
Unit 14* Magnetic Induction
... a. the number of turns of wire. b. the strength of the magnetic field. c. the speed of the magnetic flux cutting ...
... a. the number of turns of wire. b. the strength of the magnetic field. c. the speed of the magnetic flux cutting ...
Key Concept Review (Answers to in-text “Concept Checks”) Chapter
... 22. Though spreading speeds can reach a rate of 18 centimeters (7 inches) a year along parts of the Pacific plate, most plates move more slowly, about 3 centimeters (1.3 inches) each year. 23. A subducting plate's periodic downward lurches cause earthquakes and tsunami. 24. Earth’s magnetic field re ...
... 22. Though spreading speeds can reach a rate of 18 centimeters (7 inches) a year along parts of the Pacific plate, most plates move more slowly, about 3 centimeters (1.3 inches) each year. 23. A subducting plate's periodic downward lurches cause earthquakes and tsunami. 24. Earth’s magnetic field re ...
Solar System Foldable Checklist
... _____Relative size (compare to Earth) _____Number of moons (name of largest) _____Surface features (temperature) _____Type of atmosphere _____Current missions to planet (explorations) _____ Magnetic field _____ Internal structure _____Unique facts Neptune _____Relative size (compare to Earth) _____N ...
... _____Relative size (compare to Earth) _____Number of moons (name of largest) _____Surface features (temperature) _____Type of atmosphere _____Current missions to planet (explorations) _____ Magnetic field _____ Internal structure _____Unique facts Neptune _____Relative size (compare to Earth) _____N ...
electricity & magnetism
... Consists of tiny magnets called domains which has its own north and south pole. Has strong magnetic alloys that are described as ferromagnetic. ...
... Consists of tiny magnets called domains which has its own north and south pole. Has strong magnetic alloys that are described as ferromagnetic. ...
Lab 4, part one
... field, and how both are aspects of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation, as we’ve seen in previous exercises, is pervasive. Yet until the middle of the 19th century, physicists widely believed that EM waves could exist in a vacuum. Further, they did not connect EM waves to light, eve ...
... field, and how both are aspects of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation, as we’ve seen in previous exercises, is pervasive. Yet until the middle of the 19th century, physicists widely believed that EM waves could exist in a vacuum. Further, they did not connect EM waves to light, eve ...
Electromagnetism
... connected from the positive end to the negative end, the electrons will flow from the negative end to the positive end to balance the valence and drain the battery quickly. The wire will also produce a small magnetic field. The magnetic field runs perpendicular to the wire in a circular motion. By c ...
... connected from the positive end to the negative end, the electrons will flow from the negative end to the positive end to balance the valence and drain the battery quickly. The wire will also produce a small magnetic field. The magnetic field runs perpendicular to the wire in a circular motion. By c ...
Magnetism - Coach Ed Science
... magnetic. Once the paper clip is pulled outside the magnet's magnetic field, it loses its magnetism, and the electrons in the paper clip begin spinning in all sorts of ...
... magnetic. Once the paper clip is pulled outside the magnet's magnetic field, it loses its magnetism, and the electrons in the paper clip begin spinning in all sorts of ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Word Bank: Magnetic poles, like, current, magnetic domains, magnetic field lines, magnetism, repel, permanent magnet, opposite, electromagnet, magnetic field, alternating current, direct current, galvanometer ...
... Word Bank: Magnetic poles, like, current, magnetic domains, magnetic field lines, magnetism, repel, permanent magnet, opposite, electromagnet, magnetic field, alternating current, direct current, galvanometer ...
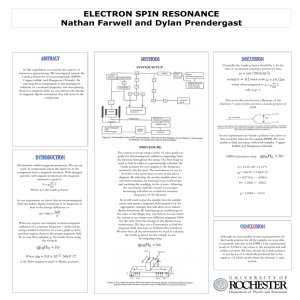
DETECTION OF UNPAIRED ELECTRONS
... states that exists only in the presence of a magnetic field. EPR is very closely related to another common type of spin resonance spectroscopy, NMR. Spin is a quantum property that has no real analogy that would make sense to us on a macroscopic level. However, we do know that spin has associated wi ...
... states that exists only in the presence of a magnetic field. EPR is very closely related to another common type of spin resonance spectroscopy, NMR. Spin is a quantum property that has no real analogy that would make sense to us on a macroscopic level. However, we do know that spin has associated wi ...
Poster: ESR
... Next will need to put the sample into the sample cavity and create a magnetic field around it of the appropriate strength that will allow us to induce dipole transitions. By hooking up an oscilloscope to the sides of the Magic Tee, (see below) we can watch the system as we sweep over different magne ...
... Next will need to put the sample into the sample cavity and create a magnetic field around it of the appropriate strength that will allow us to induce dipole transitions. By hooking up an oscilloscope to the sides of the Magic Tee, (see below) we can watch the system as we sweep over different magne ...
Plate Tectonics Continued
... Ridges and trenches support the theory of plate tectonics because ridges were formed by ____(state how plate tectonics formed ridges)___ and ocean trenches were formed by ___(state how plate tectonics formed trenches)___. ...
... Ridges and trenches support the theory of plate tectonics because ridges were formed by ____(state how plate tectonics formed ridges)___ and ocean trenches were formed by ___(state how plate tectonics formed trenches)___. ...
engineering physics ii magnetic materials
... to its random orientation some magnetic moments get cancelled and the materials possess very less magnetization in it. Effect of external field When an external field is applied, the magnetic moments of individual molecules reorient itself along the direction of the magnetic field and the material i ...
... to its random orientation some magnetic moments get cancelled and the materials possess very less magnetization in it. Effect of external field When an external field is applied, the magnetic moments of individual molecules reorient itself along the direction of the magnetic field and the material i ...
engineering physics ii magnetic materials
... to its random orientation some magnetic moments get cancelled and the materials possess very less magnetization in it. Effect of external field When an external field is applied, the magnetic moments of individual molecules reorient itself along the direction of the magnetic field and the material i ...
... to its random orientation some magnetic moments get cancelled and the materials possess very less magnetization in it. Effect of external field When an external field is applied, the magnetic moments of individual molecules reorient itself along the direction of the magnetic field and the material i ...
1] How will you show the directive property of a magnet? Suspend a
... having a glass top. The needle is free to move about its centre. The end of the needle, which indicates its north pole, is painted red. B] Magnetic field: The space around the magnet where its influence can be experienced is known as the magnetic field. C] Magnetic lines: These are curved lines used ...
... having a glass top. The needle is free to move about its centre. The end of the needle, which indicates its north pole, is painted red. B] Magnetic field: The space around the magnet where its influence can be experienced is known as the magnetic field. C] Magnetic lines: These are curved lines used ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.






















![1] How will you show the directive property of a magnet? Suspend a](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001625610_1-56f6c1434741143a0c22f345e56fb644-300x300.png)