Eco-restoration through institution strengthening, sustainable forest
... poor households’ overall requirements comes from common property resources that are natural resources owned and managed collectively by a community or society rather than by individuals. Community-based forest management and conservation through strengthened local institutions can thus be one of the ...
... poor households’ overall requirements comes from common property resources that are natural resources owned and managed collectively by a community or society rather than by individuals. Community-based forest management and conservation through strengthened local institutions can thus be one of the ...
Unit 8 -Ecology Populations, Communities, Ecosystems, and Biomes
... Changes in Communities - Section 21.4 The series of predictable changes that occur in a community over time is called succession. ___________________ is the series of changes that occur in an area where no soil or organisms exist. The first species to populate an area are called the pioneer species ...
... Changes in Communities - Section 21.4 The series of predictable changes that occur in a community over time is called succession. ___________________ is the series of changes that occur in an area where no soil or organisms exist. The first species to populate an area are called the pioneer species ...
Interactions Among Living Things
... To adapt to something means to change your behavior because of your surroundings. For example, if our school had been hit by the tornadoes, we would have to adapt to having classes at another school. ...
... To adapt to something means to change your behavior because of your surroundings. For example, if our school had been hit by the tornadoes, we would have to adapt to having classes at another school. ...
Explain - glassscience
... Explain the effects on the plants mentioned in the question and other organisms in the food chain. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. Many plants ...
... Explain the effects on the plants mentioned in the question and other organisms in the food chain. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 2. Many plants ...
ECOLOGY
... • Depends heavily on the weathering of rock • Plants absorb dissolved phosphate ions from the soil • Also, decomposers can return phosphates back to soil • Because weathering is a slow process, phosphorus is often a limiting nutrient to plant growth ...
... • Depends heavily on the weathering of rock • Plants absorb dissolved phosphate ions from the soil • Also, decomposers can return phosphates back to soil • Because weathering is a slow process, phosphorus is often a limiting nutrient to plant growth ...
Chapter 37
... Root nodules form when two types of bacteria, Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium, infect the roots of seedlings of leguminous plants (bean and pea family). Rhizobium bacteria are often called rhizobia. Each species of plant is associated with a species of bacteria. This infection is not harmful to the pla ...
... Root nodules form when two types of bacteria, Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium, infect the roots of seedlings of leguminous plants (bean and pea family). Rhizobium bacteria are often called rhizobia. Each species of plant is associated with a species of bacteria. This infection is not harmful to the pla ...
Within each ecosystem, there are habitats which may also vary in size
... interacts with the non-living world around it to form the ecosystem. The habitat must supply the needs of organisms, such as food, water, temperature, oxygen, and minerals. If the population's needs are not met, it will move to a better habitat. Two different populations can not occupy the same nich ...
... interacts with the non-living world around it to form the ecosystem. The habitat must supply the needs of organisms, such as food, water, temperature, oxygen, and minerals. If the population's needs are not met, it will move to a better habitat. Two different populations can not occupy the same nich ...
ap biology notes on ecology
... mating, reproduction, nest building habits, etc. can eliminate habitats that otherwise would be very suitable. (ex. European corn borer only deposits its eggs on corn although they eat a wide variety of plants) o Biotic Factors – Some host species may be necessary for parasites to reproduce in new a ...
... mating, reproduction, nest building habits, etc. can eliminate habitats that otherwise would be very suitable. (ex. European corn borer only deposits its eggs on corn although they eat a wide variety of plants) o Biotic Factors – Some host species may be necessary for parasites to reproduce in new a ...
Ecology - leavingcertbiology.net
... – Reduce: do not buy foods that use excess packaging – Reuse: household objects can be reused – for example ice cream tubs, glass bottles, etc. – Recycle: many materials used can be recycled, such as glass bottles, paper, plastics, metals, and organic waste ...
... – Reduce: do not buy foods that use excess packaging – Reuse: household objects can be reused – for example ice cream tubs, glass bottles, etc. – Recycle: many materials used can be recycled, such as glass bottles, paper, plastics, metals, and organic waste ...
Sixth grade science teks
... __8e. investigate how inclined planes and pulleys can be used to change the amount of force to move an object. The student knows the Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it just changes form. __9a.investigate methods of thermal energy transfer includ ...
... __8e. investigate how inclined planes and pulleys can be used to change the amount of force to move an object. The student knows the Law of Conservation of Energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, it just changes form. __9a.investigate methods of thermal energy transfer includ ...
Ecology2
... Fire Maintained Communities Natural fires caused by lightning are a part of secondary succession 1. Jack pine release seeds after exposed to heat 2. Brush and dead wood removed 3. Some animals depend on vegetation that sprouts after fire ...
... Fire Maintained Communities Natural fires caused by lightning are a part of secondary succession 1. Jack pine release seeds after exposed to heat 2. Brush and dead wood removed 3. Some animals depend on vegetation that sprouts after fire ...
Global Concerns Vocabulary
... A change in the long-term weather patterns that is characteristic of regions of the world. ...
... A change in the long-term weather patterns that is characteristic of regions of the world. ...
PAST ECOLOGY FRQ`s
... Genetically modified crops have been developed that produce a protein that makes the plants resistant to insect pests. Other genetic modifications make the crops more resistant to chemicals that kill plants (herbicides). a) DESCRIBE TWO potential biological risks of large-scale cultivation and use o ...
