Supporting Cells - Net Start Class
... serves as points along the neuron for generating a signal signals jumping from node to node travel hundreds of times faster than signals traveling along the surface of the axon. allows your brain to communicate with your toes in a few thousandths of a second. ► Insulation permits the nervous s ...
... serves as points along the neuron for generating a signal signals jumping from node to node travel hundreds of times faster than signals traveling along the surface of the axon. allows your brain to communicate with your toes in a few thousandths of a second. ► Insulation permits the nervous s ...
Document
... __C__1. The brain and the spinal cord are the a. peripheral nervous system c. central nervous system b. sympathetic nervous system d. parasympathetic nervous system __C__2. What is the basic functional unit of the nervous system? a. cell body b. reflex arc c. neuron d. neutron __A__3. Which of the f ...
... __C__1. The brain and the spinal cord are the a. peripheral nervous system c. central nervous system b. sympathetic nervous system d. parasympathetic nervous system __C__2. What is the basic functional unit of the nervous system? a. cell body b. reflex arc c. neuron d. neutron __A__3. Which of the f ...
Multiscale Approach to Neural Tissue Modeling
... In the talk a multiscale model of neural tissue will be presented. The neural tissue is usually modeled in different areas. In the microscopic approach the tissue is modeled on a cellular or ion channels level. On the macroscopic level the tissue parameters are averaged over large domains representi ...
... In the talk a multiscale model of neural tissue will be presented. The neural tissue is usually modeled in different areas. In the microscopic approach the tissue is modeled on a cellular or ion channels level. On the macroscopic level the tissue parameters are averaged over large domains representi ...
Cell types: Muscle cell Adipocyte Liver cell Pancreatic cell Example
... dependent fashion, assembles Apaf-1 (apoptotic protease-activating factor 1; the specific adaptor of caspase 9) and pro-caspase 9 into the apoptosome where caspase 9 dimerizes, resulting in a conformational change and caspase 9 activation. On the right-hand side of the Figure is the extrinsic pathw ...
... dependent fashion, assembles Apaf-1 (apoptotic protease-activating factor 1; the specific adaptor of caspase 9) and pro-caspase 9 into the apoptosome where caspase 9 dimerizes, resulting in a conformational change and caspase 9 activation. On the right-hand side of the Figure is the extrinsic pathw ...
WARM UP 3/4 - KENYON'S CLASS
... magnified, music sounds better, hearing is altered, vision can be enhanced or blurred. •Our perception of time can be affected. •Thought processes are affected: poor short term memory, alternating inability to focus and enhanced ability to focus, reduced ability to learn •Other effects would include ...
... magnified, music sounds better, hearing is altered, vision can be enhanced or blurred. •Our perception of time can be affected. •Thought processes are affected: poor short term memory, alternating inability to focus and enhanced ability to focus, reduced ability to learn •Other effects would include ...
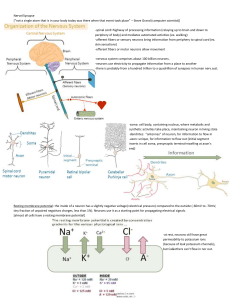
List of vocabulary used in understanding the nervous
... Feedback loops are the means through which the nervous system uses the endocrine system to regulate body conditions. The presence or absence of hormones in blood brought to the brain by the circulatory system will trigger an attempt to regulate conditions in the body. A relevant feedback loops invol ...
... Feedback loops are the means through which the nervous system uses the endocrine system to regulate body conditions. The presence or absence of hormones in blood brought to the brain by the circulatory system will trigger an attempt to regulate conditions in the body. A relevant feedback loops invol ...
Neurotransmission Notes
... The sending neuron reabsorbs any excess NT’s left in the synapse. This is called reuptake. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory (causing EPSP’s or excitatory post-synaptic potential) or inhibitory (causing IPSPs or inhibitory post-synaptic potential). Excitatory NTs bring the dendrite closer to thres ...
... The sending neuron reabsorbs any excess NT’s left in the synapse. This is called reuptake. Neurotransmitters can be excitatory (causing EPSP’s or excitatory post-synaptic potential) or inhibitory (causing IPSPs or inhibitory post-synaptic potential). Excitatory NTs bring the dendrite closer to thres ...
General_Psychology_files/Chapter Two Part One2014 - K-Dub
... Like a gun, it either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
... Like a gun, it either fires or it doesn’t; more stimulation does nothing. This is known as the “all-ornone” response. ...
This guided reading is a hybrid of two chapters: chapter 40, section
... Though we will cover all of chapter 40, we will return to sections 2-4 at a later date. ...
... Though we will cover all of chapter 40, we will return to sections 2-4 at a later date. ...
chapter_8_powerpoint_le07
... The brain carries out calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the ...
... The brain carries out calculations at synapses, the sites at which neurons interact. While hundreds of neurotransmitters and receptors have been identified, they can be functionally classified into two types: excitatory and inhibitory. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the likelihood that the ...
