Food Chain
... There must always be more prey than predators because the predators can not use all the energy that is consumed from the prey. The lower an organism is on the food chain, the higher the numbers of these organisms. The more organisms there are at a trophic level, the more mass the group of organisms ...
... There must always be more prey than predators because the predators can not use all the energy that is consumed from the prey. The lower an organism is on the food chain, the higher the numbers of these organisms. The more organisms there are at a trophic level, the more mass the group of organisms ...
Biosphere Review
... Energy is passed in one-way direction through the biotic (living organisms) in an ecosystem. Matter cycles within and between biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem. ...
... Energy is passed in one-way direction through the biotic (living organisms) in an ecosystem. Matter cycles within and between biotic and abiotic parts of an ecosystem. ...
Reflective Essay Example: Sieglinde Snapp
... learning about how biogeochemical processes in nutrient management and soil quality operate at different temporal and spatial scales. Since 2006 I have been one of the principal investigators on the NSF-funded Long-Term Ecological Research (LTER) row crop ecology project at KBS, with a focus on agr ...
... learning about how biogeochemical processes in nutrient management and soil quality operate at different temporal and spatial scales. Since 2006 I have been one of the principal investigators on the NSF-funded Long-Term Ecological Research (LTER) row crop ecology project at KBS, with a focus on agr ...
Glossary
... Natural processes that recycle nutrients in various chemical forms from the nonliving environment to living organisms and then back to the nonliving environment. Examples are the carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and hydrologic cycles. ...
... Natural processes that recycle nutrients in various chemical forms from the nonliving environment to living organisms and then back to the nonliving environment. Examples are the carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and hydrologic cycles. ...
Biome Photostory Topic Quiz
... • B. Organisms in the deep ocean are exposed to frigid temperatures and total darkness. • C. The open ocean begins at the low-tide mark and extends to the end of the continental shelf. • D. Most of the photosynthetic activity on Earth occurs in the open ocean within the photic zone. ...
... • B. Organisms in the deep ocean are exposed to frigid temperatures and total darkness. • C. The open ocean begins at the low-tide mark and extends to the end of the continental shelf. • D. Most of the photosynthetic activity on Earth occurs in the open ocean within the photic zone. ...
Standard 1: Students will understand that living organisms interact
... as the plants in the figure above. Consumers are organisms that cannot make their own food and must get energy from other living things, such as the lion in the figure above. Consumers can be herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores. Food chains might also include decomposers that get nutrients and ener ...
... as the plants in the figure above. Consumers are organisms that cannot make their own food and must get energy from other living things, such as the lion in the figure above. Consumers can be herbivores, carnivores, or omnivores. Food chains might also include decomposers that get nutrients and ener ...
Turfgrass IPM - Nc State University
... ecosystem. Some produce natural products which inhibit other fungi, including pathogens. Isolating these materials can lead to natural fungicides, eg. Heritage • Adding organic matter to soils usually stimulates general microbial activity, which can inhibit turf pathogenic fungi ...
... ecosystem. Some produce natural products which inhibit other fungi, including pathogens. Isolating these materials can lead to natural fungicides, eg. Heritage • Adding organic matter to soils usually stimulates general microbial activity, which can inhibit turf pathogenic fungi ...
the biosphere - OpenStax CNX
... of the ocean. The bottom of this zone consists of sediments. The deepest parts of the ocean are known as the abyssal zone. This zone is very cold (near freezing temperatures), and under great pressure from the overlying mass of water. Mid-ocean ridges occur on the ocean oor in abyssal zones. ...
... of the ocean. The bottom of this zone consists of sediments. The deepest parts of the ocean are known as the abyssal zone. This zone is very cold (near freezing temperatures), and under great pressure from the overlying mass of water. Mid-ocean ridges occur on the ocean oor in abyssal zones. ...
How Changes Occur Naturally in Ecosystems
... Ecological succession refers to changes that take place over time in the types of organisms that live in an area. There are two types of ecological succession: 1. Primary succession: Primary succession occurs in areas where no soil exists, such as following glaciation or a lava flow. Wind and rain c ...
... Ecological succession refers to changes that take place over time in the types of organisms that live in an area. There are two types of ecological succession: 1. Primary succession: Primary succession occurs in areas where no soil exists, such as following glaciation or a lava flow. Wind and rain c ...
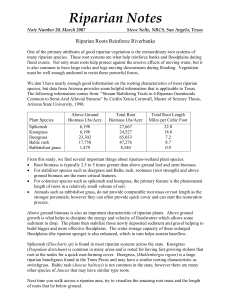
Riparian Notes 20: Riparian Roots Reinforce Riverbanks
... build bigger and more effective floodplains. The water storage capacity of these enlarged floodplains (the riparian sponge) is also enhanced, which in turn helps sustain baseflow. Spikerush (Eliocharis sp) is found in most riparian systems across the state. Knotgrass (Paspalum distichum) is common i ...
... build bigger and more effective floodplains. The water storage capacity of these enlarged floodplains (the riparian sponge) is also enhanced, which in turn helps sustain baseflow. Spikerush (Eliocharis sp) is found in most riparian systems across the state. Knotgrass (Paspalum distichum) is common i ...
2.6.5-.7 Succession
... There are two main types of succession: 1. Primary succession which begins with bare rock exposed by geologic activity eg. sere: rock -> lichen -> moss -> grass -> shrub -> trees -> maple-beech -hemlock forest 2. Secondary succession which begins on soil from which a previous community has been remo ...
