PPT
... Inhibition effect extends beyond elimination of drug due to enzyme inactivation. Effect tends to accumulate after each dose. Inhibition effect is generally greater than predicted based on ‘reversible’ IC50 or Ki values. Most compounds will have non-linear pharmacokinetics. Rare cases of hepatotoxici ...
... Inhibition effect extends beyond elimination of drug due to enzyme inactivation. Effect tends to accumulate after each dose. Inhibition effect is generally greater than predicted based on ‘reversible’ IC50 or Ki values. Most compounds will have non-linear pharmacokinetics. Rare cases of hepatotoxici ...
8th Lecture 1433
... Some capsules and tablets contain sustained-release drugs, which dissolve over an extended period of time. Administration of oral drugs is relatively easy for patients who are alert and can swallow (can not be used in unconscious patients). Certain drugs are given by the sublingual (placed und ...
... Some capsules and tablets contain sustained-release drugs, which dissolve over an extended period of time. Administration of oral drugs is relatively easy for patients who are alert and can swallow (can not be used in unconscious patients). Certain drugs are given by the sublingual (placed und ...
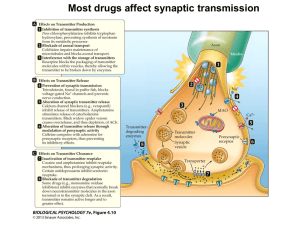
Fig 4.9a Synaptic Transmission
... – nicotinic receptors on the actual dopaminergic neuron when nicotine binds to that receptor, it turns the dopamine cell on – nicotine stimulates glutamatergic inputs, which are excitatory on the dopamine neuron which leads to more dopamine being released – nicotine stimulates GABAergic neurons • Wh ...
... – nicotinic receptors on the actual dopaminergic neuron when nicotine binds to that receptor, it turns the dopamine cell on – nicotine stimulates glutamatergic inputs, which are excitatory on the dopamine neuron which leads to more dopamine being released – nicotine stimulates GABAergic neurons • Wh ...
Drug interactions
... The risk of drug interactions increases with the number of drugs used. The rate of ADR in patients taking 6–10 drugs was 7%, rising to 40% in those taking 16–20 drugs, with the exponential rise being largely attributable to drug interactions. In a high-risk group of emergency department patients, th ...
... The risk of drug interactions increases with the number of drugs used. The rate of ADR in patients taking 6–10 drugs was 7%, rising to 40% in those taking 16–20 drugs, with the exponential rise being largely attributable to drug interactions. In a high-risk group of emergency department patients, th ...
Substance Abuse
... the APA as those listed above including at least 3 of the following in a 12 month period:. 1. Tolerance-need more of the drug to produce desired effect 2. Withdrawal-occurs when they stop using, must take the drug or alcohol to avoid these symptoms 3. Use larger amounts of the drug 4. Would ...
... the APA as those listed above including at least 3 of the following in a 12 month period:. 1. Tolerance-need more of the drug to produce desired effect 2. Withdrawal-occurs when they stop using, must take the drug or alcohol to avoid these symptoms 3. Use larger amounts of the drug 4. Would ...
INSILICO APPROACHES TOWARDS THE DRUG TARGET AURORKINASES USING THE ORTHO
... amino acid. The structure based drug designing is employed when both leads compounds and drug target protein are known for molecular docking. It is an iterative process to dock the lead compounds with specific site of the drug target protein. The active site of the protein is defined the crucial ami ...
... amino acid. The structure based drug designing is employed when both leads compounds and drug target protein are known for molecular docking. It is an iterative process to dock the lead compounds with specific site of the drug target protein. The active site of the protein is defined the crucial ami ...
Antimicrobial Agents
... – Mostly target the folic acid synthesis pathway – Many bacteria can and do synthesize a large proportion of needed cofactors – Humans require folic acid in the diet (a “vitamin”), thus folic acid synthesizing enzymes are not an available target in humans • Selectively toxic ...
... – Mostly target the folic acid synthesis pathway – Many bacteria can and do synthesize a large proportion of needed cofactors – Humans require folic acid in the diet (a “vitamin”), thus folic acid synthesizing enzymes are not an available target in humans • Selectively toxic ...
Mr. Steve Lee V. P. Technical Affairs
... glucose-induced insulin release.” In the preamble to the January 6,200O final rule on structure/function claims (see 65 FR 1000 at 1018), FDA stated that claims about the maintenance of normal cholesterol levels did not necessarily constitute implied disease claims. We stated, however, that because ...
... glucose-induced insulin release.” In the preamble to the January 6,200O final rule on structure/function claims (see 65 FR 1000 at 1018), FDA stated that claims about the maintenance of normal cholesterol levels did not necessarily constitute implied disease claims. We stated, however, that because ...
