the big picture
... The number of magnetic field lines inside the wire loop changes when the loop is rotated. The faster this change occurs, the larger the induced voltage. ...
... The number of magnetic field lines inside the wire loop changes when the loop is rotated. The faster this change occurs, the larger the induced voltage. ...
Condensed_Magnetism in solids
... linked with electric current due to revolving electrons is changed, an induced current is set up in such a direction as to oppose the change in flux. It is manifested by the very small and negative value of magnetic susceptibility. If o be the frequency of electron in the absence of applied field a ...
... linked with electric current due to revolving electrons is changed, an induced current is set up in such a direction as to oppose the change in flux. It is manifested by the very small and negative value of magnetic susceptibility. If o be the frequency of electron in the absence of applied field a ...
Magnetism (Part 1)
... South If a compass is held on the east end of the wire, in what direction is the needle deflected (assuming it can point any direction it wants to)? 8. Is it possible to orient a current-carrying loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field so that the loop of wire doesn’t rotate? Explain. 9. If a solen ...
... South If a compass is held on the east end of the wire, in what direction is the needle deflected (assuming it can point any direction it wants to)? 8. Is it possible to orient a current-carrying loop of wire in a uniform magnetic field so that the loop of wire doesn’t rotate? Explain. 9. If a solen ...
Magnets and Electromagnets
... iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. • Another kind of magnet is the electromagnet. This is a magnet made by an electric current. • Temporary magnets are made from materials that are easy to magnetize. But they tend to lose their magnetization easily. • Permanent magnets are difficult ...
... iron, nickel, cobalt, or mixtures of those metals. • Another kind of magnet is the electromagnet. This is a magnet made by an electric current. • Temporary magnets are made from materials that are easy to magnetize. But they tend to lose their magnetization easily. • Permanent magnets are difficult ...
Magnets Review
... are affected by magnetic fields. • In these materials, small groups of atoms band together in areas called domains. – The electrons of the atoms in a domain are all in the same magnetic orientation. • The electrons are all oriented in the same way! ...
... are affected by magnetic fields. • In these materials, small groups of atoms band together in areas called domains. – The electrons of the atoms in a domain are all in the same magnetic orientation. • The electrons are all oriented in the same way! ...
Lecture 2 - Purdue Physics
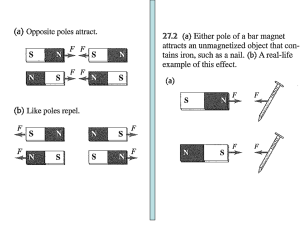
... with distance or pole strength. – The magnetic force between two poles decreases with the square of the distance between the two poles, just as the electrostatic force does. – Like poles repel one another, and unlike poles attract one another. ...
... with distance or pole strength. – The magnetic force between two poles decreases with the square of the distance between the two poles, just as the electrostatic force does. – Like poles repel one another, and unlike poles attract one another. ...
Magnetism and Electric Currents
... it produces a strong magnetic field inside of the coil • This is referred to as an electromagnet because the magnetic field only exists when current flows through the wire ...
... it produces a strong magnetic field inside of the coil • This is referred to as an electromagnet because the magnetic field only exists when current flows through the wire ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... • The reverse also works, a magnetic field can be turned inside a coil of wires. • Using steam to cause turbines to spin is the basic idea of how all generators work. • The only thing that changes is the energy source to generate the steam (coal, gas, nuclear, hydroelectric, solar, wind, etc.) ...
... • The reverse also works, a magnetic field can be turned inside a coil of wires. • Using steam to cause turbines to spin is the basic idea of how all generators work. • The only thing that changes is the energy source to generate the steam (coal, gas, nuclear, hydroelectric, solar, wind, etc.) ...
Earths-Magnetic-Field
... why Earth acts like a magnet is a relatively recent discovery. It had to wait until the development of technologies such as seismographs, which detect and measure earthquake waves. Then scientists could learn about Earth’s inner structure (see the figure below). They discovered that Earth has an inn ...
... why Earth acts like a magnet is a relatively recent discovery. It had to wait until the development of technologies such as seismographs, which detect and measure earthquake waves. Then scientists could learn about Earth’s inner structure (see the figure below). They discovered that Earth has an inn ...
Magnets and electricity - Rm. E
... Magnetic force: when you bring two magnets together, they exert a push or a pull on each other. Magnetic poles: two magnets can push each other apart because of their ends. Magnetic field: the area surrounding a magnet where magnetic forces can be detected. ...
... Magnetic force: when you bring two magnets together, they exert a push or a pull on each other. Magnetic poles: two magnets can push each other apart because of their ends. Magnetic field: the area surrounding a magnet where magnetic forces can be detected. ...
TOPIC 6.3: Magnetic Fields and Forces
... The ____________ points to the current The fingers show the direction of circular magnetic field. The space between the field lines increase with distance from the wire. Meaning a weaker field the further away. A _________________ is a long wire wrapped around a metal core which produces a m ...
... The ____________ points to the current The fingers show the direction of circular magnetic field. The space between the field lines increase with distance from the wire. Meaning a weaker field the further away. A _________________ is a long wire wrapped around a metal core which produces a m ...
Magnetic Field Variations - West Virginia University
... In general there are few corrections to apply to magnetic data. The largest non-geological variations in the earth’s magnetic field are those associated with diurnal variations, micropulsations and magnetic storms. The vertical gradient of the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field at thi ...
... In general there are few corrections to apply to magnetic data. The largest non-geological variations in the earth’s magnetic field are those associated with diurnal variations, micropulsations and magnetic storms. The vertical gradient of the vertical component of the earth’s magnetic field at thi ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.