... Genetically modified crops have been developed that produce a protein that makes the plants resistant to insect pests. Other genetic modifications make the crops more resistant to chemicals that kill plants (herbicides). a) DESCRIBE TWO potential biological risks of large-scale cultivation and use o ...
producers
... Organisms that can make their own food by photosynthesis or by chemosynthesis. Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. ...
... Organisms that can make their own food by photosynthesis or by chemosynthesis. Without a constant input of energy, living systems cannot function. Sunlight is the main energy source for life on Earth. ...
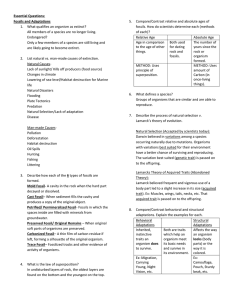
Essential Questions: Fossils and Adaptations What qualifies an
... spaces inside are filled with minerals from groundwater. Preserved Fossil/ Original Remains – When original soft parts of organisms are preserved. Carbonized Fossil– A thin film of carbon residue if left, forming a silhouette of the original organism. Trace Fossil– Fossilized tracks and other eviden ...
... spaces inside are filled with minerals from groundwater. Preserved Fossil/ Original Remains – When original soft parts of organisms are preserved. Carbonized Fossil– A thin film of carbon residue if left, forming a silhouette of the original organism. Trace Fossil– Fossilized tracks and other eviden ...
Carrying Capacity PPT
... can survive indefinitely in a given environment no population can increase its size indefinitely ...
... can survive indefinitely in a given environment no population can increase its size indefinitely ...
ecosystemnotes
... Population: all the individuals of one kind (one species) in a specified area at one time Community: all the interacting populations in a specified area Ecosystem: a system of interacting organisms and nonliving factors in a specified area Biotic: living organisms and products of organisms Abiotic: ...
... Population: all the individuals of one kind (one species) in a specified area at one time Community: all the interacting populations in a specified area Ecosystem: a system of interacting organisms and nonliving factors in a specified area Biotic: living organisms and products of organisms Abiotic: ...
Study Guide for Exam
... 4. Identify three ways the Industrial revolution changed society. Include how it affected human population growth. Switching from animal power to fossil fuels increased the efficiency of agriculture. Inventions such as the light bulb improved quality of life, increased use of artificial substances s ...
... 4. Identify three ways the Industrial revolution changed society. Include how it affected human population growth. Switching from animal power to fossil fuels increased the efficiency of agriculture. Inventions such as the light bulb improved quality of life, increased use of artificial substances s ...
Ecosystems
... 1.Assimilation 2.Ammonification 3.Nitrification 4.Denitrification N2 Makes up 80% Atmosphere! Organisms need nitrogen and phosphorus to build proteins and nucleic acids. ...
... 1.Assimilation 2.Ammonification 3.Nitrification 4.Denitrification N2 Makes up 80% Atmosphere! Organisms need nitrogen and phosphorus to build proteins and nucleic acids. ...
Ecological Design with Native Plant Communities
... In the wild, these are in cliff communities in part shade to full sun. They routinely go dormant when stressed. In cultivation, they thrive in moderate temperatures, well-drained organic soils and with a consistently moist, but not excessively damp, water regime. ◦ Examples: Zizia aurea (golden Alex ...
... In the wild, these are in cliff communities in part shade to full sun. They routinely go dormant when stressed. In cultivation, they thrive in moderate temperatures, well-drained organic soils and with a consistently moist, but not excessively damp, water regime. ◦ Examples: Zizia aurea (golden Alex ...
2Ecological Design with Native Plant Communities
... In the wild, these are in cliff communities in part shade to full sun. They routinely go dormant when stressed. In cultivation, they thrive in moderate temperatures, well-drained organic soils and with a consistently moist, but not excessively damp, water regime. ◦ Examples: Zizia aurea (golden Alex ...
... In the wild, these are in cliff communities in part shade to full sun. They routinely go dormant when stressed. In cultivation, they thrive in moderate temperatures, well-drained organic soils and with a consistently moist, but not excessively damp, water regime. ◦ Examples: Zizia aurea (golden Alex ...
Ecological Principles 2
... another (otherwise, it would only rain over the oceans). Precipitation occurs when water condenses from a gaseous state in the atmosphere and falls to earth. Evaporation is the reverse process in which liquid water becomes gaseous. Once water condenses, gravity takes over and the water is pulled to ...
... another (otherwise, it would only rain over the oceans). Precipitation occurs when water condenses from a gaseous state in the atmosphere and falls to earth. Evaporation is the reverse process in which liquid water becomes gaseous. Once water condenses, gravity takes over and the water is pulled to ...
Plant Responses to Global Environmental Change
... part of a nitrogen cycle embracing air, water, plants, animals, and soils. However, human inputs from electric power generation, industrial activity, transportation, and agriculture have disrupted this balance. Fossil fuel combustion releases N2 into the atmosphere and results in additional fixation ...
... part of a nitrogen cycle embracing air, water, plants, animals, and soils. However, human inputs from electric power generation, industrial activity, transportation, and agriculture have disrupted this balance. Fossil fuel combustion releases N2 into the atmosphere and results in additional fixation ...