STATEMENT OF JOHN ERICKSON, PhD
... infections with an emphasis on HIV/AIDS. I am also the Founder of the Institute for Global Therapeutics, a non-profit, 501(c)(3) organization founded by my wife and I to develop safe, effective and affordable new therapeutic approaches to combating drug resistant infections, with an emphasis on HIV/ ...
... infections with an emphasis on HIV/AIDS. I am also the Founder of the Institute for Global Therapeutics, a non-profit, 501(c)(3) organization founded by my wife and I to develop safe, effective and affordable new therapeutic approaches to combating drug resistant infections, with an emphasis on HIV/ ...
Document
... utilization of drugs properly and protecting the public from exposure to unnecessary drug residues. Drugs should be used only when required at the required amount and combination. Improper use of drugs may result in ineffective treatment, unnecessary wastage of resources, and may harm the patient. I ...
... utilization of drugs properly and protecting the public from exposure to unnecessary drug residues. Drugs should be used only when required at the required amount and combination. Improper use of drugs may result in ineffective treatment, unnecessary wastage of resources, and may harm the patient. I ...
Molecular imprinting - Utrecht University Repository
... main product lines focusing on compound extraction (MIP4SPE1, molecularly imprinted polymers for solid phase extraction) and separation (MIP4LC1, for HPLC). Enantiomeric separation of chiral molecules by HPLC has proven possible with MIPs as the stationary phase [11], and even separation of proteins ...
... main product lines focusing on compound extraction (MIP4SPE1, molecularly imprinted polymers for solid phase extraction) and separation (MIP4LC1, for HPLC). Enantiomeric separation of chiral molecules by HPLC has proven possible with MIPs as the stationary phase [11], and even separation of proteins ...
Prescription Drugs More Likely to Kill You than Recreational Drugs
... Chantix even out-harms the addictive troublemaker oxycodone, a potent pain medication. While an estimated 3.5 million Chantix prescriptions have been written since its FDA approval in May 2006, government estimates place oxycodone prescriptions written at more than 7 million per year. Yet despite ha ...
... Chantix even out-harms the addictive troublemaker oxycodone, a potent pain medication. While an estimated 3.5 million Chantix prescriptions have been written since its FDA approval in May 2006, government estimates place oxycodone prescriptions written at more than 7 million per year. Yet despite ha ...
Med Drugs 8 Keynote
... The two “mirror image” molecules are called enantiomers. They occur whenever there are four different groups bonded to a carbon atom (the “chiral carbon atom”). ...
... The two “mirror image” molecules are called enantiomers. They occur whenever there are four different groups bonded to a carbon atom (the “chiral carbon atom”). ...
The Psychology and Physiology of Street Drugs Amie J. Hatch
... Impervious to pain, making them difficult to restrain and control Toxicology Rounds: Dangerous new drugs hit the streetsand the ED. Emergency Medicine News.2014;36:27 ...
... Impervious to pain, making them difficult to restrain and control Toxicology Rounds: Dangerous new drugs hit the streetsand the ED. Emergency Medicine News.2014;36:27 ...
Outline
... 1. Selectivity/specificity 2. Subject to competition/ inhibition/ antagonism Where Ex. Isoniazid (anti-TB drug) is associated with a A= surface area side-effect – peripheral neuropathy, which can (C1 – C2)=concentration gradient/difference be resolved by Vitamin B6. They have similarity h=thickness ...
... 1. Selectivity/specificity 2. Subject to competition/ inhibition/ antagonism Where Ex. Isoniazid (anti-TB drug) is associated with a A= surface area side-effect – peripheral neuropathy, which can (C1 – C2)=concentration gradient/difference be resolved by Vitamin B6. They have similarity h=thickness ...
Microbiology- Ch. 12- Antimicrobial Therapy
... • Antimicrobial drugs should be selectively toxic - drugs should kill or inhibit microbial cells without simultaneously damaging host tissues. • As the characteristics of the infectious agent become more similar to the vertebrate host cell, complete selective toxicity becomes more difficult to achie ...
... • Antimicrobial drugs should be selectively toxic - drugs should kill or inhibit microbial cells without simultaneously damaging host tissues. • As the characteristics of the infectious agent become more similar to the vertebrate host cell, complete selective toxicity becomes more difficult to achie ...
John Nagelhout
... Phenytoin is an example of a drug that obeys Michaelis-Menten rather than first-order pharmacokinetics. In this case, as plasma concentration increases, the clearance decreases and the half-life becomes longer. Cytochrome P450 is a generic term for the group of enzymes that are responsible for most ...
