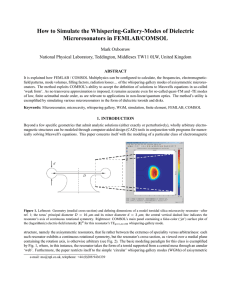
3 4 y x =
... y = mx + b from the intersections of the graphed equations. 8(5)(B) Proportionality. The student is expected to represent linear non-proportional situations with tables, graphs, and equations in the form of y = mx + b. ...
... y = mx + b from the intersections of the graphed equations. 8(5)(B) Proportionality. The student is expected to represent linear non-proportional situations with tables, graphs, and equations in the form of y = mx + b. ...
Math 678. Homework 5 Solutions. #1 Consider a
... for all heat balls E(x, t; r) ⊂ UT . (b) As in Theorem 4, it follows that maxŪT v = maxUT v. Indeed, suppose there is a point (x0 , t0 ) in UT where the function value is maximized on the entire closed domain ŪT . Then there is a sufficiently small Z Z heat ball around 2it where ...
... for all heat balls E(x, t; r) ⊂ UT . (b) As in Theorem 4, it follows that maxŪT v = maxUT v. Indeed, suppose there is a point (x0 , t0 ) in UT where the function value is maximized on the entire closed domain ŪT . Then there is a sufficiently small Z Z heat ball around 2it where ...