Ch 29 Magnetic Fields due to Currents
... Fig. 29-19 Application of Ampere’s law to a section of a long ideal solenoid carrying a current i. The Amperian loop is the rectangle abcda. ...
... Fig. 29-19 Application of Ampere’s law to a section of a long ideal solenoid carrying a current i. The Amperian loop is the rectangle abcda. ...
here - Physics Teacher
... magnetic poles repel each other. These forces can act distance across a ________________________ . In a diagram of a magnetic field, they are magnetic field lines represented by ________________________. By convention, the lines are drawn entering into coming out of ________________________ the nort ...
... magnetic poles repel each other. These forces can act distance across a ________________________ . In a diagram of a magnetic field, they are magnetic field lines represented by ________________________. By convention, the lines are drawn entering into coming out of ________________________ the nort ...
Magnetism
... Magnetic monopoles do not exist! • If I have a magnet, it has a north and south pole • If I cut the magnet in half… ...
... Magnetic monopoles do not exist! • If I have a magnet, it has a north and south pole • If I cut the magnet in half… ...
Abstract_Kee Hoon Kim
... power law, thus constituting experimental evidences of a multiferroic critical end point. In the latter Ba2CoGe2O7, wherein a new p-d hybridization model can generate P [2], a spontaneous antiferromagnetic order of Co2+ (3d7) spins sitting in the center of tetrahedra network forming a quasi-2D squar ...
... power law, thus constituting experimental evidences of a multiferroic critical end point. In the latter Ba2CoGe2O7, wherein a new p-d hybridization model can generate P [2], a spontaneous antiferromagnetic order of Co2+ (3d7) spins sitting in the center of tetrahedra network forming a quasi-2D squar ...
Sea Floor Spreading - Sterlingmontessoriscience
... The Earth has an invisible magnetic field. All free-floating magnets at the Earth’s surface point to magnetic north. Iron-rich minerals crystallizing from molten rock will orient towards magnetic north when they cool below the Curie point, the temperature above which permanent magnetism is impossibl ...
... The Earth has an invisible magnetic field. All free-floating magnets at the Earth’s surface point to magnetic north. Iron-rich minerals crystallizing from molten rock will orient towards magnetic north when they cool below the Curie point, the temperature above which permanent magnetism is impossibl ...
Magnetized_Phase_Diagram_Loewe
... Huge Magnetic fields are produced in perhipheral heavy-ion collisions ...
... Huge Magnetic fields are produced in perhipheral heavy-ion collisions ...
Study Guide Questions for Continents Change Position Over Time:
... Study Guide Questions on Plates move apart: 1. Define the following vocabulary: divergent boundary, convergent boundary, transform boundary, rift valley, magnetic reversal, hot spot 2. What features are found at divergent boundaries in the ocean? Mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys 3. What creates a r ...
... Study Guide Questions on Plates move apart: 1. Define the following vocabulary: divergent boundary, convergent boundary, transform boundary, rift valley, magnetic reversal, hot spot 2. What features are found at divergent boundaries in the ocean? Mid-ocean ridges and rift valleys 3. What creates a r ...
Magnetic Reversals
... the journals as too speculative) and by Drummond Matthews and Fred Vine. They all proposed that the sea floor was in constant motion, pulling away from the central ridge at a rate of about one inch (2.5 cm) per year. As the "plates" on each side are pulled away, lava emerges from the middle, solidif ...
... the journals as too speculative) and by Drummond Matthews and Fred Vine. They all proposed that the sea floor was in constant motion, pulling away from the central ridge at a rate of about one inch (2.5 cm) per year. As the "plates" on each side are pulled away, lava emerges from the middle, solidif ...
Magnetic Forces Practice
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
... to the plane formed by the field and the moving charge, and is greatest when the magnetic field and current are perpendicular to each other. The force on the current carrying wire shown above is therefore into the plane of the page and is determined by using the left-hand finger rule. ...
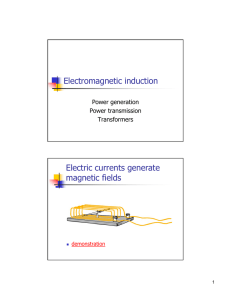
Electromagnetic induction Electric currents generate magnetic fields
... Electric currents are pushed on by magnetic fields ...
... Electric currents are pushed on by magnetic fields ...
Unit 07 Magnetic Fields
... we call them “north” and “south.” However, unlike electric charges, magnetic charges never appear by themselves – they only appear together. If you take a bar magnet and break it in half, you don’t end up with one north pole and one south pole; rather, you end up with two smaller magnets! Today, the ...
... we call them “north” and “south.” However, unlike electric charges, magnetic charges never appear by themselves – they only appear together. If you take a bar magnet and break it in half, you don’t end up with one north pole and one south pole; rather, you end up with two smaller magnets! Today, the ...
Hall Probes for Magnetic Field Measurement
... – Using two or three Hall sensors allows 2-axis or 3-axis detection of the magnetic field direction. – Hall sensor can be readily integrated with microelectronics. Jun Zou ...
... – Using two or three Hall sensors allows 2-axis or 3-axis detection of the magnetic field direction. – Hall sensor can be readily integrated with microelectronics. Jun Zou ...
Electromagnetic Rules
... through a magnetic field. In concept, when the wire crosses magnetic field lines a current tries to flow. A current (or EMF) is ONLY produced where the magnetic field is changing. A complete circuit is needed for the current to actually flow so instead of discussing the current flow which only happe ...
... through a magnetic field. In concept, when the wire crosses magnetic field lines a current tries to flow. A current (or EMF) is ONLY produced where the magnetic field is changing. A complete circuit is needed for the current to actually flow so instead of discussing the current flow which only happe ...
Advanced Higher Physics - stuckwithphysics.co.uk
... Magnitude of EMF is related to rate of change of magnetic flux ...
... Magnitude of EMF is related to rate of change of magnetic flux ...
Earth's magnetic field

Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from the Earth's interior to where it meets the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. Its magnitude at the Earth's surface ranges from 25 to 65 microteslas (0.25 to 0.65 gauss). Roughly speaking it is the field of a magnetic dipole currently tilted at an angle of about 10 degrees with respect to Earth's rotational axis, as if there were a bar magnet placed at that angle at the center of the Earth. Unlike a bar magnet, however, Earth's magnetic field changes over time because it is generated by a geodynamo (in Earth's case, the motion of molten iron alloys in its outer core).The North and South magnetic poles wander widely, but sufficiently slowly for ordinary compasses to remain useful for navigation. However, at irregular intervals averaging several hundred thousand years, the Earth's field reverses and the North and South Magnetic Poles relatively abruptly switch places. These reversals of the geomagnetic poles leave a record in rocks that are of value to paleomagnetists in calculating geomagnetic fields in the past. Such information in turn is helpful in studying the motions of continents and ocean floors in the process of plate tectonics.The magnetosphere is the region above the ionosphere and extends several tens of thousands of kilometers into space, protecting the Earth from the charged particles of the solar wind and cosmic rays that would otherwise strip away the upper atmosphere, including the ozone layer that protects the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation.