Unit 6 Ecology Part 2 - Energy Flow in a System
... nutrient back into the system – Bacteria + fungi ...
... nutrient back into the system – Bacteria + fungi ...
TERRESTRIAL ECOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
... 4. What happens to biological production and biomass as energy flows up a food chain? 5. What does it mean to “eat lower in the food chain?” 6. What is ecological succession? 7. List examples of ecological disturbances both natural and human caused. 8. What is primary succession? How does it differ ...
... 4. What happens to biological production and biomass as energy flows up a food chain? 5. What does it mean to “eat lower in the food chain?” 6. What is ecological succession? 7. List examples of ecological disturbances both natural and human caused. 8. What is primary succession? How does it differ ...
Unit 3: Pre
... b. Two organisms cannot survive if both are using the same resource. c. When resources are abundant, there will only be one species. d. None of the above. 7. An interaction in which one organism kills and eats another is called: a. predation c. adaptation b. symbiosis d. competition 8. An organism t ...
... b. Two organisms cannot survive if both are using the same resource. c. When resources are abundant, there will only be one species. d. None of the above. 7. An interaction in which one organism kills and eats another is called: a. predation c. adaptation b. symbiosis d. competition 8. An organism t ...
Chapter 19 * Introduction to Ecology
... Abiotic components: water temperature, amount of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide, the pH level Biotic components: insects, fish, algae, aquatic plants, turtles Some ecosystems can be considered the habitat of an organism. ...
... Abiotic components: water temperature, amount of dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide, the pH level Biotic components: insects, fish, algae, aquatic plants, turtles Some ecosystems can be considered the habitat of an organism. ...
STAAR Biology Category 5 Vocab flash cards
... dead organic matter; primarily fungi and bacteria ...
... dead organic matter; primarily fungi and bacteria ...
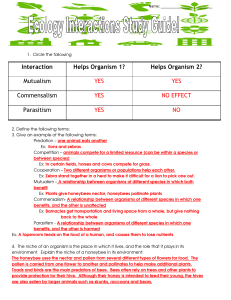
Interaction Helps Organism 1? Helps Organism 2? Mutualism YES
... Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection for their hive. Although their honey is intended to feed their young, the hives are also eaten by larger animals such as skunks, raccoons and bears. ...
... Toads and birds are the main predators of bees. Bees often rely on trees and other plants to provide protection for their hive. Although their honey is intended to feed their young, the hives are also eaten by larger animals such as skunks, raccoons and bears. ...
primary productivity - Broadneck High School
... • symbiosis - relation between 2 species 0 if no effect, + if benefited, – if harmed • neutralism [ 0 0 ] - no effect on either species • competition [ – – ] - both species harmed – leads to evolution of different species ...
... • symbiosis - relation between 2 species 0 if no effect, + if benefited, – if harmed • neutralism [ 0 0 ] - no effect on either species • competition [ – – ] - both species harmed – leads to evolution of different species ...
bioch2a - Otterville R
... An ecosystem is a community of different species interacting with one another and their no-living environment of matter and energy. All the Earth’s ecosystems make up what is called the ecosphere or biosphere Climate is the main factor that determines whether a given species will thrive in an area. ...
... An ecosystem is a community of different species interacting with one another and their no-living environment of matter and energy. All the Earth’s ecosystems make up what is called the ecosphere or biosphere Climate is the main factor that determines whether a given species will thrive in an area. ...
This variation makes it possible for a population to evolve over time
... of suitable land is limited and there are increasing demands for land for uses other than agriculture, eg building, recreation, etc. In addition some productive land is being lost because of desertification, influx of sea water and coastal erosion for example. As a result the land that is available ...
... of suitable land is limited and there are increasing demands for land for uses other than agriculture, eg building, recreation, etc. In addition some productive land is being lost because of desertification, influx of sea water and coastal erosion for example. As a result the land that is available ...
Chapter 2
... 3. How can humans bring about change in a population of organisms? Selective breeding (example, horses, Kale and plants) 4. What is a species? A group of organisms whose members very closely resemble each other because they share many key characteristics. 5. What would happen according to Mayr if al ...
... 3. How can humans bring about change in a population of organisms? Selective breeding (example, horses, Kale and plants) 4. What is a species? A group of organisms whose members very closely resemble each other because they share many key characteristics. 5. What would happen according to Mayr if al ...
Ecology Unit: Part 1 The Biosphere
... Examples of ecosystems: (they don’t have to be huge!) Rotting Log Koi Pond Mountain A hillside Clump of Dirt A field A maple tree A puddle ...
