Chapter 29:Electromagnetic Induction and Faraday*s Law
... A 100-loop square coil of wire, with side l = 5.00 cm and total resistance 100 Ω, is positioned perpendicular to a uniform 0.600-T magnetic field. It is quickly pulled from the field at constant speed (moving perpendicular to BB) to a region where B drops abruptly to zero. At t = 0, the right edge o ...
... A 100-loop square coil of wire, with side l = 5.00 cm and total resistance 100 Ω, is positioned perpendicular to a uniform 0.600-T magnetic field. It is quickly pulled from the field at constant speed (moving perpendicular to BB) to a region where B drops abruptly to zero. At t = 0, the right edge o ...
Study Guide
... object becomes magnetized it experiences a torque because it will seek to align parallel, or anitparallel with the magnetic field. When an object becomes magnetized it seeks to align itself somehow due to the magnetic field because of the magnetic dipole moment per unit volume (magnetization) that o ...
... object becomes magnetized it experiences a torque because it will seek to align parallel, or anitparallel with the magnetic field. When an object becomes magnetized it seeks to align itself somehow due to the magnetic field because of the magnetic dipole moment per unit volume (magnetization) that o ...
Magnetic fraud
... plane. You could say that these frames with their magnetic poles N and S coincide. And what happens if at such a moment in one frame you switch the direction of the electric current to the opposite? Then on the same side in relation to the plane of the frames, one frame will gain magnetic pole S and ...
... plane. You could say that these frames with their magnetic poles N and S coincide. And what happens if at such a moment in one frame you switch the direction of the electric current to the opposite? Then on the same side in relation to the plane of the frames, one frame will gain magnetic pole S and ...
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance, NMR
... and easily removed from the sample after the measurement, it should give a single sharp nmr signal that does not interfere. Tetramethylsilane, (CH3)4Si, usually referred to as TMS, meets all these characteristics, and has become the reference compound of choice for proton and carbon nmr. One additio ...
... and easily removed from the sample after the measurement, it should give a single sharp nmr signal that does not interfere. Tetramethylsilane, (CH3)4Si, usually referred to as TMS, meets all these characteristics, and has become the reference compound of choice for proton and carbon nmr. One additio ...
Electric and Magnetic Forces and the Modern Day
... Even though magnets can come in different shapes, strengths, and sizes, they all have a magnetic north pole and a magnetic south pole. The earth’s North Pole, in the Canadian Arctic, is actually around where the earth’s magnetic south pole is located; and the earth’s So ...
... Even though magnets can come in different shapes, strengths, and sizes, they all have a magnetic north pole and a magnetic south pole. The earth’s North Pole, in the Canadian Arctic, is actually around where the earth’s magnetic south pole is located; and the earth’s So ...
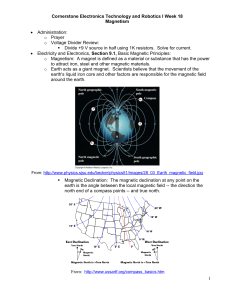
doc - Cornerstone Robotics
... See lines of force demonstration setup at: http://blog.teachersource.com/tag/magnetic-fields/ See applet: http://www.ndted.org/EducationResources/HighSchool/Magnetism/magneticfields.htm See applet: http://falstad.com/vector3dm/ Change current line to magnetic sphere Display: Field Lines Formula ...
... See lines of force demonstration setup at: http://blog.teachersource.com/tag/magnetic-fields/ See applet: http://www.ndted.org/EducationResources/HighSchool/Magnetism/magneticfields.htm See applet: http://falstad.com/vector3dm/ Change current line to magnetic sphere Display: Field Lines Formula ...
Magnets and Electromagnets - School Masters Consulting
... e.g. opposite poles of two magnets. electromagnet – A magnet made by passing electricity through a coil of wire, which often has a core inside. magnet – An object that has a magnetic field and can attract magnetic materials. magnetic field – The area around a magnet where its magnetic force can be f ...
... e.g. opposite poles of two magnets. electromagnet – A magnet made by passing electricity through a coil of wire, which often has a core inside. magnet – An object that has a magnetic field and can attract magnetic materials. magnetic field – The area around a magnet where its magnetic force can be f ...
Magnets 2-24-17
... 17. Name one thing that causes domains of a magnet’s atoms to lose alignment. Possible answers: dropping a magnet; hitting it too hard; putting the magnet in a strong magnetic field opposite to its own; increasing its temperature 18. How do you magnetize something made of iron, cobalt, or nickel? by ...
... 17. Name one thing that causes domains of a magnet’s atoms to lose alignment. Possible answers: dropping a magnet; hitting it too hard; putting the magnet in a strong magnetic field opposite to its own; increasing its temperature 18. How do you magnetize something made of iron, cobalt, or nickel? by ...
CHEM 251L: Inorganic Chemistry Laboratory Professor Jonathan
... Applied electromagnetic radiation can induce a transition between the mI = +½ and mI = ½ states, resulting in a measurable absorption of energy. The nucleus is said to be in resonance when this absorption occurs, hence the name of “nuclear magnetic resonance.” This resonance can only occur when the ...
... Applied electromagnetic radiation can induce a transition between the mI = +½ and mI = ½ states, resulting in a measurable absorption of energy. The nucleus is said to be in resonance when this absorption occurs, hence the name of “nuclear magnetic resonance.” This resonance can only occur when the ...
Chapter 19
... There cannot be large masses of permanently magnetized materials since the high temperatures of the core prevent materials from retaining permanent magnetization The most likely source of the Earth’s magnetic field is believed to be electric currents in the liquid part of the core ...
... There cannot be large masses of permanently magnetized materials since the high temperatures of the core prevent materials from retaining permanent magnetization The most likely source of the Earth’s magnetic field is believed to be electric currents in the liquid part of the core ...
phys1444-spring06-032006
... • The pole in the north is still called geomagnetic north pole just because it is in the north ...
... • The pole in the north is still called geomagnetic north pole just because it is in the north ...
CHAPTER - 13 MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF ELECTRIC CURRENT CLASS
... sprinkling iron filings around a magnet. It can also be observed by moving a magnetic compass around a magnet. i) The magnetic field lines emerge at the north pole and merge at the south pole. ii) The magnetic field lines are closer at the poles. iii) The magnetic field lines do not intersect each o ...
... sprinkling iron filings around a magnet. It can also be observed by moving a magnetic compass around a magnet. i) The magnetic field lines emerge at the north pole and merge at the south pole. ii) The magnetic field lines are closer at the poles. iii) The magnetic field lines do not intersect each o ...
a) Direct current
... sprinkling iron filings around a magnet. It can also be observed by moving a magnetic compass around a magnet. i) The magnetic field lines emerge at the north pole and merge at the south pole. ii) The magnetic field lines are closer at the poles. iii) The magnetic field lines do not intersect each o ...
... sprinkling iron filings around a magnet. It can also be observed by moving a magnetic compass around a magnet. i) The magnetic field lines emerge at the north pole and merge at the south pole. ii) The magnetic field lines are closer at the poles. iii) The magnetic field lines do not intersect each o ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.