Geometry - Eleanor Roosevelt High School
... Make a Conjecture Give five colinear points, make a conjecture about the number of ways to connect different pairs of the points No of Points ...
... Make a Conjecture Give five colinear points, make a conjecture about the number of ways to connect different pairs of the points No of Points ...
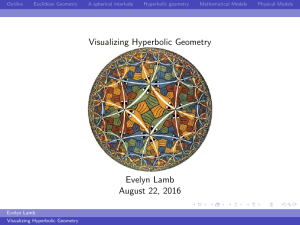
Visualizing Hyperbolic Geometry
... One of these postulates is not like the others A straight line segment can be drawn joining any two points. A straight line segment can be extended indefinitely in a straight line. Given any straight line segment, a circle can be drawn having the segment as a radius and one endpoint as center. All r ...
... One of these postulates is not like the others A straight line segment can be drawn joining any two points. A straight line segment can be extended indefinitely in a straight line. Given any straight line segment, a circle can be drawn having the segment as a radius and one endpoint as center. All r ...
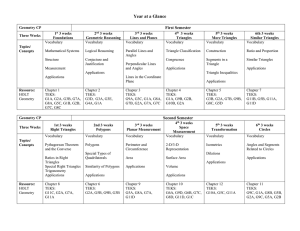
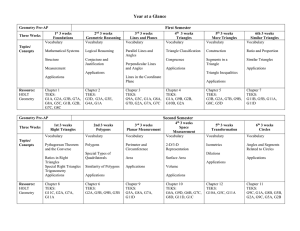
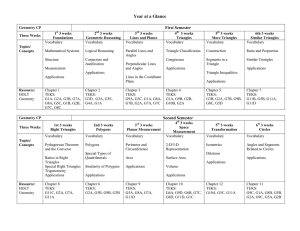
Geometry Pre AP Scope and Sequence
... Structure of a Mathematical System (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) ELOs TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) The student will: -identify and model points, lines, and planes. -identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. -find segment and angle measures using segmen ...
... Structure of a Mathematical System (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) ELOs TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) The student will: -identify and model points, lines, and planes. -identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. -find segment and angle measures using segmen ...
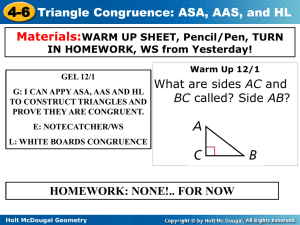
Holt McDougal Geometry 4-6
... can be used to find the position of points A, B, and C. List the important information: The bearing from A to B is N 65° E. From B to C is N 24° W, and from C to A is S 20° W. The distance from A to B is 8 mi. ...
... can be used to find the position of points A, B, and C. List the important information: The bearing from A to B is N 65° E. From B to C is N 24° W, and from C to A is S 20° W. The distance from A to B is 8 mi. ...
Analytic geometry
In classical mathematics, analytic geometry, also known as coordinate geometry, or Cartesian geometry, is the study of geometry using a coordinate system. This contrasts with synthetic geometry.Analytic geometry is widely used in physics and engineering, and is the foundation of most modern fields of geometry, including algebraic, differential, discrete and computational geometry.Usually the Cartesian coordinate system is applied to manipulate equations for planes, straight lines, and squares, often in two and sometimes in three dimensions. Geometrically, one studies the Euclidean plane (two dimensions) and Euclidean space (three dimensions). As taught in school books, analytic geometry can be explained more simply: it is concerned with defining and representing geometrical shapes in a numerical way and extracting numerical information from shapes' numerical definitions and representations. The numerical output, however, might also be a vector or a shape. That the algebra of the real numbers can be employed to yield results about the linear continuum of geometry relies on the Cantor–Dedekind axiom.