Earth
... Now some people may guess that the seasons are caused by the Earth’s tilted axis. Thinking about the second diagram of the Earth’s orbit, does this make sense? ...
... Now some people may guess that the seasons are caused by the Earth’s tilted axis. Thinking about the second diagram of the Earth’s orbit, does this make sense? ...
Chapter 16
... Another kind of magnet is the ________________________. This is a magnet made by an electric current. _________________ magnets are made from materials that are easy to magnetize. But they tend to lose their magnetization easily. _______________ magnets are difficult to magnetize, but tend to ...
... Another kind of magnet is the ________________________. This is a magnet made by an electric current. _________________ magnets are made from materials that are easy to magnetize. But they tend to lose their magnetization easily. _______________ magnets are difficult to magnetize, but tend to ...
Magnetism - WordPress.com
... The space around a magnet where the magnet can attract or repel magnetic materials is called Magnetic field. The Magnetic field lines: - show the direction of the magnetic force at each point. - never cross each other. - are more near the poles of the magnet. (So that the poles have more magnetic st ...
... The space around a magnet where the magnet can attract or repel magnetic materials is called Magnetic field. The Magnetic field lines: - show the direction of the magnetic force at each point. - never cross each other. - are more near the poles of the magnet. (So that the poles have more magnetic st ...
electrom - studylib.net
... Electromagnetic propulsion systems can provide motive power for spacecraft. Electromagnets are also essential to magnetic levitation systems. NASA has developed a free-floating camera that will be used by astronauts in space. The camera will allow the astronauts 'extra eyes' that they can use while ...
... Electromagnetic propulsion systems can provide motive power for spacecraft. Electromagnets are also essential to magnetic levitation systems. NASA has developed a free-floating camera that will be used by astronauts in space. The camera will allow the astronauts 'extra eyes' that they can use while ...
PHYS632_C12_32_Maxwe..
... Iron, cobalt, nickel, and rare earth alloys exhibit ferromagnetism. The so called exchange coupling causes electron magnetic moments of one atom to align with electrons of other atoms. This alignment produces magnetism. Whole groups of atoms align and form domains. (See Figure 32-12 on page 756) A m ...
... Iron, cobalt, nickel, and rare earth alloys exhibit ferromagnetism. The so called exchange coupling causes electron magnetic moments of one atom to align with electrons of other atoms. This alignment produces magnetism. Whole groups of atoms align and form domains. (See Figure 32-12 on page 756) A m ...
Electromagnets - Cornell Center for Materials Research
... will be made available to each group. In order to pick up these materials, groups must establish an initial plan for their experiment, and have it approved by the facilitator, so that they do not overwhelm themselves with unnecessary materials. Materials can always be changed or added later in the e ...
... will be made available to each group. In order to pick up these materials, groups must establish an initial plan for their experiment, and have it approved by the facilitator, so that they do not overwhelm themselves with unnecessary materials. Materials can always be changed or added later in the e ...
TEP Earth`s magnetic field with Cobra4 Mobile
... slightly turned away from its resting position several times. Possible friction resistance can be reduced by gently tapping the instrument. In order to determine the horizontal component hBE of the earth-magnetic field, the deflection angle α of the magnetic needle is measured from its resting posit ...
... slightly turned away from its resting position several times. Possible friction resistance can be reduced by gently tapping the instrument. In order to determine the horizontal component hBE of the earth-magnetic field, the deflection angle α of the magnetic needle is measured from its resting posit ...
Magnetism Magnetic Force What causes magnetism?
... • Place 2 conductors in proximity, change the current in one conductor, current flows in other conductor ...
... • Place 2 conductors in proximity, change the current in one conductor, current flows in other conductor ...
Continental Drift, Mountain Building, and Plate Tectonics
... Spinning liquid metal core causes electromagnetic field Magnetic minerals (mainly magnetite) is magnetized and aligned with earth’s mag. Field below the CURIE POINT. These fossil magnets reflect changes in the magnetic field through time. INCLINATION is the angle the magnetic makes with the earth’s ...
... Spinning liquid metal core causes electromagnetic field Magnetic minerals (mainly magnetite) is magnetized and aligned with earth’s mag. Field below the CURIE POINT. These fossil magnets reflect changes in the magnetic field through time. INCLINATION is the angle the magnetic makes with the earth’s ...
Magnetism
... poles • Magnetic field – region around a magnet in which magnetic effects are observed, which is produced by the motion of the electric charge. • Lines of force – closed arc from north to south pole, never cross, most concentrated at poles ...
... poles • Magnetic field – region around a magnet in which magnetic effects are observed, which is produced by the motion of the electric charge. • Lines of force – closed arc from north to south pole, never cross, most concentrated at poles ...
Forming, Probing and Transforming Carbon Nanostructures*
... When magnetic materials are exposed to external magnetic field the change in magnetization extends beyond the simple linear regime. Under these conditions it is found that the response of the materials is no longer reversible. This phenomenon, hysteresis, is well documented in the experimental liter ...
... When magnetic materials are exposed to external magnetic field the change in magnetization extends beyond the simple linear regime. Under these conditions it is found that the response of the materials is no longer reversible. This phenomenon, hysteresis, is well documented in the experimental liter ...
Chapter 7:2 pages 198-201
... Earth’s magnetic poles changes…When Earth’s magnetic poles change places, this change is called a magnetic reversal. ...
... Earth’s magnetic poles changes…When Earth’s magnetic poles change places, this change is called a magnetic reversal. ...
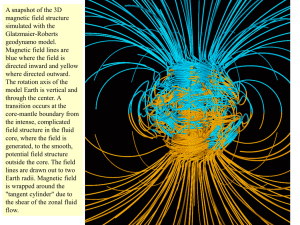
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.