Name Date ______ Nervous System and Endocrine System Exam
... 2. The electrochemical message that travels through the nervous system is called an ____________________. 3. The change in the environment that starts an impulse in a receptor is called a ___________________________. 4. The structure that detects a stimulus is called a _____________________________. ...
... 2. The electrochemical message that travels through the nervous system is called an ____________________. 3. The change in the environment that starts an impulse in a receptor is called a ___________________________. 4. The structure that detects a stimulus is called a _____________________________. ...
Tutorial 5: Sodium and Potassium Gradients at Rest
... rest. This resting membrane potential of -70 millivolts (mV) is due to the difference in electrical charge found on the inside of the cell versus the outside of the cell, and is similar to the electrical condition found in a battery. The potential inside a neuron is approximately 70 mV less than tha ...
... rest. This resting membrane potential of -70 millivolts (mV) is due to the difference in electrical charge found on the inside of the cell versus the outside of the cell, and is similar to the electrical condition found in a battery. The potential inside a neuron is approximately 70 mV less than tha ...
doc Nerve and synapses
... tiny fraction of unpaired negatives charges, less than 1%). Neurons use it as a starting point for propagating electrical signals. [almost all cells have a resting membrane potential] ...
... tiny fraction of unpaired negatives charges, less than 1%). Neurons use it as a starting point for propagating electrical signals. [almost all cells have a resting membrane potential] ...
neuron
... • axon: the long, cable-like extension that delivers messages to other neurons • myelin sheath: layer of fatty tissue that insulates the axon and helps speed up message transmission – multiple sclerosis: deterioration of myelin leads to slowed communication with muscles and impaired sensation in lim ...
... • axon: the long, cable-like extension that delivers messages to other neurons • myelin sheath: layer of fatty tissue that insulates the axon and helps speed up message transmission – multiple sclerosis: deterioration of myelin leads to slowed communication with muscles and impaired sensation in lim ...
10.6: Cell Membrane Potential
... • If a neuron axon responds at all, it responds completely – with an action potential (nerve impulse) • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
... • If a neuron axon responds at all, it responds completely – with an action potential (nerve impulse) • A nerve impulse is conducted whenever a stimulus of threshold intensity or above is applied to an axon • All impulses carried on an axon are the same strength ...
Neurons - Honors Biology 10 - 2222-03
... Neurons have a charge, or electrical potential, across their cell membranes. The inside of a neuron has a voltage of –70 millivolts (mV) compared to the outside. This difference is known as the resting potential. ...
... Neurons have a charge, or electrical potential, across their cell membranes. The inside of a neuron has a voltage of –70 millivolts (mV) compared to the outside. This difference is known as the resting potential. ...
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE Medical Diagnostic Systems
... The typical neuron of a vertebrate animal can carry time impulses for a considerable distance. The neuron depicted here, with its various parts drawn to scale, is enlarged 250 times. The nerve impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches ...
... The typical neuron of a vertebrate animal can carry time impulses for a considerable distance. The neuron depicted here, with its various parts drawn to scale, is enlarged 250 times. The nerve impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches ...
BN4402 - ECE@NUS
... been an increase in the number, and complexity of models of single neurons, and neural networks (Bower and Koch 1992). Modeling is attractive because it provides a deeper understanding of what is still unknown about the system, and thus helps us to guide our experiments so that we avoid generating m ...
... been an increase in the number, and complexity of models of single neurons, and neural networks (Bower and Koch 1992). Modeling is attractive because it provides a deeper understanding of what is still unknown about the system, and thus helps us to guide our experiments so that we avoid generating m ...
SBI4U - 9.2
... 1.The cytoplasmic core of a nerve cell offers great resistance to the movement of electric current 1.Electric currents diminish as they move through a wire ...
... 1.The cytoplasmic core of a nerve cell offers great resistance to the movement of electric current 1.Electric currents diminish as they move through a wire ...
Receptive Fields
... Receptive Fields Introduction: Given the enormity of the sensory space through which our nervous system must guide us, it comes as intuitive that our sensory systems should parcel out sensitivity to specific sensory regions over large populations of neurons. Within these large populations, there are ...
... Receptive Fields Introduction: Given the enormity of the sensory space through which our nervous system must guide us, it comes as intuitive that our sensory systems should parcel out sensitivity to specific sensory regions over large populations of neurons. Within these large populations, there are ...
Psychology 210
... Then the ________________________________brings the K back inside the cell and the Na back outside the cell 2 K for every 3 Na Uses energy (ATP) The action potential The Sodium Potassium pump restores the original environment of the resting potential so that the neuron can fire yet again This is kno ...
... Then the ________________________________brings the K back inside the cell and the Na back outside the cell 2 K for every 3 Na Uses energy (ATP) The action potential The Sodium Potassium pump restores the original environment of the resting potential so that the neuron can fire yet again This is kno ...