Measuring Metal Magnetism - Name
... The common ions of transition metals have 0-10 valence electrons in their d-orbitals. Magnetic measurements can be used to study these valence electrons, as the magnetic moment of a transition metal ion typically depends only on the number of unpaired electrons. The number of unpaired electrons is b ...
... The common ions of transition metals have 0-10 valence electrons in their d-orbitals. Magnetic measurements can be used to study these valence electrons, as the magnetic moment of a transition metal ion typically depends only on the number of unpaired electrons. The number of unpaired electrons is b ...
Earth`s Layers
... • The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces called (lithospheric) plate. • The plates “float” on the soft, semi rigid asthenosphere ...
... • The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces called (lithospheric) plate. • The plates “float” on the soft, semi rigid asthenosphere ...
Lab 10: Reverse Time Depth Migration
... stacked seismic volume (3D), provides a geometrically accurate image of the subsurface. However, deviations from horizontal stratigraphy and wave effects both distort the sections and volumes. In unmigrated seismic data, dipping reflections appear displaced down dip and at shallower dip angles than ...
... stacked seismic volume (3D), provides a geometrically accurate image of the subsurface. However, deviations from horizontal stratigraphy and wave effects both distort the sections and volumes. In unmigrated seismic data, dipping reflections appear displaced down dip and at shallower dip angles than ...
the sun part 2
... Spicules and coronal heating are due to magnetic field and happen all the time. Sunspots are also due to magnetic field but they form only when the Sun is (magnetically) “active”. In addition there are more processes on different scales that are due to the magnetic activity of the Sun. See next figu ...
... Spicules and coronal heating are due to magnetic field and happen all the time. Sunspots are also due to magnetic field but they form only when the Sun is (magnetically) “active”. In addition there are more processes on different scales that are due to the magnetic activity of the Sun. See next figu ...
Chapter 4
... Age of the Sea Floor Evidence from ocean drilling • Age of deepest sediments indicates ocean crust much younger than continental crust, which supports both subduction and seafloor spreading hypotheses. • Lack of sediments at at mid ocean ridges supports seafloor spreading. • Age distribution of oc ...
... Age of the Sea Floor Evidence from ocean drilling • Age of deepest sediments indicates ocean crust much younger than continental crust, which supports both subduction and seafloor spreading hypotheses. • Lack of sediments at at mid ocean ridges supports seafloor spreading. • Age distribution of oc ...
The Seven Earths DOC
... The inner core is solid and unattached to the mantle, suspended in the molten outer core. It is believed to have solidified as a result of pressure-freezing which occurs to most liquids when temperature decreases or pressure increases. (2) The Liquid Outer core: 30.8% of Earth’s mass; depth of 2,890 ...
... The inner core is solid and unattached to the mantle, suspended in the molten outer core. It is believed to have solidified as a result of pressure-freezing which occurs to most liquids when temperature decreases or pressure increases. (2) The Liquid Outer core: 30.8% of Earth’s mass; depth of 2,890 ...
The Seven Earths PDF
... The inner core is solid and unattached to the mantle, suspended in the molten outer core. It is believed to have solidified as a result of pressure-freezing which occurs to most liquids when temperature decreases or pressure increases. (2) The Liquid Outer core: 30.8% of Earth’s mass; depth of 2,890 ...
... The inner core is solid and unattached to the mantle, suspended in the molten outer core. It is believed to have solidified as a result of pressure-freezing which occurs to most liquids when temperature decreases or pressure increases. (2) The Liquid Outer core: 30.8% of Earth’s mass; depth of 2,890 ...
File
... Magnets attract and repel other magnets Suppose you get home from school and open the __________________to get some milk. As you ____________the door, it swings freely until it suddenly seems to ____________ by itself. There is a ________________ inside the refrigerator door that ___________________ ...
... Magnets attract and repel other magnets Suppose you get home from school and open the __________________to get some milk. As you ____________the door, it swings freely until it suddenly seems to ____________ by itself. There is a ________________ inside the refrigerator door that ___________________ ...
Chapter 29 Magnetic Fields Due to Currents
... cross section, and placed 1 m apart in vacuum, would produce on each of these conductors a force of magnitude 2 × 10-7 newton per meter of wire length. Rail Gun In this device, a magnetic force accelerates a projectile to a high speed in a short time. the currents in the rails produce magnetic field ...
... cross section, and placed 1 m apart in vacuum, would produce on each of these conductors a force of magnitude 2 × 10-7 newton per meter of wire length. Rail Gun In this device, a magnetic force accelerates a projectile to a high speed in a short time. the currents in the rails produce magnetic field ...
Magnetic investigation of zero-field-cooled dextran
... value higher than the 13 mark. In conclusion, the temperature dependence of the ZFC magnetization of dextran-coated magnetite-based MF samples has been investigated in this study. Neither particle–particle interaction (low particle concentration) nor the particle size polydispersity profile, the latt ...