... Phenytoin is an example of a drug that obeys Michaelis-Menten rather than first-order pharmacokinetics. In this case, as plasma concentration increases, the clearance decreases and the half-life becomes longer. Cytochrome P450 is a generic term for the group of enzymes that are responsible for most ...
BIOM 255: Molecular basis of drug action and disease therapy
... vaccinations) has been a major factor that has increased life span and improved the quality of life – New scientific insights—in some cases, inferred from novel mechanisms of action– have been essential to this progress, together with controlled clinical trials, in particular, randomized, double-bli ...
... vaccinations) has been a major factor that has increased life span and improved the quality of life – New scientific insights—in some cases, inferred from novel mechanisms of action– have been essential to this progress, together with controlled clinical trials, in particular, randomized, double-bli ...
DOC
... The inter-individual variability in xenobiotic metabolism and drug response is extensive. The drug level in plasma can vary more than 1000-fold between two individuals having the same weight and with the same drug dosage. The causes for this variation are of genetic, physiological, pathophysiologica ...
... The inter-individual variability in xenobiotic metabolism and drug response is extensive. The drug level in plasma can vary more than 1000-fold between two individuals having the same weight and with the same drug dosage. The causes for this variation are of genetic, physiological, pathophysiologica ...
SUSTAINED RELAEASE MULTIPARTICULATE DRUG DELIVERY
... of the drug since multiparticulates are known to disperse freely in the gastric fluids covering greater surface of absorption. In addition they also offer benefits of reducing the dose required, and providing uniform drug delivery. So in the present study, attempts will be made to establish a optimu ...
... of the drug since multiparticulates are known to disperse freely in the gastric fluids covering greater surface of absorption. In addition they also offer benefits of reducing the dose required, and providing uniform drug delivery. So in the present study, attempts will be made to establish a optimu ...
Answer Key of MCQ of AMO Exam
... 1. Total 110 multiple choice questions are provided out of which any 80 questions will have to be answered. Each question carries one mark. 2. No provision of negative marking. 3. Total 07 short answer questions (to be answered maximum in 75 words) out of which any 04 Questions will have to be answe ...
... 1. Total 110 multiple choice questions are provided out of which any 80 questions will have to be answered. Each question carries one mark. 2. No provision of negative marking. 3. Total 07 short answer questions (to be answered maximum in 75 words) out of which any 04 Questions will have to be answe ...
introduction to drug discovery
... the early 1990's it was believed that combinatorial chemistry would revolutionize the drug discovery industry. Ten years later the route from design and synthesis of compound libraries to identification of lead structures is still long and costly. Synthesis of an almost unlimited number of organic c ...
... the early 1990's it was believed that combinatorial chemistry would revolutionize the drug discovery industry. Ten years later the route from design and synthesis of compound libraries to identification of lead structures is still long and costly. Synthesis of an almost unlimited number of organic c ...
The Use of Ontologies in Drug Discovery
... are created using Protégé as the ontology development tool, but are exported from this environment into a relational database, for use in information retrieval. Because of the dynamic nature of the language used in the life sciences, automated methods for updating the ontologies and synonyms knowled ...
... are created using Protégé as the ontology development tool, but are exported from this environment into a relational database, for use in information retrieval. Because of the dynamic nature of the language used in the life sciences, automated methods for updating the ontologies and synonyms knowled ...
Drug design
Drug design, sometimes referred to as rational drug design or simply rational design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which in turn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. In the most basic sense, drug design involves the design of molecules that are complementary in shape and charge to the biomolecular target with which they interact and therefore will bind to it. Drug design frequently but not necessarily relies on computer modeling techniques. This type of modeling is often referred to as computer-aided drug design. Finally, drug design that relies on the knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the biomolecular target is known as structure-based drug design. In addition to small molecules, biopharmaceuticals and especially therapeutic antibodies are an increasingly important class of drugs and computational methods for improving the affinity, selectivity, and stability of these protein-based therapeutics have also been developed.The phrase ""drug design"" is to some extent a misnomer. A more accurate term is ligand design (i.e., design of a molecule that will bind tightly to its target). Although design techniques for prediction of binding affinity are reasonably successful, there are many other properties, such as bioavailability, metabolic half-life, side effects, etc., that first must be optimized before a ligand can become a safe and efficacious drug. These other characteristics are often difficult to predict with rational design techniques. Nevertheless, due to high attrition rates, especially during clinical phases of drug development, more attention is being focused early in the drug design process on selecting candidate drugs whose physicochemical properties are predicted to result in fewer complications during development and hence more likely to lead to an approved, marketed drug. Furthermore, in vitro experiments complemented with computation methods are increasingly used in early drug discovery to select compounds with more favorable ADME (absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion) and toxicological profiles.