Ecology: Energy Flow
... • expressed as grams of organic matter per unit area • biomass pyramid represents the potential amount of food available at each trophic level • normally the greatest biomass is at the base ...
... • expressed as grams of organic matter per unit area • biomass pyramid represents the potential amount of food available at each trophic level • normally the greatest biomass is at the base ...
Israa Dorgham
... and competition on different trophic levels including decomposers, producers, and predators. The paper attempts to suggest which of these key factors plays a larger role in limiting population size. Hairston et al. base the paper on widely accepted observations in order to demonstrate a pattern of p ...
... and competition on different trophic levels including decomposers, producers, and predators. The paper attempts to suggest which of these key factors plays a larger role in limiting population size. Hairston et al. base the paper on widely accepted observations in order to demonstrate a pattern of p ...
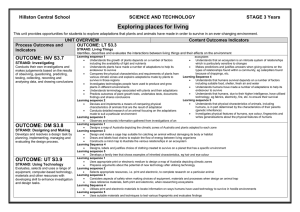
Exploring places for living
... Living things depend on other living things and non-living things such as water, soil, and a suitable temperature, for their survival Living things have adaptations such as structures and behaviours that enable them to live in their particular habitat, eg size colour, shape, habits Every organism ha ...
... Living things depend on other living things and non-living things such as water, soil, and a suitable temperature, for their survival Living things have adaptations such as structures and behaviours that enable them to live in their particular habitat, eg size colour, shape, habits Every organism ha ...
CHAPTER 41 ANIMAL NUTRITION Discussion questions
... 13. Explain how the small intestine is specialized for digestion and absorption. 14. Compare the uptake of an amino acid and a fatty acid in the small intestine. Trace the path of each molecule following its uptake. 15. Describe the major functions of the large intestine. Evolutionary Adaptations of ...
... 13. Explain how the small intestine is specialized for digestion and absorption. 14. Compare the uptake of an amino acid and a fatty acid in the small intestine. Trace the path of each molecule following its uptake. 15. Describe the major functions of the large intestine. Evolutionary Adaptations of ...
Recommendations for the Collection and Use of Native Plants
... Native ecosystems can never be replaced. Conservation of remaining plant communities must be considered an important priority because of the many economic, spiritual, medicinal, and sociological values that are associated with them. The genetic diversity of these well adapted ecosystems is also of k ...
... Native ecosystems can never be replaced. Conservation of remaining plant communities must be considered an important priority because of the many economic, spiritual, medicinal, and sociological values that are associated with them. The genetic diversity of these well adapted ecosystems is also of k ...
Structure Of The Forest Habitat
... species. The forest home is furnished luxuriantly with creepers and perching plants. Creepers like bush lawyer, use their thorns to climb up the trunks of canopy trees to reach the sunlight. Perching plants, or epiphytes, grow on other plants without harming them. Lichens and mosses growing on the b ...
... species. The forest home is furnished luxuriantly with creepers and perching plants. Creepers like bush lawyer, use their thorns to climb up the trunks of canopy trees to reach the sunlight. Perching plants, or epiphytes, grow on other plants without harming them. Lichens and mosses growing on the b ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 13
... IV. Food Chains and Food Webs (13.4) A. Food chain- sequence that links species by their feeding relationships. 1. only follows connections between one producer and single chain of consumers 2. simplest way to look at energy flow in an ecosystem ...
... IV. Food Chains and Food Webs (13.4) A. Food chain- sequence that links species by their feeding relationships. 1. only follows connections between one producer and single chain of consumers 2. simplest way to look at energy flow in an ecosystem ...
17 Plants, Fungi, and the Colonization of Land Chapter 17
... Describe the alternation of generation life cycle. Explain why it appears that this cycle has evolved independently in algae and land plants. Describe the key events of the moss and fern life cycles. Explain how coal is formed. Explain why coal, oil, and natural gas are called fossil fuels. Describe ...
... Describe the alternation of generation life cycle. Explain why it appears that this cycle has evolved independently in algae and land plants. Describe the key events of the moss and fern life cycles. Explain how coal is formed. Explain why coal, oil, and natural gas are called fossil fuels. Describe ...
Lab 7 Adaptive modification of stems, roots and leaves Self
... The copper pin wheel plant (Aeonium decorum) has prickles along its leaf margins. How do prickles differ from thorns and spines? Do they differ in function than these other structures? ...
... The copper pin wheel plant (Aeonium decorum) has prickles along its leaf margins. How do prickles differ from thorns and spines? Do they differ in function than these other structures? ...
File - Paxson Science
... 7. Compare and contrast primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers. Provide at least three examples each of organisms that can feed at the designated trophic level. 8. Do organisms always fall into a given trophic level? Explain, using examples. 9. Compare and contrast herbivores and carnivores in t ...
... 7. Compare and contrast primary, secondary, and tertiary consumers. Provide at least three examples each of organisms that can feed at the designated trophic level. 8. Do organisms always fall into a given trophic level? Explain, using examples. 9. Compare and contrast herbivores and carnivores in t ...
Open Access - Ghent University Academic Bibliography
... of toxic hydrogen cyanide from preformed cyanide-containing compounds is one of the best ...
... of toxic hydrogen cyanide from preformed cyanide-containing compounds is one of the best ...
Ecology
... and eat only other animals. – Scavengers- animals that do not kill for food; instead they eat animals that have already ...
... and eat only other animals. – Scavengers- animals that do not kill for food; instead they eat animals that have already ...
14_Foraging
... In rare tree species, individual trees vary in their level of alkaloids and tannins Young leaves have more water and higher nutritive value than old leaves Leaf petiole has lower alkaloids than leaf blade ...
... In rare tree species, individual trees vary in their level of alkaloids and tannins Young leaves have more water and higher nutritive value than old leaves Leaf petiole has lower alkaloids than leaf blade ...
All living organisms are made up of cells.
... The feeding of one organism upon another in a sequence of food transfers is known as a food chain. Another definition is the chain of transfer of energy (which typically comes from the sun) from one organism to another. ...
... The feeding of one organism upon another in a sequence of food transfers is known as a food chain. Another definition is the chain of transfer of energy (which typically comes from the sun) from one organism to another. ...
Interactions
... Without predators, certain species like mice would crowd out other species and would also destroy their habitat. ...
... Without predators, certain species like mice would crowd out other species and would also destroy their habitat. ...
Interactions
... Without predators, certain species like mice would crowd out other species and would also destroy their habitat. ...
... Without predators, certain species like mice would crowd out other species and would also destroy their habitat. ...
Introduction to Ecology
... – Feed On Dead Plant & Animal Remains (buzzards) • Decomposers – Fungi & Bacteria ...
... – Feed On Dead Plant & Animal Remains (buzzards) • Decomposers – Fungi & Bacteria ...
HANDCRAFTED HERBALISM - Chestnut School of Herbal Medicine
... their native habitat while ensuring an abundant renewable supply of medicinal plants for generations to come. Here is a description from the UpS regarding their designations of “At risk” and “To watch”: “For the benefit of the plant communities, wild animals, ...
... their native habitat while ensuring an abundant renewable supply of medicinal plants for generations to come. Here is a description from the UpS regarding their designations of “At risk” and “To watch”: “For the benefit of the plant communities, wild animals, ...
Herbivore
_grazing_-_20050809.jpg?width=300)
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material.