... value higher than the 13 mark. In conclusion, the temperature dependence of the ZFC magnetization of dextran-coated magnetite-based MF samples has been investigated in this study. Neither particle–particle interaction (low particle concentration) nor the particle size polydispersity profile, the latt ...
Eliana Harrison, Grade 8 Ms. Lawson (teacher) Palos Verdes
... Field?" Reddit.) If we had a Mars base and explored its magnetic field, or rather, lack thereof, we could potentially unlock secrets to all planets' magnetic fields! These handy fields serve many purposes, but their main purpose is to protect the planet from charged space particles, such as solar wi ...
... Field?" Reddit.) If we had a Mars base and explored its magnetic field, or rather, lack thereof, we could potentially unlock secrets to all planets' magnetic fields! These handy fields serve many purposes, but their main purpose is to protect the planet from charged space particles, such as solar wi ...
Earth`s Layered Structure
... c. the San Andreas Fault b. a mountain range d. a small inland lake 3. Which of the following is used in an attempt to make short-range predictions of when earthquakes will ...
... c. the San Andreas Fault b. a mountain range d. a small inland lake 3. Which of the following is used in an attempt to make short-range predictions of when earthquakes will ...
here
... the rest of them are far enough from the coils, we may mainly conconsider the screening efficiency of the iron tubes around the 3 closest detectors. And furthermore, since the distances among these 3 tubes are large compared to their dimensions, we can simplify the problem to study only one tube, i. ...
... the rest of them are far enough from the coils, we may mainly conconsider the screening efficiency of the iron tubes around the 3 closest detectors. And furthermore, since the distances among these 3 tubes are large compared to their dimensions, we can simplify the problem to study only one tube, i. ...
Physical science - State of New Jersey
... Experimental evidence should allow students to support claims about how an electric current can produce a magnetic field, and how a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current. Claims should be supported and modeled mathematically when appropriate. Students should choose and interpret un ...
... Experimental evidence should allow students to support claims about how an electric current can produce a magnetic field, and how a changing magnetic field can produce an electric current. Claims should be supported and modeled mathematically when appropriate. Students should choose and interpret un ...
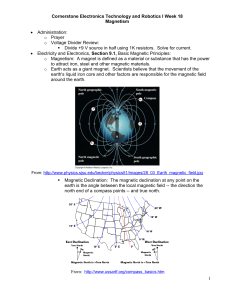
doc - Cornerstone Robotics
... than 30 microteslas (0.00003 T) in an area including most of South America and South Africa to over 60 microteslas around the magnetic poles in northern Canada and south of Australia, and in part of Siberia. Internet site: http://geomag.usgs.gov/charts/ The strongest continuous magnetic field,(45 ...
... than 30 microteslas (0.00003 T) in an area including most of South America and South Africa to over 60 microteslas around the magnetic poles in northern Canada and south of Australia, and in part of Siberia. Internet site: http://geomag.usgs.gov/charts/ The strongest continuous magnetic field,(45 ...
Earthquakes! Causes. Predictions.
... draining down these faults and into the outer core slowly increases the volume of the liquid outer core, so periodically the least-locked mantle block will be suddenly lifted. A disturbance large enough to vertically shift one weakly anchored block can suddenly shift. 3. Frictional heat generated by ...
... draining down these faults and into the outer core slowly increases the volume of the liquid outer core, so periodically the least-locked mantle block will be suddenly lifted. A disturbance large enough to vertically shift one weakly anchored block can suddenly shift. 3. Frictional heat generated by ...
answer key
... The earth is not a static planet; the large slabs of the earth’s crust (tectonic plates) are in continual slow motion. An earthquake occurs when these plates move. The movement causes rock to be squeezed, bent and stretched. This tremendous pressure eventually forces the rock to break and the plates ...
... The earth is not a static planet; the large slabs of the earth’s crust (tectonic plates) are in continual slow motion. An earthquake occurs when these plates move. The movement causes rock to be squeezed, bent and stretched. This tremendous pressure eventually forces the rock to break and the plates ...
Magnetotellurics

Magnetotellurics (MT) is an electromagnetic geophysical method for inferring the earth's subsurface electrical conductivity from measurements of natural geomagnetic and geoelectric field variation at the Earth's surface. Investigation depth ranges from 300m below ground by recording higher frequencies down to 10,000m or deeper with long-period soundings. Developed in the USSR and France during the 1950s, MT is now an international academic discipline and is used in exploration surveys around the world. Commercial uses include hydrocarbon (oil and gas) exploration, geothermal exploration, mining exploration, as well as hydrocarbon and groundwater monitoring. Research applications include experimentation to further develop the MT technique, long-period deep crustal exploration, and earthquake precursor prediction research.