MY-402 (Advanced Materials)
... Ferromagnetic materials are also good conductors, and a core made from such a material also constitutes a single short-circuited turn throughout its entire length. Eddy currents therefore circulate within the core in a plane normal to the flux, and are responsible for resistive heating of the core m ...
... Ferromagnetic materials are also good conductors, and a core made from such a material also constitutes a single short-circuited turn throughout its entire length. Eddy currents therefore circulate within the core in a plane normal to the flux, and are responsible for resistive heating of the core m ...
Is the Long Wavelength Crustal Magnetic Field
... strong at the poles than at the equator. Consequently, any induced magnetisation must increase with latitude, while the strength of remanent magnetisation is likely to be independent of latitude. This unequal behaviour can be utilised to distinguish between induced and remanent contributions to the ...
... strong at the poles than at the equator. Consequently, any induced magnetisation must increase with latitude, while the strength of remanent magnetisation is likely to be independent of latitude. This unequal behaviour can be utilised to distinguish between induced and remanent contributions to the ...
Electron Spin Resonance
... Making sure, first, that the DC power supply is off and the Variac is turned to 0 Volts. Place the DPPH sample inside coil F (which should still be plugged into the oscillator) and place the coil, with DPPH, inside the Helmholtz coils set-up, as shown in Figure 7. Make sure that the part of the ampu ...
... Making sure, first, that the DC power supply is off and the Variac is turned to 0 Volts. Place the DPPH sample inside coil F (which should still be plugged into the oscillator) and place the coil, with DPPH, inside the Helmholtz coils set-up, as shown in Figure 7. Make sure that the part of the ampu ...
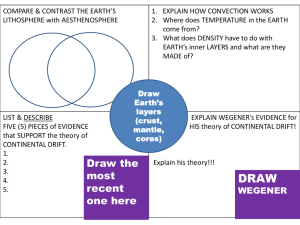
Plate Tectonics 1
... – Dominantly dipolar magnetic field • like a bar magnet aligned near the rotation axis ...
... – Dominantly dipolar magnetic field • like a bar magnet aligned near the rotation axis ...
Magnetism and Matter
... magnetite had the property of attracting small pieces of iron. The word magnetism originates from the place magnesia in Greece. This property of attraction is called magnetism. The iron ore showing this property was called a magnet. Later it was discovered by the Chinese that a long piece of magnet, ...
... magnetite had the property of attracting small pieces of iron. The word magnetism originates from the place magnesia in Greece. This property of attraction is called magnetism. The iron ore showing this property was called a magnet. Later it was discovered by the Chinese that a long piece of magnet, ...
The Power of Magnets
... permanent magnet, though its magnetic field is quite weak relative to its size. Humans have used the magnetic field of the Earth for navigation since the compass was invented in ancient China. Even the most powerful permanent magnet is not as strong as the stronger electromagnets, so their applicati ...
... permanent magnet, though its magnetic field is quite weak relative to its size. Humans have used the magnetic field of the Earth for navigation since the compass was invented in ancient China. Even the most powerful permanent magnet is not as strong as the stronger electromagnets, so their applicati ...
Period 17 Activity Solutions: Induction Motors and Transformers
... When the magnet is moved into place above the disc, its motion creates a changing magnetic field that induces a current in the disc. The current flowing in the disc induces a magnetic field around the disc. The magnet floats because it is repelled by the magnetic field around the disc. 4) Why is a s ...
... When the magnet is moved into place above the disc, its motion creates a changing magnetic field that induces a current in the disc. The current flowing in the disc induces a magnetic field around the disc. The magnet floats because it is repelled by the magnetic field around the disc. 4) Why is a s ...
Effects of High Magnetic Field Postannealing on Microstructure and
... the annealed films with and without a magnetic field. The as-deposited film with a rough surface shown in Figure 1(a) consisted of the grape-like spherical clusters, which were Cobased solid solution cell with high content of Ni and P formed under a higher overpotential. After being annealed at 673 ...
... the annealed films with and without a magnetic field. The as-deposited film with a rough surface shown in Figure 1(a) consisted of the grape-like spherical clusters, which were Cobased solid solution cell with high content of Ni and P formed under a higher overpotential. After being annealed at 673 ...
Device for Controlled Distribution of FePt
... to create magnetic forces. It also shows that the force on a single particle is directly proportional to its volume. The second relation, which is equivalent to the first one, states that the force on particles is along the gradient of the magnetic field intensity squared – i. e. ferro-magnetic part ...
... to create magnetic forces. It also shows that the force on a single particle is directly proportional to its volume. The second relation, which is equivalent to the first one, states that the force on particles is along the gradient of the magnetic field intensity squared – i. e. ferro-magnetic part ...
Geology Library Notes Wk8.cwk (WP)
... Certain minerals (e.g. magnetite) can act like little bar magnets. ...
... Certain minerals (e.g. magnetite) can act like little bar magnets. ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.