... There are two main types of succession: 1. Primary succession which begins with bare rock exposed by geologic activity eg. sere: rock -> lichen -> moss -> grass -> shrub -> trees -> maple-beech -hemlock forest 2. Secondary succession which begins on soil from which a previous community has been remo ...
A Qualitative Model of Plant Growth Based on Exploitation of
... causal processes and controlling parameters that would lead to the behavior seen in Figure 1C. These essential ingredients are: Resource supply: this process describes the amount of resources flowing into the system. Eq. 2 includes this concept as the first term after the equal sign, which describes ...
... causal processes and controlling parameters that would lead to the behavior seen in Figure 1C. These essential ingredients are: Resource supply: this process describes the amount of resources flowing into the system. Eq. 2 includes this concept as the first term after the equal sign, which describes ...
2 - Edmodo
... 1. Nutrients All living things need nutrients in order to survive. Nutrients are substances that an organism uses to build and repair the cells of its body. Nutrients also provide energy, which all organisms need to grow and maintain their bodies and to reproduce. Animals eat food in order to get nu ...
... 1. Nutrients All living things need nutrients in order to survive. Nutrients are substances that an organism uses to build and repair the cells of its body. Nutrients also provide energy, which all organisms need to grow and maintain their bodies and to reproduce. Animals eat food in order to get nu ...
10-Landscape_Ecology
... pressure, outbreaks in plant disease or insect infestation, fire, and growing season length. • Annual net production changes with age. In general, it increases in terrestrial ecosystems during succession or stand development, followed by a decline as time progresses. ...
... pressure, outbreaks in plant disease or insect infestation, fire, and growing season length. • Annual net production changes with age. In general, it increases in terrestrial ecosystems during succession or stand development, followed by a decline as time progresses. ...
2.5 Food Webs and Ecological Pyramids
... essential for all living things. By examining how energy flow is depicted in these diagrams, you will gain a better understanding of the relationships between species, including why some species are much more abundant than others. As one organism consumes another, it obtains both the physical matter ...
... essential for all living things. By examining how energy flow is depicted in these diagrams, you will gain a better understanding of the relationships between species, including why some species are much more abundant than others. As one organism consumes another, it obtains both the physical matter ...
Ecology Study Guide:
... 18. How are the organisms in an ecosystem affected when a producer begins to disappear? 19. Explain the processes that occur in the following cycles: Nitrogen, Carbon & Oxygen, and H2O 20. Define carrying capacity. What factors might prevent a population from reaching its carrying capacity? 21. What ...
... 18. How are the organisms in an ecosystem affected when a producer begins to disappear? 19. Explain the processes that occur in the following cycles: Nitrogen, Carbon & Oxygen, and H2O 20. Define carrying capacity. What factors might prevent a population from reaching its carrying capacity? 21. What ...
Biodiversity_and_Conservation
... life in an ecosystem. This includes all species of animal, plant and invertebrate life. It can be described at many levels from species diversity (how many different species there are) to ecosystem diversity (the number of different ecosystems that exist). The Nile River basin contains a diversity o ...
... life in an ecosystem. This includes all species of animal, plant and invertebrate life. It can be described at many levels from species diversity (how many different species there are) to ecosystem diversity (the number of different ecosystems that exist). The Nile River basin contains a diversity o ...
Section Review #1
... Chaos Theory: Math theory that says that large changes are due to very small changes. The initial state of an ecosystem is crucial to its later development. a. The small changes often have unpredictable and unknowable results. b. Chaos theory tends to use terms like probability to discuss outcome. ...
... Chaos Theory: Math theory that says that large changes are due to very small changes. The initial state of an ecosystem is crucial to its later development. a. The small changes often have unpredictable and unknowable results. b. Chaos theory tends to use terms like probability to discuss outcome. ...
No Slide Title
... that goes beyond any of the observations that led up to the conclusion. (Based on probabilities) ...
... that goes beyond any of the observations that led up to the conclusion. (Based on probabilities) ...
No Slide Title
... Conservancy's Wildland Invasive Species Team. It describes many of the consequences of non-native plant species invasions in wildlands. If you use this presentation unaltered, please include the first page which gives us credit for creating the presentation. If you alter the presentation, please not ...
... Conservancy's Wildland Invasive Species Team. It describes many of the consequences of non-native plant species invasions in wildlands. If you use this presentation unaltered, please include the first page which gives us credit for creating the presentation. If you alter the presentation, please not ...
Midterm Review
... is highly concentrated, is typically found near the earth’s surface, and has great potential for use as a resource. ...
... is highly concentrated, is typically found near the earth’s surface, and has great potential for use as a resource. ...
Regents Review 4
... • Define food web. • Number of intertwining/connected food chains • Why is the food web more stable than a food chain? • More energy pathways so energy flow will not be completely stopped if one organism is lost ...
... • Define food web. • Number of intertwining/connected food chains • Why is the food web more stable than a food chain? • More energy pathways so energy flow will not be completely stopped if one organism is lost ...
Ecology Unit
... simple structures, so most of their primary energy production is consumed and used for energy by the primary consumers that feed on them. Land plants, however, have large amounts of unusable parts in terms of providing a source of energy to what eats them. The roots, trunks, and branches of plants c ...
... simple structures, so most of their primary energy production is consumed and used for energy by the primary consumers that feed on them. Land plants, however, have large amounts of unusable parts in terms of providing a source of energy to what eats them. The roots, trunks, and branches of plants c ...