Neurons and Neurotransmission - Milton
... “One-third of humanity has perished from the plague. 2.3 billion people have died, and countless more are quickly moving towards the final stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, a ...
... “One-third of humanity has perished from the plague. 2.3 billion people have died, and countless more are quickly moving towards the final stages of the disease. There is reason to believe that in a short time, nearly everyone on Earth will be infected. The virus continues to spread exponentially, a ...
Chapter 28
... • When Na+ channels open, Na+ floods into the neuron from the outside. • For a brief moment, the inside of the neuron is “depolarized,” becoming more positive. • The open Na+ channels in the small patch of depolarized membrane remain open for only one half of a millisecond. • If the voltage change o ...
... • When Na+ channels open, Na+ floods into the neuron from the outside. • For a brief moment, the inside of the neuron is “depolarized,” becoming more positive. • The open Na+ channels in the small patch of depolarized membrane remain open for only one half of a millisecond. • If the voltage change o ...
The Nervous System
... • The positive charge carried by the Na+ spreads as a wave of depolarization through the cytoplasm (much like the ripples created by a stone tossed into a pond). • As the Na+ drifts, some of it will leak back out of the membrane. – What this means is that the degree of depolarization caused by the g ...
... • The positive charge carried by the Na+ spreads as a wave of depolarization through the cytoplasm (much like the ripples created by a stone tossed into a pond). • As the Na+ drifts, some of it will leak back out of the membrane. – What this means is that the degree of depolarization caused by the g ...
Neurotransmission Notes
... 4. The voltage sensitive Na+ gates only stay open a moment and then K+ gates open. These allow K+ to rush out of the axon, bringing it back to a negative charge (when called this repolarization or hyperpolarization). 5. Although the charge is back to rest, the Na+ and K+ ions are on opposite sides ...
... 4. The voltage sensitive Na+ gates only stay open a moment and then K+ gates open. These allow K+ to rush out of the axon, bringing it back to a negative charge (when called this repolarization or hyperpolarization). 5. Although the charge is back to rest, the Na+ and K+ ions are on opposite sides ...
nervous system physiology 1
... - the process that extends into the CNS from this unipolar neuron is easily recognized as an axon because it carries information away from the cell body. - the process that extends to sensory receptors in the skin and elsewhere is less easily defined. It is a typical axon in the sense that it can co ...
... - the process that extends into the CNS from this unipolar neuron is easily recognized as an axon because it carries information away from the cell body. - the process that extends to sensory receptors in the skin and elsewhere is less easily defined. It is a typical axon in the sense that it can co ...
Chapter 3: Biological Bases of Behavior
... secreted by the endocrine glands. • The pituitary gland -- sometimes called the “_65_ gland”, -secretes substances influencing the operation of all the other glands, as well as growth hormone. The actions of the pituitary/endocrine system is controlled by the nervous system through the hypothalamus. ...
... secreted by the endocrine glands. • The pituitary gland -- sometimes called the “_65_ gland”, -secretes substances influencing the operation of all the other glands, as well as growth hormone. The actions of the pituitary/endocrine system is controlled by the nervous system through the hypothalamus. ...
The Nervous System
... Neurotransmitters diffuse from the end of one neuron to receptors on the next neuron. When they land on the specific receptor they allow gates to open that allow sodium to enter - this ignites the electro-chemical impulse to begin in the the next neuron. ...
... Neurotransmitters diffuse from the end of one neuron to receptors on the next neuron. When they land on the specific receptor they allow gates to open that allow sodium to enter - this ignites the electro-chemical impulse to begin in the the next neuron. ...
Audition, the Body Senses, and the Chemical Senses
... A neuron located in the olfactory bulb that receives information from olfactory receptors; axons of mitral cells bring information to the rest of the brain. ...
... A neuron located in the olfactory bulb that receives information from olfactory receptors; axons of mitral cells bring information to the rest of the brain. ...
Chapter 12 Notes: Nervous Tissue 2014
... 7. The neurotransmitter, Ach, diffuses over to the postsynaptic membrane where it interacts with chemical channel proteins to produce either a IPSP (-), or EPSP (+) effect. EPSP (+) = excitatory post-synaptic potential = IMPULSE GENERATION. IPSP (-) = inhibitory post-synaptic potential = IMPULSE INH ...
... 7. The neurotransmitter, Ach, diffuses over to the postsynaptic membrane where it interacts with chemical channel proteins to produce either a IPSP (-), or EPSP (+) effect. EPSP (+) = excitatory post-synaptic potential = IMPULSE GENERATION. IPSP (-) = inhibitory post-synaptic potential = IMPULSE INH ...
The Nervous System
... • Carries on many conversations with different neurons at same time • Lacks rough ER and Golgi apparatus – Relies on cell body to renew proteins and membranes ...
... • Carries on many conversations with different neurons at same time • Lacks rough ER and Golgi apparatus – Relies on cell body to renew proteins and membranes ...
Chapt13 Lecture 13ed Pt 1
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) sensory (afferent) nerves — carry sensory information into brain and spinal cord ...
... Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) sensory (afferent) nerves — carry sensory information into brain and spinal cord ...
