A Design Pattern Language for Engineering (Parallel) Software
... Our Pattern Language Software architecture defines the components that make up a software system, the roles played by those components, and how they interact. Good software architecture makes design choices explicit and the critical issues addressed by a solution clear. A software architecture is hi ...
... Our Pattern Language Software architecture defines the components that make up a software system, the roles played by those components, and how they interact. Good software architecture makes design choices explicit and the critical issues addressed by a solution clear. A software architecture is hi ...
Experience with Distributed Programming in Orca,
... Other differences between the two models are the way shared data are addressed and modified. Data in Tuple Space are addressed associatively and are modified by first taking them out of Tuple Space, then modifying them, and then putting them back. In our model, shared objects are addressed and modif ...
... Other differences between the two models are the way shared data are addressed and modified. Data in Tuple Space are addressed associatively and are modified by first taking them out of Tuple Space, then modifying them, and then putting them back. In our model, shared objects are addressed and modif ...
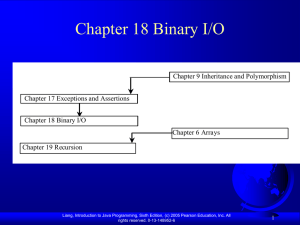
Chapter 18 Binary I/O
... non-serializable instance data fields, can the object be serialized? The answer is no. To enable the object to be serialized, you can use the transient keyword to mark these data fields to tell the JVM to ignore these fields when writing the object to an object stream. ...
... non-serializable instance data fields, can the object be serialized? The answer is no. To enable the object to be serialized, you can use the transient keyword to mark these data fields to tell the JVM to ignore these fields when writing the object to an object stream. ...
Dynamically Parameterized Architectures for Power Aware Video
... Compilation: especially Partitioning, Mapping ...
... Compilation: especially Partitioning, Mapping ...