerve and the muscles is called the neuromuscular junction. ...
... Neuromuscular System (Peripheral Nerves, come from the spinal cord to control the muscles of the limbs) The junction between the peripheral nerve and the muscles is called the neuromuscular junction. ...
Chapter 27 - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... – Gather information - This is how any organism detects information from the outside world to integrate it into the brain (if present) and determine if a response is necessary. – It is essential for homeostasis ...
... – Gather information - This is how any organism detects information from the outside world to integrate it into the brain (if present) and determine if a response is necessary. – It is essential for homeostasis ...
Stimulus (physiology)
In physiology, a stimulus (plural stimuli) is a detectable change in the internal or external environment. The ability of an organism or organ to respond to external stimuli is called sensitivity. When a stimulus is applied to a sensory receptor, it normally elicits or influences a reflex via stimulus transduction. These sensory receptors can receive information from outside the body, as in touch receptors found in the skin or light receptors in the eye, as well as from inside the body, as in chemoreceptors and mechanorceptors. An internal stimulus is often the first component of a homeostatic control system. External stimuli are capable of producing systemic responses throughout the body, as in the fight-or-flight response. In order for a stimulus to be detected with high probability, its level must exceed the absolute threshold; if a signal does reach threshold, the information is transmitted to the central nervous system (CNS), where it is integrated and a decision on how to react is made. Although stimuli commonly cause the body to respond, it is the CNS that finally determines whether a signal causes a reaction or not.