Central nervous system
... allows sodium (Na+) to flow inside the membrane • The exchange of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... allows sodium (Na+) to flow inside the membrane • The exchange of ions initiates an action potential in the neuron Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Notes0112
... signal such as the binding of a ligand to a receptor that forms part of the channel, eg, the acetylcholine receptor channel involved in neuromuscular transmission; and (iii) mechanically gated channels, in which the sensor is sensitive to mechanical deformation of the membrane, eg, stretch-activated ...
... signal such as the binding of a ligand to a receptor that forms part of the channel, eg, the acetylcholine receptor channel involved in neuromuscular transmission; and (iii) mechanically gated channels, in which the sensor is sensitive to mechanical deformation of the membrane, eg, stretch-activated ...
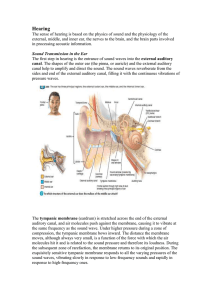
Ear
... to chemical changes in the internal environment, two examples being the oxygen and hydrogen-ion receptors in certain large blood vessels. Others respond to external chemical changes, and in this category are the receptors for taste and smell, which affect a person’s appetite, saliva flow, gastric se ...
... to chemical changes in the internal environment, two examples being the oxygen and hydrogen-ion receptors in certain large blood vessels. Others respond to external chemical changes, and in this category are the receptors for taste and smell, which affect a person’s appetite, saliva flow, gastric se ...
Chapter 7 Part 1 Nervous Tissue
... • Short, tapering, and diffusely branched processes • They are the receptive, or input, regions of the neuron ...
... • Short, tapering, and diffusely branched processes • They are the receptive, or input, regions of the neuron ...
Exam I
... 11) In order for a presynaptic neuron to send a bigger signal to a postsynaptic neuron it must… A) send larger action potentials. B) increase the frequency with which it is sending action potentials. C) All of the above. D) None of the above. Use the following figure of an action potential to answer ...
... 11) In order for a presynaptic neuron to send a bigger signal to a postsynaptic neuron it must… A) send larger action potentials. B) increase the frequency with which it is sending action potentials. C) All of the above. D) None of the above. Use the following figure of an action potential to answer ...
Mathematical neuroscience: from neurons to circuits to systems
... carry an electrical charge. Potassium (Kþ ), for instance, has a higher concentration inside the cell and carries a positive charge. Diffusive forces drive Kþ out of the cell. The subsequent loss of positive ions leads to a net negative charge inside the membrane. The resulting electrical force attra ...
... carry an electrical charge. Potassium (Kþ ), for instance, has a higher concentration inside the cell and carries a positive charge. Diffusive forces drive Kþ out of the cell. The subsequent loss of positive ions leads to a net negative charge inside the membrane. The resulting electrical force attra ...
Aim of Research
... Whereas the essential proteins governing the SV cycle have been identified in the last decades, we still have only little knowledge about their exact operation and sequence in which they interact to carry out the individual steps of the SV cycle. Like other trafficking mechanisms, the vesicle cycle ...
... Whereas the essential proteins governing the SV cycle have been identified in the last decades, we still have only little knowledge about their exact operation and sequence in which they interact to carry out the individual steps of the SV cycle. Like other trafficking mechanisms, the vesicle cycle ...
ch 48 nervous system
... • Postsynaptic potentials fall into two categories – Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are depolarizations that bring the membrane potential toward threshold – Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold ...
... • Postsynaptic potentials fall into two categories – Excitatory postsynaptic potentials (EPSPs) are depolarizations that bring the membrane potential toward threshold – Inhibitory postsynaptic potentials (IPSPs) are hyperpolarizations that move the membrane potential farther from threshold ...
Chp 9: NERVOUS TISSUE
... outside a plasma membrane. A membrane that has potential is said to be ____________________. When muscle fibers and neurons are ‘at rest’, the voltage across the plasma membrane is termed the __________________________________________. In living tissues, the flow of ions constitutes electrical curre ...
... outside a plasma membrane. A membrane that has potential is said to be ____________________. When muscle fibers and neurons are ‘at rest’, the voltage across the plasma membrane is termed the __________________________________________. In living tissues, the flow of ions constitutes electrical curre ...
In This Issue - The Journal of Cell Biology
... sites where neurites contact each other. The trapping of NCAM and its associated organelles at contact sites is followed by the development of the contacts into ...
... sites where neurites contact each other. The trapping of NCAM and its associated organelles at contact sites is followed by the development of the contacts into ...
Electrophysiology
Electrophysiology (from Greek ἥλεκτρον, ēlektron, ""amber"" [see the etymology of ""electron""]; φύσις, physis, ""nature, origin""; and -λογία, -logia) is the study of the electrical properties of biological cells and tissues. It involves measurements of voltage change or electric current on a wide variety of scales from single ion channel proteins to whole organs like the heart. In neuroscience, it includes measurements of the electrical activity of neurons, and particularly action potential activity. Recordings of large-scale electric signals from the nervous system such as electroencephalography, may also be referred to as electrophysiological recordings.