... Examples of ecosystems: (they don’t have to be huge!) Rotting Log Koi Pond Mountain A hillside Clump of Dirt A field A maple tree A puddle ...
Lesson Plan: Environmental Science, Ecology
... 2. How do organisms depend on one another and adapt to changing ecosystems when affected by humans? 3. What biological and chemical processes help or harm the environment? ...
... 2. How do organisms depend on one another and adapt to changing ecosystems when affected by humans? 3. What biological and chemical processes help or harm the environment? ...
Chapter 4: Principles of Ecology: How Ecosystems Work
... The position of an organism in a food chain is called its trophic level. Producers are on the first trophic level. Herbivores are on the second level. Carnivores are on the third level. The length of a food chain is limited by the loss of energy from one trophic level to another. The largest number ...
... The position of an organism in a food chain is called its trophic level. Producers are on the first trophic level. Herbivores are on the second level. Carnivores are on the third level. The length of a food chain is limited by the loss of energy from one trophic level to another. The largest number ...
Ecology Study Guide – ANSWERS!
... Producers use Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis to make their food. Photosynthesis is most common. 7. What is biomass? Biomass is the amount of living material in each tropic level. 8. What are the five different types of consumers? What is another name for a consumer? Herbivore – Eats Plants Omnivo ...
... Producers use Photosynthesis and Chemosynthesis to make their food. Photosynthesis is most common. 7. What is biomass? Biomass is the amount of living material in each tropic level. 8. What are the five different types of consumers? What is another name for a consumer? Herbivore – Eats Plants Omnivo ...
Ecology 1: Ecosystems - Miami Beach Senior High School
... • Extinction – dying out of species • Mass extinction – dying off of large numbers of species in a short period of time • Habitat place where an organism usually lives • Habitat destruction – habitat is destroyed or changed so that it can no longer support the species that had lived there • Invasive ...
... • Extinction – dying out of species • Mass extinction – dying off of large numbers of species in a short period of time • Habitat place where an organism usually lives • Habitat destruction – habitat is destroyed or changed so that it can no longer support the species that had lived there • Invasive ...
DEFINING KEY TERMS 1points each (14 points)
... 11. Which of the following small molecules are converted to form sugar in photosynthesis? a. oxygen an water b. hydroxyl ion and hydrogen c. carbon dioxide and oxygen d. water and carbon dioxide 12. Bioaccumulation of pollutants in the food chain results in: a. a low concentration of pollutants in t ...
... 11. Which of the following small molecules are converted to form sugar in photosynthesis? a. oxygen an water b. hydroxyl ion and hydrogen c. carbon dioxide and oxygen d. water and carbon dioxide 12. Bioaccumulation of pollutants in the food chain results in: a. a low concentration of pollutants in t ...
Objective 3 - Canyon ISD
... A scientist has hypothesized that the existence of life on Mars is likely because Mars’s atmosphere is 95% carbon dioxide. 36 Which question is valid in testing this hypothesis? F Do most other scientists agree with the hypothesis? G Could abiotic processes account for the carbon dioxide? H What is ...
... A scientist has hypothesized that the existence of life on Mars is likely because Mars’s atmosphere is 95% carbon dioxide. 36 Which question is valid in testing this hypothesis? F Do most other scientists agree with the hypothesis? G Could abiotic processes account for the carbon dioxide? H What is ...
Midterm Final Review
... atmosphere will cause a 2º C increase in the average temperature of Earth. • Rising temperatures could cause polar ice cap melting, which could flood coastal areas. – It is important that humans attempt to stabilize their use of fossil fuels. ...
... atmosphere will cause a 2º C increase in the average temperature of Earth. • Rising temperatures could cause polar ice cap melting, which could flood coastal areas. – It is important that humans attempt to stabilize their use of fossil fuels. ...
Ecology Review
... atmosphere will cause a 2º C increase in the average temperature of Earth. • Rising temperatures could cause polar ice cap melting, which could flood coastal areas. – It is important that humans attempt to stabilize their use of fossil fuels. ...
... atmosphere will cause a 2º C increase in the average temperature of Earth. • Rising temperatures could cause polar ice cap melting, which could flood coastal areas. – It is important that humans attempt to stabilize their use of fossil fuels. ...
Biodiversity Holds the Key to Sustainable Biofuel Production
... Furthermore, the results of the study showed that ecosystems containing many different plant species are more productive than those containing only one of those species. In particular, diverse prairie grasslands were found to be more than 200 percent more productive than grasslands with a single pra ...
... Furthermore, the results of the study showed that ecosystems containing many different plant species are more productive than those containing only one of those species. In particular, diverse prairie grasslands were found to be more than 200 percent more productive than grasslands with a single pra ...